* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen-vacancy center wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Atomic absorption spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Franck–Condon principle wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
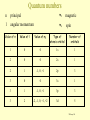
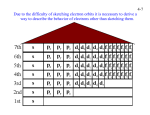
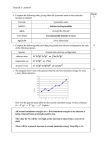
Quantum numbers n principal m1 magnetic l angular momentum ms spin Value of n Value of l Value of m1 Type of atomic orbital Number of orbitals 1 0 0 1s 1 2 0 0 2s 1 2 1 -1, 0, +1 2p 3 3 0 0 3s 1 3 1 -1, 0, +1 3p 3 3 2 -2, -1, 0, +1, +2 3d 5 MM 2007 AH Pauli Exclusion Principle No 2 electrons in any one atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers • the maximum number of electrons in any orbital is 2 • 2 electrons occupying the same orbital must have opposite spin MM 2007 AH Electronic configuration H 1s1 or 1s He 1s2 or 1s MM 2007 AH Aufbau principle • Lowest energy orbitals filled first • Electrons assigned to orbitals in order of increasing n + l • Where 2 subshells have same n + l, that with lowest n filled first Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity Degenerate orbitals occupied singly, with electrons keeping their spin parallel before spin pairing occurs N 1s2 2s2 2p3 1s 2s 2p MM 2007 AH Electronic arrangement of Noble gases Ne 1s2 2s2 2p6 Ar 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 Electronic configuration of other elements can be abbreviated taking account of previous Noble gas e.g. magnesium [Ne] 3s2 MM 2007 AH Periodic table blocks Periodic table subdivided into s, p, d and f blocks depending on which subshell occupied by outermost electrons s-block d-block Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 f-block p-block N 1s2 2s2 2p3 MM 2007 AH Ionisation energies E (g) E+ (g) E+ (g) + eE2+ (g) + e- Three main factors affecting ionisation energies • atomic size - the bigger the smaller! • nuclear charge - the bigger the bigger! • screening effect - the bigger the smaller! MM 2007 AH First ionisation energies He 1s2 Ne 1s2 2s2 2p6 Ar 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 In general, across a period … ionisation energy increases down a group …. ionisation energy decreases Be 1s2 2s2 N 1s2 2s2 2p3 B 1s2 2s2 2p1 O 1s2 2s2 2p4 Second and third ionisation energies? MM 2007 AH Spectroscopy Spectral lines correspond to transitions between energy levels Lines usually in visible of UV region of electromagnetic spectrum Atomic emission spectroscopy • gaseous sample excited with thermal or electrical energy • qualitative and quantitative intensity of radiation increases with amount of element • helium discovered using this technique - Sir Norman Lockyer MM 2007 AH Spectroscopy • radiation passed through gaseous sample of substance • qualitative and quantitative absorbance proportional to concentration of element Atomic absorption spectroscopy MM 2007 AH Atomic absorption spectroscopy Calibration curve 80 Absorbance 60 40 20 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Concentration Allows determination of concentrations of elements in samples MM 2007 AH