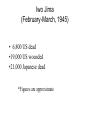* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War Two (1939
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
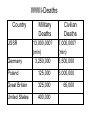
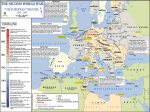
World War Two (1939-1945) I. German Conquest (1939-42) A. Poland B. France C. Battle of Britain D. Russian Invasion II. US (1939-12/7/41) A. Neutrality & Japan III. Defeating Germany (1942-45) A. Diplomacy/Big Three B. The “Tide Turns” IV. Defeating Japan V. Results • • • • • • • • • • • • Key Terms Blitzkrieg Axis & Allies Pearl Harbor Churchill Stalin FDR Stalingrad D-day Eisenhower Yalta Conference Dresden Island Hopping WWII Themes • Technology-from the Blitz to A-bomb & in between • Diplomacy-Allies cooperate • “Total War”-civilian casualties Poland Faces A Blitzkrieg German air force targeted railroads • Germany invaded Poland September 1, 1939 New Technologies = Success • Blitzkrieg = “Lightening Warfare” – Air attacks combined with rapid troop movement • Poland fell within one month WWII Alliances Following Germany’s invasion Alliances were formed: Allies • Great Britain • France Axis • Germany • Italy • Japan France Falls To Germany • 1940 France fell to Germany in 6 weeks (successful Blitz) Victorious German Soldiers The British Stand Alone: Battle of Britain • Cities were bombed June, 1940-June 1941 • British radar helped & radio influenced morale London under fire Russian Invasion • June, 1941 Germany invaded Russia (in violation of previous treaty) • German “Blitzkrieg” again VERY successful (initially) Hitler switched tactics Pearl Harbor Attack (12/7/41) • 19 Ships sunk • About 2,000 dead USS Arizona explosions killed about 1,100 WWII Alliances Allies • Great Britain • France • USSR • US Axis • Germany • Italy • Japan “Big Three” Winston Churchill (1874-1965) • Prime Minster of Great Britain • Goal: Attack “Soft Underbelly” of Europe Italy “Big Three” Joseph Stalin (1879-1953) • Leader of Soviet Union (USSR) • Goal: A Second Front in western Europe • 20-30 million Soviets died during WWII “Big Three” Franklin D. Roosevelt (FDR) (1882-1945) • US President • Goal: Defeat Germany first with fewest US casualties Battles Of Stalingrad & Leningrad (Leningrad: 1941-44) • Turning point of European war • USSR turned back Germans • Leningrad/ St. Petersburg was under seige The “Tide Turns” In Italy • In 1943 following defeats in North Africa Mussolini was deposed & Italy surrendered. D-Day (June 6, 1944) Dwight Eisenhower • Allied invasion in western France (2nd Front). • Technological success – 500,000 troops – 11,000 aircraft – 4,000 vessels (1890-1969) Dresden, Germany • Major German cultural center • Site of massive allied bombing campaign February 1945 – Up to 130,000 civilians killed Yalta Conference (February, 1945) It was decided that following Germany’s defeat… 1. Free elections would be held in Poland. 2. Germany would be occupied by Allied Powers. 3. USSR would join the war against Japan. 4. Allied Powers would participate in the United Nations. Germany’s Defeat • Germany surrendered May 8, 1945. Island Hopping • US strategy to defeat Japan. • US forces went from Island to Island in the Pacific on their way to the Japanese mainland. War In The Pacific: Midway (June 1942) • Location of an important US based in the Pacific • US won a decisive victory • Significance: Turning point in the war in the Pacific Iwo Jima (February-March, 1945) • 6,800 US dead •19,000 US wounded •21,000 Japanese dead *Figures are approximate Okinawa April-June, 1945 • 12,500 US/Allied dead • 35,000 US/Allied wounded • 100,000 Japanese soldiers dead • 80,000 Japanese civilians dead or wounded *Figures are approximate “Kamikaze” • Japanese “suicide” planes increased as the Americans neared the Japanese mainland. Tokyo Was Firebombed •March, 1945 (two days) •About 80,000 dead •250,000 buildings destroyed Atomic Warfare • US ultimatum rejected • Hiroshima (8/6/45): 100,000 Japanese dead • Nagasaki (8/9/45): 40,000 Japanese dead • Japanese Surrender (8/14/45) The Aftermath of the Atomic Bombs Image Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. WWII-Deaths Country USSR Germany Military Deaths 13,000,000? (min) 3,250,000 Civilian Deaths 7,000,000? (min) 3,500,000 Poland 125,000 6,000,000 Great Britain 325,000 65,000 United States 400,000 World War Two (1939-1945) I. German Conquest (1939-42) A. Poland B. France C. Battle of Britain D. Russian Invasion II. US (1939-12/7/41) A. Neutrality & Japan III. Defeating Germany (1942-45) A. Diplomacy/Big Three B. The “Tide Turns” IV. Defeating Japan V. Results • • • • • • • • • • • • Key Terms Blitzkrieg Axis & Allies Pearl Harbor Churchill Stalin FDR Stalingrad D-day Eisenhower Yalta Conference Dresden Island Hopping