* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Acute inflammation
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Ulcerative colitis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Inflammatory bowel disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuromyelitis optica wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Periodontal disease wikipedia , lookup
IgA nephropathy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Ankylosing spondylitis wikipedia , lookup
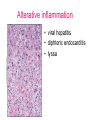
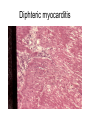
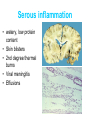
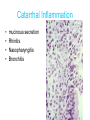
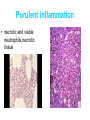
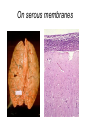
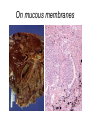
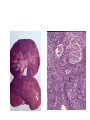
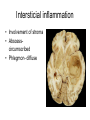
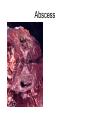
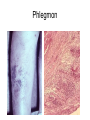
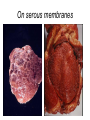
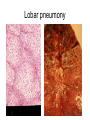
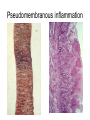
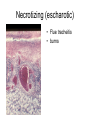
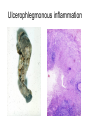
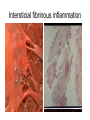
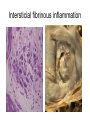
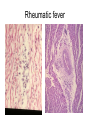
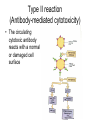
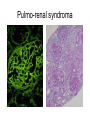
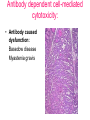
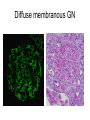
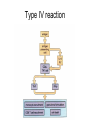
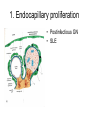
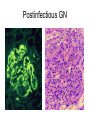
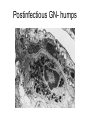
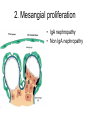
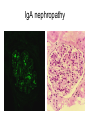
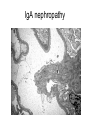
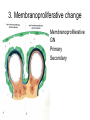
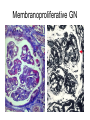
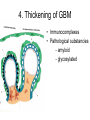
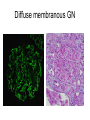
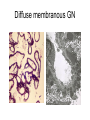
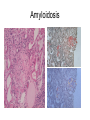
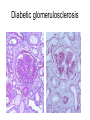
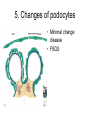
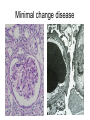
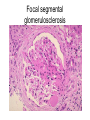
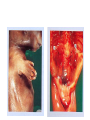
Inflammation • Local response of living mammalian tissues to injury do to: • Physical agens • Chemical agents • Infective agens • Immunological agents Signs of Inflammation • • • • • Rubor (redness) Tumor (swelling) Calor (heat) Dolor (pain) Functio laesa Types of inflammation • Acute inflammation: short duration, early body reaction, followed by repair • Chronic inflammation: longer duration, occur when• healing of acute inflammation is incomplet • Stimulus induces chronic inflammation from the begining Acute inflammation • Acute inflammatory process involves: • Vascular events- vasodilatation increased permeability • Cellular events- influx of inflammatory cells phagocytosis release of inflammatory enzymes Morphologic types of acute Inflammation 1. Alterative 2. Exudative – appearance of escaped plasma determinates the morphological type 3. Proliferative Alterative inflammation • viral hepatitis • diphteric endocarditis • lyssa Diphteric myocarditis Exudative inflammation Type of exudation • Serous • Catarrhal • Purulent (pyogenic, suppurative) • Fibrinous Serous inflammation • watery, low protein content • Skin blisters • 2nd degree thermal burns • Viral meningitis • Effusions Catarrhal Inflammation • • • • mucinous secretion Rhinitis Nasopharyngitis Bronchitis Bronchitis Purulent inflammation • necrotic and viable neutrophils,necrotic tissue On serous membranes On mucous membranes Intersticial inflammation • Involvement of stroma • Abscesscircumscribed • Phlegmon- diffuse Abscess Phlegmon Fibrinous inflammation • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. • great vascular permeability – fibrinogen On serous membranes On mucous membranes Crupous Pseudomembranous Necrotizing Ulcerative