* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endokrin Sistem - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
Survey
Document related concepts
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
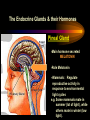
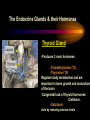
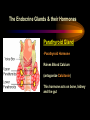
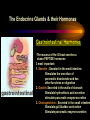
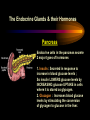
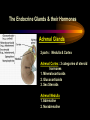
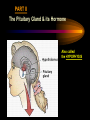
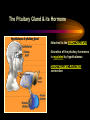
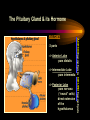
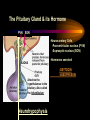
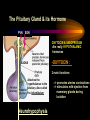
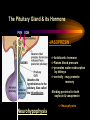
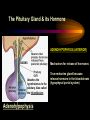
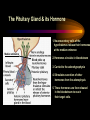
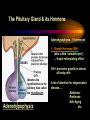
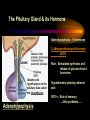
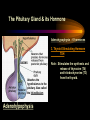
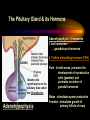
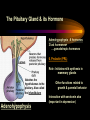
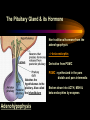
PART I The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Basic principles in hormone actions: Many effects of one hormone are antagonized by another hormone This helps maintain HOMEOSTASIS The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Pineal Gland -Main hormone secreted MELATONIN -Role Melatonin --Mammals : Regulate reproductive activity in response to environmental light cycles e.g. Some mammals mate in summer (lot of light), while others mate in winter (low light). The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Thyroid Gland -Produces 3 main hormones -Triiodothyronine (T3) -Thyroxine (T4) Regulate body metabolism and are important in bone growth and maturation of the brain -Congenital lack of thyroid hormones: Cretinism. -Calcitonin Acts by reducing calcium levels The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Parathyroid Gland -Parathyroid Hormone Raises Blood Calcium (antagonize Calcitonin) This hormone acts on bone, kidney and the gut The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Thymus Gland -Thymosin : Stimulates the production of Lymphocytes -Thymostatin : Inhibits the production of Lymphocytes Thymus : Important for the neonatal production of antibodies Thymus : Gland being at the center of endocrine, neural, and immune systems The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Heart -Granular cells in the heart muscle secrete Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF) ..ANF : Regulates blood pressure, blood volume, and excretion of water, sodium and potassium ..ANF : Also a neuropeptide in the brain The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Gastrointestinal Hormones -The mucosa of the GI tract secretes a dozen PEPTIDE hormones 3 most important: 1. Secretin : Secreted in the small intestine Stimulates the secretion of pancreatic bicarbonate and has other functions on digestion 2. Gastrin: Secreted in the walls of stomach Stimulate hydrochloric acid secretion stimulate pancreatic enzyme secretion 3. Cholecystokinin : Secreted in the small intestine Stimulate gall bladder contraction Stimulate pancreatic enzyme secretion The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Pancreas Endocrine cells in the pancreas secrete 2 major types of hormones 1. Insulin : Secreted in response to increase in blood glucose levels ; So insulin LOWERS glucose levels by INCREASING glucose UPTAKE in cells where it is stored as glycogen. 2. Glucagon : Increases blood glucose levels by stimulating the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver. A parte : Insulin & Diabetes Insulin & Diabetes Diabetes : Hyperglycemia, ie. Elevated Blood Sugar 2 Types : The distinction is based upon whether the blood sugar problem is caused by insulin deficiency (Type 1) or insulin resistance (Type 2) Type 1- Insulin Deficiency : There is not enough insulin produced by the pancreas so the patient must inject insulin on a daily basis Type 2 - Insulin Resistance : There is plenty of insulin but the cells of the body are resistant to its action so, increase in blood sugar This form is controlled by a strict diet The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Adrenal Glands 2 parts : Medulla & Cortex Adrenal Cortex : 3 categories of steroid hormones 1. Mineralocorticoids 2. Glucocorticoids 3. Sex Steroids Adrenal Medulla 1. Adrenaline 2. Noradrenaline The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Adrenal Cortex Androgen Influence sexual differentiation and bodily changes during puberty Estrogen Stress Hormone, converts stored proteins to carbohydrate during stress. Antiinflammatory and Immunosuppressive functions. If there is a sodium deprivation, Aldosterone is secreted and acts to increase reabsorption of sodium ions (NA+) in the kidneys salivary glands, and sweat glands. The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Adrenal Medulla Adrenaline : Released following stress due to environmental extremes; Increases heart rate and blood glucose levels so, increases the amount of work the muscles can do (FLIGHT) Noradrenaline : As Adrenaline, act as a NT in the brain Periphery; increase blood pressure and constrict blood vessels (noradrenaline, stress, and heart disease…) The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Gonads ; Testes The male gonads : produces Androgens Primary androgen = TESTOSTERONE Other androgen : Dihydrotestosterone Androstenedione Testosterone : Important for masculinization Control of sperm production Development of male sexual characteristics Activation of sexual and aggressive behaviors The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Gonads ; Ovaries 2 major classes of hormones ESTROGENS PROGESTINS Primary ESTROGEN : Estradiol others : Estriol Estrone Synthetic estrogens : Birth control pills Estrogens : -Development of sexual characteristics at puberty -Influence metabolic rate -Influence sexual and maternal behavior The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Gonads ; Ovaries PROGESTIN : Progesterone -Stimulates breast and uterine