* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 9-21-11a
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Hartree–Fock method wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
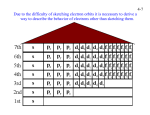
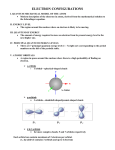
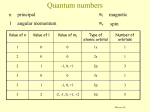
Lecture September 21 Goal for today: Start Chapter 8 (+ a bit of 7) Quantum Numbers and Electronic Structure of Atoms HW and Quiz 3(2)/7(1) due Monday Sept. 26 Posted an Extra Practice for Naming Compounds Will post a Practice Exam and a Review Sheet by Friday evening CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 1 Quantum Numbers The quantum numbers from the solution to the Schrodinger Equation n, ℓ, and mℓ n principle q.n. - determines the mean distance of the electron from the nucleus same as n for the Bohr atom ℓangular momentum q. n. - shape of the orbital mℓmagnetic q. n. - orientation in space CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 2 Rules for the Quantum Numbers 2 n are whole number integers as in the Bohr atom mℓ = -ℓ < n Spectroscopic notation for ℓ m ℓ ℓ to +ℓ 0 s 0 0 integers 1 p -1,0,+1 0,1 3 0,1,2 ℓ n 1 2 d -2,-1,0,+1,+2 3 f etc. CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 3 The 1s Orbital ℓ= 0 See Figures 7.22 - 7.24 CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 4 2s and 3s Orbitals Figure 7.25 Still a sphere - but there are NODES in the internal distribution A node is where the electron probability density is ZERO CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 5 More S Orbitals All s orbitals are spherical mℓ = 0 n=1 no nodes n=2 1 node n=3 2 nodes n=6 H atom 5 nodes CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 6 p Orbitals All p orbitals are dumbbell shaped mℓ = -1, 0, +1 Three orientations px, py, pz CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 7 d Orbitals Figure 7.27 5 orbitals f Orbitals Figure 7.28 7 orbitals CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 8 Chapter 8 - Multielectron Atoms Concept of SPIN - electrons have spin 1/2 and are FERMIONS New Quantum Number s = 1/2 ms = +1/2 ( spin up ↑) or -1/2 (spin down ↓) Pauli exclusion principle applies to all FERMIONS No two electrons in an atom can have the same 4 quantum numbers CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 9 Building Atoms n=1 ℓ 0s mℓ 0 0 -1,0,+1 ms ± 1/2 # of electrons 2 n=2 0s 1p ± 1/2 ± 1/2 2 6 n=3 0s 0 ± 1/2 1p -1,0,+1 ± 1/2 2 d -2,-1,0,+1,+2 ± 1/2 2 6 10 CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 10 Energies of the Orbitals See Fig. 8.6 Periodic Table follows this energy ordering H He 1s1 1s2 B ↑ 1s ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 1s Li Be 1s2 2s1 1s2 2s2 ↑↓ ↑ 1s 2s ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 1s2 2s2 2p1 2s CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 2s ↑ px Orbital diagrams 11 Rest of Period 2 (n=2) C 1s2 2s2 2p2 ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s ↑ ↑ px py N 1s2 2s2 2p3 ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s ↑ ↑ ↑ These are following Hund’s Rule the order of filling is to go in UNPAIRED first px py pz CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 12 Periodic Table and Electron Configurations Similar to Figure 8.8 s and p electrons are the VALENCE electrons outer electrons CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 13 Representative Elements Filling the s and p orbitals Electronic configuration of P 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 OR [Ne] 3s2 3p3 Core Notation Orbital Diagram ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s [Ne] ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ 2p 3s ↑ ↑ ↑ 3p CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 14 Quiz of the Day Give the electronic configurations of the following using the core notation a) S b) Mg [Ne] 2 3s [Ne] 2 3s 4 3p CHEM131 - Fall 11 - September 21 15