* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Empire of Japan wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Italian Social Republic wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda of Fascist Italy wikipedia , lookup
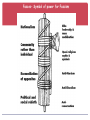
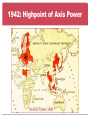
World War II AP World History Road to War: Europe 1. Treaty of Versailles “MORE than fourteen years have passed since the unhappy day when the German people, blinded by promises from foes at home and abroad, lost touch with honor and freedom, thereby losing all. Since that day of treachery, the Almighty has withheld his blessing from our people.” Adolf Hitler, February 1, 1933 2. The Great Depression 3. Rise of Nazi Germany Rise of Nazi Germany 4. German Expansion 1936 – German troops move into the Rhine river valley Breaks Treaty of Versailles 1938 – Germany annexes Austria & the Sudetenland Munich Conference- England’s Appeasement 1939 – Nazi-Soviet non- aggression pact September 1, 1939 – Germany invades Poland Road to War: Japan 1. Treaty of Versailles 2. Washington Conference 3. Japanese Imperialism 1910 – Annex Korea 1931 – Attack Manchuria Mukden Incident 1936 – Battle near Beijing Used as an excuse to invade mainland China 1937: Rape of Nanking Massacre, rape of thousands 1940 – French Indo-China “Comfort Women”- women forced into sexual slavery in Japanese occupied territory, numbers range from 20,000 (Japan) to 400,000 (China) – most likely around 200,000 Comfort Women Memorial Glendale, CA 4. Japanese Aggression Document Analysis: The Invasion of Nanking Context: Japan, 1930 Japan suffered from economic problems. Japan was geographically small. Goals of Japan’s military leaders expand Japan’s empire to gain more raw materials restore Japan’s power in Asia and the world World View of Japan Invasion of China Japan invaded China’s northern region of Manchuria in 1931. This area was rich with iron and coal. Japanese soldiers in Manchuria Invasion of Nanking Nanking was China’s capital. Japan invaded Nanking in December 1937. Japanese Soldiers entering Nanking Central Historical Question: Central Historical Question What happened during the invasion of Nanking? Rise to Power: Italy Benito Mussolini (1883-1945) What is fascism? A system of government with centralized authority under a dictator. Power is kept by extensive military control. Usually involves terror, censorship, nationalism, and racism. Benito Mussolini Fasces- Symbol of power for Fascism Mussolini gains power Mussolini set up a Fascist Party and promised to solve Italy’s problems Promised to rebuild Italy and recreate the Roman Empire Organized armed gangs called the “Blackshirts” Came to power in 1922 and was appointed Prime Minister by King Victor Emmanuel II to prevent a Communist Revolution in Italy March on Rome, 1922 Mussolini and Hitler Hitler and Mussolini had a close relationship. May 1939- Mussolini signed a full defensive alliance with Nazi Germany in the Pact of Steel. Mussolini and Hitler Anti-Semitism About 50,000 Jews lived in Italy in the 1930s. Mussolini did NOT implement an extermination program in Italy. 75% of Italian Jews survived World War II. 8,000 died in German extermination camps. 1938 anti-Semitic laws passed Manifesto degli Scienziati Razzisti [The Manifesto of the Racist Scientists]. • Excluded foreign Jews [most of them were sent to German death camps]. • Forbade all Jews from teaching. • Excluded Jews from serving in the government or in the military. Cult of Personality: Mussolini Mussolini’s Execution • Allied invasion of Western Europe quickly weakened Italy • Mussolini and his mistress Clara Petacci were taken prisoner by the Allied forces. A few days later they were shot to death by Italian partisan forces. • In April of 1945, their bodies were hung along with the bodies of other fascist leaders. Axis Powers Quick Note on Japan… Emperor Hirohito Technical leader from 1926-1989 AKA Emperor Showa Never put on trial for war crimes Hideki Tojo Head of military 1935 Named Prime Minister in 1941 Quickly names himself: • Minister of Education • Minister of Commerce and Industry • Home Minister • Foreign Minister Captured in 1944, put on trial for war crimes and executed Fighting World War II Blitzkrieg- Lighting War Video Clip Hitler Unleases the Blitzkrieg New Technology Other technological advancements: radar, synthetic rubber, antibiotics, etc. Dec. 7, 1941 Pearl Harbor Video clip "A date which will live in infamy...." Was it really a surprise? US claims neutrality, but definitely not neutral. Four months earlier, the US had imposed an oil embargo, knowing full well that Japan was dependent on US oil. The US Pacific Fleet had been moved to Pearl Harbor, which was not the home port for the ships. US plan of attack against the Japanese fleet that had been unearthed and published in the Chicago Tribune Japan warned that they would attack Pearl Harbor 1942: Highpoint of Axis Power Winning the War European Theater Notable Battles 1 – Blitzkrieg of Poland 5 – Surrender of Paris 6 – Battle of Britain 9 – Germany invades USSR 21 – Battle of Stalingrad *Turning Point of WWII 22 – Battle of El Alamein *Monty defeats Rommel 26 – Allies invade Sicily *U.S. troops led by Patton 29 – Battle of Normandy *Largest amphibious assault in world history 32 – Battle of the Bulge *Last German offensive 35 – Soviets enter Berlin July ’42- Feb ’43: Battle of Stalingrad Video Clip A turning point in the war Stops Nazi invasion of Soviet Union Over 2 million died in this battle alone- one of the bloodiest of all time. Battle of Stalingrad Amphibious Assaults June 6, 1944: Battle of Normandy (D-day) D-Day Invasion From June to August 1944 Largest amphibious military assault in history Liberates Western Europe from Nazi control 1945: Firebombing of Dresden http://www.telegraph.co.uk/history/world-war- two/11393917/The-firebombing-of-Dresdenarchive-footage.html Hitler commits suicide April 30, 1945 VE Day (Victory in Europe Day)- May 8, 1945 Unconditional surrender of Nazi Germany Allied Victory in the Pacific Island-Hopping 1944-45: Firebombing of Tokyo Island Hopping in the Pacific Firebombing of Tokyo Atomic Bomb Effects of the Atomic Bomb http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-ii/bombing- of-hiroshima-and-nagasaki Aug 6, 1945: US drops bomb on Hiroshima Aug 9, 1945: US drops bomb on Nagasaki Aug 14, 1945: Japan surrenders unconditionally, officially ending World War II DBQ Essay (due Tuesday) “Was President Truman’s decision to use atomic weapons against Japan justified?” Things to consider: Was it a military necessity? Was it justifiable for a reason other than military strategy? How did this decision impact the people of Japan? How did this decision impact foreign relations?