* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter Fifteen
Survey
Document related concepts
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
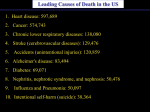
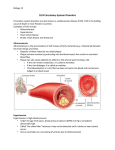
Chapter Fifteen Cardiovascular Health The Cardiovascular System • Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States • Heart attacks and strokes are the most common lifethreatening types of heart diseases • Much of these incidences are due to lifestyle concerns Characteristics of the Heart • • • • 4 chambered pump (atria, ventricles) Size of a fist Weighs about 1 pound Function - creates pressure to circulate blood throughout the body • Blood enters via the Vena Cava into the right atrium (see Figure 15-2 on blood circulation) Heart Beat Stimulation • Signal sends impulses from the heart • SA node (pacemaker of the heart) creates an electrical impulse • An electrical impulse spreads from the right side to the left (ECG) • The pace of the heart is regulated by the brain Risk Factors for Heart Disease That Can Be Changed (AHA) • Tobacco Smoking • Physical inactivity • High cholesterol (Figure 15-2) • Hypertension • Diabetes Mellitus • Obesity and Overweight Reference: American Heart Association Contributing Risk Factors for Heart Disease That Can Be Changed • • • • • • • High Triglyceride Levels Stress Chronic hostility and Anger Type D Personalities Depression/Anxiety Social Isolation Low socioeconomic status Major Risk Factors That Cannot Be Changed • • • • Heredity Aging Being Male Ethnicity Possible Risk Factors Currently Being Studied • Inflammation and CReactive Protein • Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome • Homocysteine • Infectious agents • Lipoprotein (A) • • • • LDL Particle size Fibrinogen Blood viscosity and Iron Uric acid Major Forms of Cardiovascular Disease • CAD (coronary artery disease) • Atherosclerosis: build up of plaque on the arteries • Hypertension • Stroke • Congestive heart failure Hypertension • Blood pressure exceeds a systolic (pressure at contraction) over 140 mm/hg and/or a diastolic (pressure between contraction) over 90 mm/hg • Symptoms – the “silent killer” (no symptoms) • Diagnosis – regular checks of resting blood pressure (average blood pressure < 120/80) • Treatment – medication, exercise, dietary changes) • A cause of heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease Atherosclerosis • Atheroschlerosis is a form of arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) • Arteries become narrow due to plaque buildup • This process deprives blood and vital oxygen to specific organs, such as the heart, brain, etc. • Results in the following: • Coronary Heart Disease • Stroke • Peripheral Arterial Disease *Atherosclerosis often begins during childhood Heart Attack • Damage to vessels of the coronary artery • Principal cause – atherosclerosis (narrowing of artery) – Myocardial infarction: heart attack • Caused by a coronary thrombosis • When the need for oxygen exceeds the supply, the result is chest pain called angina pectoris Recognizing and Treating a Heart Attack • Symptoms – shortness of breath, long-term chest pain (angina), numbness in the left side of face and arm • Diagnosis – ECG, angiogram, MRI • Surgical Treatment – bypass, angioplasty, heart transplant • Non-surgical Treatment- platelet inhibitors, aspirin, alcohol Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is considered an emergency response for heart attack emergencies Stroke (Cerebrovascular Accident) • Blood supply to the brain is cut off • Types –ischemic strokes (blockage), hemorrhagic strokes (ruptures) • Diagnosis – CT scan, MRI • Treatment – clot dissolving drug therapy (TPAs) Congestive Heart Failure • Swollen heart due to the lack of strength known as Pulmonary edema • Causes – various causes from other illnesses to damaging heart to existing injury to the heart • Treatment – drugs, modified lifestyle Other Forms of Heart Disease • • • • Congenital Heart Disease Peripheral Artery Disease Rheumatic Heart Disease Heart Valve Disorders Protecting Yourself Against Cardiovascular Disease • Eat Heart-Healthy • Decrease Fat and Cholesterol Intake • Increase Fiber Intake • Moderate the amount of alcohol consumption • Decrease Sodium and increase Potassium Intake • Exercise Regularly • DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) • Avoid Tobacco • Know and manage your Blood Pressure • Know and manage your Cholesterol levels • Develop ways to handle stress and anger Chapter Fifteen Cardiovascular Health