enlargement at puberty & during menstrual cycle -Maintains pregnancy (inhibits menstrual cycle during pregnancy) Other hormone released at the end of pregnancy : Relaxin Acts to prepare the birth canal. Estrogen and Progesterone act in synergy. The Endocrine Glands & their Hormones Placenta -Hormones secreted by the fertilized egg (Used in pregnancy tests) Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) Act by keeping progesterone high at the beginning of a pregnancy Human Placental Lactogen (HPL) Stimulates the mammary glands to begin to secrete milk PART II The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone Also called the HYPOPHYSIS The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone -Attached to the HYPOTHALAMUS -Secretion of the pituitary hormones is regulated by hypothalamus -HYPOTHALAMIC-PITUITARY connection The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone ANATOMY --> Anterior Lobe -pars distalis --> Intermediate Lobe -pars intermedia --> Posterior Lobe -pars nervosa (“neural” cells) direct extension of the hypothalamus ADENOhypophysis NEUROhypophysis -3 parts The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone PVN SON -Neuroscretory Cells -Paraventricular nucleus (PVN) -Supraoptic nucleus (SON) AXONS -Hormones secreted -OXYTOCIN -VASOPRESSIN Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Neurohypophysis The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone PVN SON OXYTOCIN & VASOPRESSIN -Are really HYPOTHALAMIC hormones AXONS -OXYTOCIN : 2 main functions Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Neurohypophysis --> promotes uterine contractions --> stimulates milk ejection from mammary glands during lactation The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone PVN SON -VASOPRESIN : AXONS Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum --> Antidiuretic hormone --> Raises blood pressure --> promotes water reabsorption by kidneys --> centrally : may promote memory - Binding proteins for both oxytocin & vasopressin --> Neurophysins Neurohypophysis The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone ADENOHYPOPHYSIS (ANTERIOR) AXONS Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Adenohypophysis Mechanism for release of hormones True endocrine gland because release hormone in the bloodstream (hypophysal portal system) The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone 1. Neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus release their hormones at the median eminence Median eminence 2. Hormones circulate in bloodstream 3. Carried to the adenohypophysis 4. Stimulates secretion of other hormones from the adenophysis 5. These hormones are then released in the bloodstream to reach their target cells. The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone Adenohypophysis : 6 hormones 1. Growth Hormone (GH) (also called ‘somatotropin’) …’tropic’=stimulating effect AXONS GH = promotes growth in almost all body cells Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Adenohypophysis A lot of attention for degenerative disease….. -Alzheimer -Parkinson -Anti-Aging etc. The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone Adenohypophysis : 6 hormones 2. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone ACTH AXONS Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Adenohypophysis Role : Stimulates synthesis and release of glucocorticoid hormones ‘Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis’ 1970’s : Role of memory ….little problems….. The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone Adenohypophysis : 6 hormones 3. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone TSH AXONS Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Adenohypophysis Role : Stimulates the synthesis and release of thyroxine (T4) and triiodochyronine (T3) from the thyroid. The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone Adenohypophysis : 6 hormones 3 last hormones= ….gonadotropic hormones 4. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) AXONS Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Adenohypophysis Role : In both sexes, promotes the development of reproductive cells (gametes) and promotes secretion of gonadal hormones Males : stimulates sperm production Females : stimulates growth of primary follicle of ovary The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone Adenohypophysis : 6 hormones 3 last hormones= ….gonadotropic hormones 5. Luteinizing hormone (LH) AXONS Role : Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Adenohypophysis Female : Stimulates ovulation and formation of progesteronesecreting cells Males : Stimulates cells that secrete androgens (e.g. testosterone) The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone Adenohypophysis : 6 hormones 3 last hormones= ….gonadotropic hormones 6. Prolactin (PRL) AXONS Role : Initiates milk synthesis in mammary glands Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Adenohypophysis Other functions related to growth & parental behavior Interaction with serotonin also (important in depression) The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone Non traditional hormone from the adenohypophysis --> beta-endorphin AXONS Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Adenohypophysis Derivative from POMC POMC : synthesized in the pars distalis and pars intermedia Broken down into ACTH, MSH & beta-endorphins by enzymes The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone Beta-Endorphin : Role to play in --> Analgesia --> Learning and Memory --> Psychiatric diseases --> Feeding, Thermoregulation, --> Blood pressure --> also called the ‘drug of the jogger’….. The Pituitary Gland & its Hormone Pars Intermedia : Not present in adult humans but present in fetal humans and mammals AXONS Attaches the hypothalamus to the pituitary. Also called the Infundibulum Pars Intermedia Synthesize the hormone called Melanocyte stimulating hormones which acts in amphibian to change skin color…. Our friend Watson : Sex & Sunshine MSH….. http://www.psych.mcgill.ca/courses/342/h& b.htm