* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical reactions
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
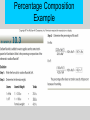
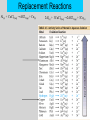
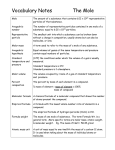
PowerPoint Lectures to accompany Physical Science, 8e Chapter 10 Chemical Reactions Start Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Core Concept Chemical symbols, formulas, and equations can be used to concisely represent elements, compounds, and what happens in a chemical reaction. –3 types of formulas Chemical Formulas 1. Empirical formula – Identifies elements present in terms of simplest whole number ratios – Examples: table salt, NaCl; water, H2O 2. Molecular formula – Identifies actual number of atoms in a molecular compound – Example: water, H2O; not table salt, NaCl (ionic compound) Chemical Formulas, cont. 3. Structural formula – Represents arrangement of atoms within a molecule – Related to 3-D structure of molecule Empirical or Molecular Formula? Empirical • Ionic - lacking discrete unit, or molecule • Composed of both metallic and nonmetallic elements • Electronegativity difference > 1.7 Molecular • Covalent compounds • Usually nonmetals bound to nonmetals • Molecular and empirical formulas can be different – Glucose – molecular C6H12O6 versus empirical CH2O Molecular and Formula Weights • Formula weight – Sum of atomic weights of all atoms in chemical formula • Molecular weight – Formula weight of a molecular substance – Term often used for nonmolecular substances, as well Percent Composition of Compounds • Finding the mass percentage of an individual element from the formula weight Percentage Composition Example Chemical Reactions • Occur through formation and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms • Involve changes in matter, creation of new materials and energy exchange • Chemical equations - concise representation of chemical reactions Chemical Equations • • • • Reactants - substances existing before reaction Products - substances existing after reaction Word representation not sufficiently precise Chemical symbols and formulas needed for quantitative purposes Balancing Equations • Law of conservation of mass - atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions • Change coefficients in front of chemical formulas, not subscripts within formulas, to balance mass of reactants = mass of products Meaning of Subscripts and Coefficients with a Chemical Formula Stepwise Balancing Procedure Generalizing Equations • Combustion reaction – A hydrocarbon in the presence of oxygen reacts to produce carbon dioxide and water. CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O Alternative Classification 1. Combination reactions 2. Decomposition reactions 3. Replacement reactions (1-3 = redox reaction subclasses) 4. Ion exchange reactions Oxidation – Reduction Reaction • Oxidation – loss of electrons • Reduction – gain of electrons Combination Reactions • Synthesis reaction in which two or more substances combine to form single compound • X + Y XY Decomposition • A compound is broken down into simpler substances • XY X + Y Replacement Reactions • An atom or polyatomic ion is replaced in a compound by a different atom or polyatomic ion. Replacement Reactions Al(s) + CuCl2(aq) →AlCl3(aq) + Cu(s) 2Al(s) + 3CuCl2(aq) →2AlCl3(aq) + 3Cu(s) Ion Exchange Reactions • A reaction that takes place when the ions of one compound interact with the ions of another compound forming – A solid precipitate – A gas – Water AX + BY AY + BX Ion Exchange Reactions __Ca(OH)2(aq) + __Al2(SO4)3(aq) __CaSO4(aq) + __Al(OH)3(s) 3 Ca(OH)2(aq) + Al2(SO4)3(aq) 3 CaSO4(aq) + 2 Al(OH)3(s) Information - Chemical Equations • Atoms are conserved • Mass is conserved • Law of combining volumes (gases) – Gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules Units of Measurement Used with Equations • Atomic mass unit = 1/12 mass of carbon-12 • One mole of a substance contains Avogadro’s number (6.02x1023) of the basic chemical unit of that substance (atoms, molecules, ions, …) • A mole of carbon-12 atoms is defined as having a mass of 12.00g Molar Weights • Gram atomic weight mass in grams equal to atomic weight • Gram formula weight mass in grams equal to formula weight • Gram molecular weight mass in grams equal to molecular weight Quantitative Use of Equations Possible interpretations: 1. Molecular ratios of reactants and products 2. Mole ratios of reactants and products 3. Mass ratios of reactants and products