* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Battles
Kriegsmarine wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Allied naval bombardments of Japan during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
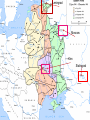
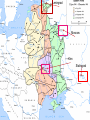
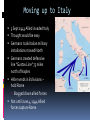
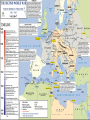
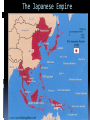
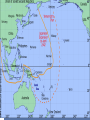
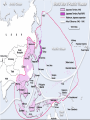
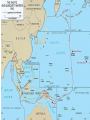
WWII: European Theater The Battle of the Atlantic Battle of the Atlantic Battle of the Atlantic – major threat to the Allied Powers Longest continuous military battle Winston Churchill once wrote that, '... the only thing that ever really frightened me during the war was the U-boat peril' Sept 3, 1939-1945 Britain needed tons of food & supplies imported If sunk 150 ships a month would starve the British German wolf packs Attacked at night Especially easy after France fell German control until 43’, “happy time” Allied power technology changes game http://sillysoft.net/plugins/images/WWII%20Europe.jpg U-boats succeeded in sinking three million tons of Allied shipping ... 1939 : 222 ships sunk (114 by submarine) 1940 : 1059 ships sunk (471 by submarine) 1941 : 1328 ships sunk (432 by submarine) 1942 : 1661 ships sunk (1159 by submarine) 1943 : 597 ships sunk (463 by submarine) 1944 : 247 ships sunk (132 by submarine) 1945 : 105 ships sunk (56 by submarine) Operation Barbarossa In 1941, Hitler violated nonaggression pact and invaded the USSR Why? Ironic? Hubert Menzel (German-Army) 'We knew that in two years' time, that is by the end of 1942, beginning of 1943, the English would be ready, the Americans would be ready, the Russians would be ready too, and then we would have to deal with all three of them at the same time.... We had to try to remove the greatest threat from the East.... At the time it seemed possible.' Germans invaded Russia: Purpose & Attitudes Desired: Soviet oil fields living space (lebensraum) SS to kill all Communists, “total disregard for human life” Hitler ordered that Leningrad should “vanish from the surface of the earth” So arrogant only gave summer gear What does this tell you? Leningrad Moscow Kiev Stalingrad N, Leningrad; C, Moscow, S, Kiev One week into the German invasion, 150,000 Soviet soldiers were either dead or wounded Destroyed everything they could find Utilities Stalin removed many industries and industrial workers but left civilians - 800,000 civilians starved at Leningrad alone 506 day siege of Leningrad Stalin: no retreating, ordered deserters shot, 8,000 killed Moscow for “cowardness” , blame ethnic minorities, killed “disloyal” Leningrad Moscow Kiev Stalingrad Battle of Stalingrad, Aug 1942 – Feb 43’ 1,000 tons of bombs dropped http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-ii/world-war-ii-history/videos/world-war-ii-battle-of-stalingrad New Soviet policy – FIGHTING RETREAT!!! Hand to hand combat “I was like a beast. I wanted only one thing – to kill. You know how it looks when you squeeze a tomato and juice comes out? Well, it looked like that when I stabbed them. Blood everywhere. Every step in Stalingrad meant death. Death in our pockets. Death was walking with us”, Soviet General Av. Life expectancy private soldier 24 hours! Soviets lost 1.1 million (death & wounded) Stalin, at first, forbade evacuation of the city Winter arrives, German supplies stretched thin Germans had to stop eastern offensive Such huge losses Winter in Stalingrad The Winter Arrives "My hands are done for, and have been ever since the beginning of December. The little finger of my left hand is missing and - what's even worse - the three middle fingers of my right one are frozen. I can only hold my mug with my thumb and little finger. I'm pretty helpless; only when a man has lost any fingers does he see how much he needs then for the smallest jobs. The best thing I can do with the little finger is to shoot with it. My hands are finished." 43 below zero Stalingrad – Hitler’s Big Mistake "I was horrified when I saw the map. We're quite alone, without any help from outside. Hitler has left us in the lurch. Whether this letter gets away depends on whether we still hold the airfield. We are lying in the north of the city. The men in my unit already suspect the truth, but they aren't so exactly informed as I am. No, we are not going to be captured. When Stalingrad falls you will hear and read about it. Then you will know that I shall not return." Anonymous German soldier Psychological loss, man power loss, strategic loss http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T6b1PNWqpbM Images stalingrad http://www.history.co.uk/explorehistory/ww2/stalingrad/video.html;jsessionid=E5B94C334258967A0CEA989FF3798F88 British propaganda video send support stanlingrad Where are England, USA and other Allied Powers???? North African First…. North African Campaign Why North Africa? European controlled, Suez Canal, oil fields, link to raw materials Asia MEDITERRANEAN Italy enters war 40’ fighting spreads N Africa where Axis and Allied Powers had colonies Also opens a new front Why is that good???? http://www.history.com/shows/wwii-inhd/videos/north-africa-campaign#north-africacampaign North Africa campaign – 1.5 min North African Campaign Spans 1940-1943 Part I: Western Desert Sept 1940 Italians attacked British in Egypt from base in Libya Dec 1940 British counterattack in December Feb 1941 German General Erwin Rommel “the desert fox” arrived to reinforce Italians and take command March – Nov 41’ launched offensive to reach Egypt More in spring in summer of 42’! Fall 42’ - British halted Axis attacks and Axis withdrew! North African Campaign Part II: Operation Torch Nov 8 1942-Nov 11 1942 D. Eisenhower led British and Americans 3 beach invasions (Morocco & Algeria) German troops to Tunisia End of Nov, 1942 - Allied powers entered Tunisia Eisenhower & Patton North African Campagin Part III: Tunisia Campaign Jan 1943 Allied amphibious landing in Eastern Tunisia Feb 43’ More movement into Tunisia Germans cut off from supply base By May 43’ Allied captured Tunis (capital) May 13, 1943 Axis surrendered What is Tunisia a perfect based for?? Taking Italy! Remove Mediterranean threat completely & take back parts of Europe (controversial) Taking Italy: Where do you start? Sicily first: Operation Husky Operation “Mincemeat” diversion plan Hitler sent his men to Sardinia and Corsica Italians already weak from North Africa, Allied won easily, but Axis armies fled July 24, 1943, Mussolini = deposed and arrested – new gov’t helped allies Italy now part of ALLIED POWERS Moving up to Italy 3 Sept 1943 Allied invaded Italy Thought would be easy Germans took Italian military installations moved North Germans created defensive line “Gustav Line” 75 miles north of Naples Hitler sends in 8 divisions – hold Rome Bogged down allied forces Not until June 4, 1944 Allied forces capture Rome By mid 1943…. Axis advances stopped -Soviet Union pushing west from Poland -Britain moving up from Italy -Constant bombing of German cities & industrial installations -Destroy materials, demoralize German population & get ready take back France - Force German air force protect Germany Taking Back France: The Invasion of Normandy June 6, 1944 – D Day Gen’l Dwight D. Eisenhower – led Air & amphibious (water) attack Canadian, UK, Free French & US 5 beaches, 50 mile stretch Within a week coast taken back 4,000 landing craft 600 warships 11,000 planes Largest land-sea-air operation in history http://www.history.com/videos/d-day-allied-invasion-at-normandy#d-day-allied-invasion-at-normandy news real video Normandy http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uPU4p7UQOtU Images Normandy August 25, 1944 Paris liberated French resistance movement Luxembourg and Belgium next (by Sept) http://videos.howstuffworks.com/battle-of-normandy-videos-playlist.htm#video47114 http://www.cyberlearning- world.com/lessons/ushistory/ww2/europeant heater.htm Moving into Germany – Ending the War in Europe Sept 1944 at Germany’s border Ruhr valley goal – Siegfried Line Oct 1944, Aachen Heavy casualties First German city taken Continue moving east Battle of Bulge , Dec 1944 German offensive – Ardennes mountains Germans were winning in the beginning, Allied counteroffensive & Germans run out supplies 120,000 Germans died (also lost 600 tanks and guns and 1,600 planes – leading to defeat)) ~100,000 Americans casualties Soviets move west through Poland and storm Berlin, April 25, 1945 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6rjtFurTyv8 German http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iCgc8hTlRbM British Planning the End in Europe Feb 1945: Yalta Conference: Discuss post-war Europe April 12, 1945 April 28, 1945: Mussolini executed April 28, 1945: Hitler Married Eva Braun April 30, 1945: Hitler & Eva commit suicide Gunshot & cyanide Bodies buried in the street May 8, 1945: Unconditional Surrender VE Day Eisenhower accepts surrender Potsdam Conference July – August 1945 Truman, (Churchill and then Clement Atlee) and Stalin met in Potsdam, Germany Drew up a blueprint to disarm Germany and eliminate the Nazi regime Division of Germany & Berlin ALSO TALK ABOUT JAPAN…. “unconditional surrender” WWII: The Pacific Front Japan - Post-Pearl Harbor Immediately after PH, the Japanese seize Guam, Wake Island, Hong Kong, Burma, Malaya, Borneo, Philippines Philippines under control of Army General Douglas MacArthur Invasion anticipated Mixed Filipino force versus best Japanese troops Feb 12th, “I shall return” American/Filipino surrender 4/9 Bataan Death March Bataan “Death March” (42’) 70,000 – 60 miles About ¼ died Surrender forfeit rights Hell ships Sent to Japan to work "A Japanese soldier took my canteen, gave the water to a horse, and threw the canteen away," “The stronger were not permitted to help the weaker. We then would hear shots behind us." The Japanese Empire Trying to Contain the Japanese Doolittle’s Raid (April 18, 1942) Attempt to attack Japanese homeland with B-25 bombs via aircraft carriers 16 bombers; 5 man crew “The Japanese people had been told they were invulnerable ... An attack on the Japanese homeland would cause confusion in the minds of the Japanese people and sow doubt about the reliability of their leaders. There was a second, and equally important, psychological reason for this attack ... Americans badly needed a morale boost..” James Doolittle Psychological Impact Battle of Coral Sea (May, 1942) Japanese attempt to take Port Moresby in New Guinea and Solomon Islands Australia isolated so unable to help Allied Aircraft carriers (equally matched) Fought entirely with planes! American loses Yorktown, but stopped the Japanese from taking Port Moresby & isolating Australia Battle of Midway (June 3-6,42) Admiral Nimitz Japanese wanted bring out Pac Fleet Turning point (cryptology) JN-25 Allied go on the offensive Japanese lost 4 carriers, a heavy cruiser, 3 destroyers, some 275 planes, at least 4,800 men American losses included 1 carrier, a destroyer, about 150 planes, and 307 men America on the Offensive: Island Hopping Army (Macarthur) versus Navy (Nimitz) Naval Plan initiated - Island Hopping Take strategic islands to get closer and closer to Japan Bypass strongly held islands Bases & air control Bomb and then invade islands More resistance than expected, reconnaissance problems Fight till the death http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n79CRrEBCh0 Intro island hopping Americans On the Offensive Guadalcanal , Solomon Islands Huge American offensive Aug 42’-Feb 43’ American victory Control air base - communication Fighting in the jungle Every 2 killed in battle, 5 killed by disease Foxholes/dugouts Major supply problems Gilbert Islands Hopping Away! Reefs 17 Japanese alive Marshall Islands Naval & aerial bombardment Marianas – airfields! “Great Mariana Turkey Shoot Out” Saipan – mass suicides 14,111 US casaulties What now? http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-ii/battle-of-saipan/videos/peleliu Reconnaissance Marines Foxholes Close contact Constant fear Reclaiming the Philippines Macarthur convinced FDR to allow an invasion of the Philippines Outer islands first (Sept 44’ – East Indies as a base) Oct –Dec 44’ - Battle of Leyte Gulf All 4 Japanese carriers destroyed – Navy should be finished! Kamakaze – “divine wind” – better to die than live as a coward Jan 45’- Luzon, Philippines – OIL Blocked!!!!!! On land - Strap mines to body throw under tanks largest campaign of Pacific (March 45’ taken) Japanese lost 200,000 plus – US 8,000 plus Fighting continued until the Japanese surrender on August 15, 1945 Capt. Motoharu Okamura: “I firmly believe that the only way to swing the war in our favor is to resort to crash-dive attacks with our planes…. There will be more than enough volunteers for this chance to save our country.” Closing in on the Homeland Iwo Jima – Feb-March 45’ About 600 miles Japan – base for bombers & stop Japanese from detecting American bombing raids (2 airfields) Bombing, but 22,000 men in caves (6800 tons of bombs, 2 months) Japanese technique no longer by shore – now inland Large marine casualties first day 3 days later take Mnt (center defense) Fighting continues… surprise attacks from tunnels All Japanese (23,000 killed) except 1,00o POW US 6,000 dead, 18,000 wounded Mt. Suribachi http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5Y0gdFi sD9k&feature=relmfu Okinawa - April-June 1945 4 air bases – launch bombing raids Japanese heartland 300 miles away mainland Thought 65,000 really 130,000 about 450,000 civilians War of attrition Kamikazes attacked allied fleet 12,000 Americans died – 40% from kamikaze Damage American carriers - 21 sunk ships; 66 damaged from Kamikazes ~70,000 Japanese killed and 7,400 men taken prisoner Fire Bombing of Tokyo – March 1945 2,000 tons over 48 hours Fire – firestorm (windy) Worst single fire storm in history Many suffocated to death 16 square miles around Tokyo destroyed 80,000-130,000 killed 100,000 injured Women, children, elderly suffered men at war! Operation Downfall Nov 1, 1945 – Kyushu No beaches… Resistance from citizens Harry Stimson - 1.7-4 million casualties..? Potsdam Conference July – August 1945 Truman, (Churchill and then Clement Atlee) and Stalin met in Potsdam, Germany Call for unconditional surrender of Japan , “surrender or face prompt and utter destruction” Bombs versus Invasion (Operation Downfall) Dropping the Bombs August 6, 1945: “Little Boy” on Hiroshima 140,000 August 9, 1945: “Fat Man” on Nagasaki 80,000 War in the Pacific: Atomic Bomb 32’ atomic split; 33’ Germany’s nuclear program’, 33’ Hitler fires Jewish scientists 39’ Einstein wrote letter FDR; 40’ US & UK creates Uranium Committee; 41’ “all out effort” to make bomb Manhattan Project: New Mexico, Washington, Tennessee Oppenheimer Truman takes over April 45’ – learns about bomb Potsdam - “Surrender or suffer prompt and utter destruction,” US & UK told to Japan Oppenheimer said it reminded him of, Hindu holy text, the Bhagavad-Gita: “Now I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds.“ 45’ = Trinity test in New Mexico = release double anticipated