Intesticial type On serous membranes On mucous membranes: Crupous Lobar pneumony Pseudomembranous inflammation Necrotizing (escharotic) • Flue tracheitis • burns Ulcerative Ulcerophlegmonous inflammation Intersticial fibrinous inflammation Intersticial fibrinous inflammation Rheumatic fever Proliferative inflammation • productive polyserositis, • palmar fasciitis Chronic Inflammation • Granulomatous • Nonspecific Immunopathology • Abnormally amplified mechanisms • Hypersensitivity reactions • Gill and Coombs- 4 types on the basis of the immunological mechanisms that mediate disease Type I reaction (immediate hypersensitivity) • Occur in minutes • Reexposure to an antigen to whisch the host has been previously sensitised 1. exposure to the A which stimulate IgE 2. reexposure 3. rapid release of preformed potent chemicals from mast cells Type I reaction • Local (depends on the portal of entry) symptoms- swelling, erythema, edema, pruritus Alergic rhinitis Atopic dermatitis Allergic conjunctivitis Extrinsic allergic asthma Food allergies Type I reaction • Generalized Symptomes: nausea, vomiting, bronchoconstriction, hypotension, urticaria, circullatory collaps, shockAnaphylactic shock Type II reaction (Antibody-mediated cytotoxicity) • The circulating cytotoxic antibody reacts with a normal or damaged cell surface •Complement-mediated cytotoxicity: • • • • • • binding of antibody with cell surface antigen causes activation of complement and MAC directly lyses cell membrane Immune hemolytic anemia hemolytic anemia of newborn autoimmune hemalytic anemia incompatibile blood transfusion Antibody induced thrombocytopenic purpura Rheumatic fever Pemphigus and pemphigoid group Goodpasture syndroma Wegener granulomatosis Pulmo-renal syndroma •Antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity: • Antibody caused cell death defense against parasites Hashimoto thyreoiditis Autoimmune gastritis Hyperacute graft rejection og a renal transplant Antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity: • Antibody caused dysfunction: Basedow disease Myastenia gravis Type III reaction Type III reaction (immunocomplex disease) • Circulating immunocomplexes • In situ immunocomplex formation • Antigens: exogenous- bacteria, viry, protozoa, drugs (heroin) autoantigens: tumour cells, DNA, RNA, ribosomes, immunoglobulins Type III reaction • Acute: postinfectious GN, membranous GN, polyarteritis nodosa • Chronic: Cryoglobulinemia type II and III, SLE, dermatomyositis, rheumatoide arthritis, autoimmune hepatitis Diffuse membranous GN Type IV reaction (cell mediated hypersensitivity) • Not require the presence of antibody • Is delayd anywhere from 24 h to 2 weeks • Iniciated by specifically sensitized T lymphocytes • 2 subtypes Type IV reaction 1. Delayed type hypersensitivity • Persistent antigen in macrophages • Infections with intracellular bacteria: Mycobacterium, Spirochets,Brucella, Yersinie, Fungi, some parasits • Tuberculin-type: • Granulomatous type: Sarcoidosis 2. Cell mediated cytotoxicity • • • • • • CD 8+ T cells or NK cells Chronic rejection – GVHD Polymyositis Sclerodermia Spontaneous regression of tumours Kontaktalergie Non-organ-specific autoimmune disease Morphological patterns of glomerular reaction on injury 1. Endocapillary proliferation • Postinfectious GN • SLE Postinfectious GN Postinfectious GN- humps 2. Mesangial proliferation • IgA nephropathy • Non IgA nephropathy IgA nephropathy IgA nephropathy 3. Membranoproliferative change • Membranoproliferative GN • Primary • Secondary Membranoproliferative GN 4. Thickening of GBM • Immunocomplexes • Pathological substancies - amyloid - glycosylated Diffuse membranous GN Diffuse membranous GN Amyloidosis Diabetic glomerulosclerosis 5. Changes of podocytes • Minimal change disease • FSGS Minimal change disease Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Case report • abcd