* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 21 Sec 3 Guided Reading
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Residual-current device wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic generator wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
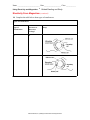
Name__________________________ Date ___________________ Class____________ Using Electricity and Magnetism ■ Guided Reading and Study Electricity From Magnetism (pp. 736-743) This section explains how an electric current can be produced in a conductor. It also describes how generators and transformers work. Use Target Reading Skills When you preview, you look ahead at the material to be read. Preview Figure 13. Then write two questions that you have about the diagram in the graphic organizer below. As you read, answer your questions. Generators Q. What are the parts of a generator? A. Q. A. Induction of Electric Current (pp. 736-739) 1. What is the key when using a magnet and a conductor to induce a current in the conductor? 2. An electric current is induced in a conductor when the conductor moves through a(n) 3. What is electromagnetic induction? 4. What are two ways to induce a current in a conductor with a magnet? a. b. © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. Name _________________________ Date ___________________ Class ___________ Using Electricity and Magnetism ■ Guided Reading and Study Electricity From Magnetism (continued) 5. Is the following sentence true or false? In an induced current, charges may flow in one direction only, or they may alternate directions. 6. What does the direction of an induced current depend on? 7. Is the following sentence true or false? An induced current may change direction. 8. Complete the table about induced currents. Induced Currents Induced Current Abbreviation Description Example a. AC b. Circuits in the home c. DC d. Batteries Generators (pp. 740-741) 9. A device that transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy is called a(n) 10. How is an electric motor the opposite of an electric generator? 11. Is the following sentence true or false? Large generators use armatures similar to those in a motor. 12. The parts of a generator that rotate with the wire loop and make contact with the brushes are called © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. Name__________________________ Date __________________ Class ____________ Using Electricity and Magnetism ■ Guided Reading and Study Transformers (pp. 741-743) 13. A device that increases or decreases voltage is called a(n) 14. In a transformer, what induces a current in the secondary coil? 15. Why won't a transformer work with direct current? 16. If there are more loops in the secondary coil of a transformer than in the primary coil, will the voltage in the secondary coil be higher or lower than in the primary coil? 17. Why is a transformer necessary so that electrical energy can be brought into a home? Continues on Back--> Name _________________________ Date ___________________ Class ___________ Using Electricity and Magnetism ■ Guided Reading and Study Electricity From Magnetism (continued) 18. Complete the table below about types of transformers. Types of Transformers Type of Transformer Increases or Decreases Voltage? a. b. c. b. Setup © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved.