* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7.3 ANIMAL and PLANT CELL STRUCTURE HO
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
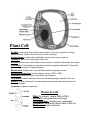
Animal and Plant Cells: Organelles All living things are made up of cells and these cells are made up of different parts. The parts are called organelles. Organelles are structures that are scattered throughout the cytoplasm of the cell and carry out the activities that keep the cell alive. Plant and animal cells have many of the same organelles, but they also have some major differences. These different cellular structures have a huge impact on how these different living things go about the business of life. Animal Cell Cell Membrane: encloses cell and acts like a gatekeeper regulating what goes in and out. Cytoplasm: a gel-like fluid that takes up most of the space inside the cell. Mostly H20. Nucleus: Control center of the cell, that holds the cell’s chromosomes. Chromosomes are made of DNA and hold the cell’s genes (inside is nucleolus that makes ribosomes). Vesicles: storage containers of the cells. Store wastes and other substances temporarily. Mitochondria: power house of the cell. Uses O2 to transform energy in food to a form that the cell can use. Endoplasmic Reticulum: internal delivery system for the cell. Rough ER works together with ribosomes to make proteins and lipids. Smooth ER transports things. Ribosomes: protein producers. Very small organelles that work with the endoplasmic reticulum to make proteins using DNA as the blueprints. Golgi Bodies: package products made by the ER and distribute them around the cell and to the outside of the cell. Lysosome: small vesicles that contain digestive chemicals to break down food for the cell. Plant Cell Cell Wall: outer barrier that provides extra support to the cell and gives it a shape. Mostly cellulose, which is the main fiber in wood and paper Cell membrane: encloses cell, gatekeeper controls what goes in and out Cytoplasm: gel-like fluid filling much of the cell Nucleus: control center where DNA is found (inside is nucleolus that makes ribosomes) Chloroplast: Food-making structure that contains the pigment chlorophyll. Chlorophyll uses sunlight energy to do photosynthesis Mitochondria: powerhouse of the cell where cellular respiration occurs Endoplasmic Reticulum: Internal delivery system. (RER + SER) Ribosomes: protein factories using DNA for the blueprint Golgi Bodies: makes cellulose for the cell wall and packages materials in the cell Vacuole: storage structure for the cell storing mostly mostly water and help the cell maintain its shape. Lysosomes: digestive organelles Bacteria Cell DNA: No nucleus, circular DNA or RNA Cell Wall: outer protection and shape. Cell membrane: encloses cell, gatekeeper Cytoplasm: gel-like fluid filling much of the cell Ribosomes: protein factories