* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download real numbers
Survey
Document related concepts
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
P-adic number wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Division by zero wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
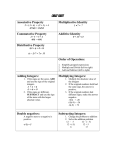
WARM UP 1 The least common denominator of the fractions and is 24 2 The variable in the expression 5x – 3 is _________ X 3 Fill in the blank with an inequality symbol 6 ___ > 4 4 In the fraction denominator ________ 5 According to the order of operations, what is the first step in simplifying the expression (3 +4) – 8? 5 is the numerator _______ and 12 is the Add 3 + 4 (PEMDAS) PROPERTIES OF REAL NUMBERS INTEGERS AND RATIONAL NUMBERS OBJECTIVES Performing operations with real numbers Applying properties of real numbers Classifying and reasoning with real numbers. To add positive and negative numbers. To subtract positive and negative numbers. To use real number in solving problems. VOCABULARY Absolute value Additive inverse Differenc e Distributive property Equivalent expressions Integers Irrational numbers Multiplicative inverse Natural numbers Number line Opposite Rational numbers Real numbers Subtraction Whole numbers Using integers & rational numbers Whole numbers are numbers 0, 1, 2, 3,………….. Integers are the numbers ….-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,……… Positive integers are the integers that are greater than 0 and negative integers are less than 0. The integer 0 is neither negative nor positive. REAL NUMBERS The most important set of numbers in algebra is the set of real numbers. The sets of natural numbers [1, 2, 3, 4,……..], whole numbers [0, 1, 2, 3, 4,……] and integers [-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,….] are all subsets of the set of real numbers. RATIONAL NUMBERS A number where a and b are integers and b is not equal to zero. For example - is a rational number. The rational number belongs to the set of numbers called real numbers. NUMBER LINE Negative integers Positive integers left side of zero right side of zero Zero is the center of the number line EXAMPLE Graph and compare integers Graph -3 and -4 on the number line. Then tell which number is greater. - 6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 OPPOSITES The numbers that are the same distance from 0 on a number line but are on opposite sides of 0 are called opposites. For example, 4 and -4 are opposites because they are both 4 units from 0 but are opposite sides of 0. 4 units to the left of zero 4 units to the right of zero ABSOLUTE VALUE The absolute value of a number a is the distance between a and 0 on a number line. The symbol represents the absolute value of a. If a is positive, then If a is 0, then =a =0 If a is negative, then = -a Example: =2 =0 = -(-2) = 2 EXAMPLE Tell whether each of the following numbers is a whole number, integer, or rational number: 5, 0.6, -2 , and -24. Number Whole Number? Integer? Rational Number? 5 Yes Yes Yes 0.6 No No Yes 2 No No Yes 24 Yes Yes Yes REAL NUMBERS ADDITION • One way to add or subtract two real numbers is to use the number line. To add a positive number move right - 6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 To add a negative number, move left 2 3 4 5 6 REAL NUMBER SUBTRACTION Subtraction rule To subtract b from a, add the opposite of b to a. a – b = a + (-b) Example: 14 – 8 = 14 + (-8) Find the difference: -12 – 19 = -12 + (-19) You can then use the number line to start at negative 12 and go left 19 units because you are adding a negative number. REAL NUMBER MULTIPLICATION The product of two real numbers with the same sign is positive. Examples: 3(4) = 12 -6(-3) = 18 The product of two real numbers with the different signs is negative. Examples: 2(-5) = -10 -7(2) = -14 More examples: Find the product -3(6) = -18 Different signs; product is negative 2(-5)(-4) = (-10)(-4) = 40 Multiply 2 & -5, same sign; product is positive PROPERTIES OF MULTIPLICATION Commutative Property : The order in which you multiply two numbers does not change the product. axb=bxa 4 x (-5) = -5 x 4 Associative Property: The way you group three numbers in a product does not change the product: (a x b) x c = a x (b x c) (-2 x 7) x 4 = -2 x (7 x 2) Identity Property: The product of a number and 1 is that number. ax1=1xa=1 (-5) x 1 = 1 x (-5) = -5 Property of Zero: The product of a number and 0 is 0 ax0=0 0xa=0 3x0=0 0x3=0 Property of negative one (-1): The product of a number and -1 is the opposite of the number. a x (-1) = -1 x a = -a -2 x (-1) = 2 REAL NUMBER DIVISION Reciprocals are opposite fractions that when multiplied equal =1 The reciprocal of a nonzero number a written , is called the multiplicative inverse of a. Zero does not have a multiplicative inverse because there is no number a such that 0 a = 1 (not true) Example: a 8 = 1, when a is not equal to 0 =1 Division Rule: to divide a number a by a nonzero number b, multiply a by the multiplicative inverse a b=a , when b 0 5 2=5 DIVISION AND ZERO Division by zero is impossible. We can divide zero by any nonzero number . The answer is always zero. On the other hand, we can never divide by zero. By definition of division such that . But for any number c, so the only possible number that n could be is 0. Let’s consider what might be. might be 5 because 0 = 0 5 might be 267 because 0 = 0 267 It looks as if could be any number. Thus, we cannot define and must exclude division by 0. Zero is the only real number that does not have a reciprocal. FINDING RECIPROCALS Many scientific calculators have a reciprocal key: 1/x Find the reciprocal of 63 0.015873 SUMMARY OF OPERATIONS Addition of Real Numbers: To add when there are like signs, add the absolute values. The sum has the same sign as the addends. Subtraction of Real Numbers: Every real number has exactly one additive inverse or opposite. It is the number added to it to get 0 and is symbolized by -x Multiplication of Real Numbers: If numbers are both positive or both negative, their product is positive. If one number is positive and the other negative, their product is negative. Division of Real Numbers: Every nonzero real number has a multiplicative inverse or reciprocal. The reciprocal of a number is the number we multiply to get 1. If numbers are both positive or both negative, the quotient is positive. If one number is positive and the other negative, the quotient is negative