* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Model of Earth`s Interior
Survey
Document related concepts
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
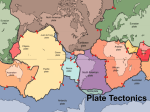
A MODEL OF EARTH’S INTERIOR Scientists infer most if the properties of the Earth’s interior through the study of seismic (earthquake) waves. Through many studies and experiments, scientists have found that seismic waves refract, reflect, change velocity, and become absorbed by various parts of the Earth’s interior. • ZONES OF EARTH The studies of seismic waves indicate that the Earth is composed of many layers. The crust is the outermost part of the Earth below the atmosphere or hydrosphere. This layer is mostly solid rock, but includes soil and eroded/weathered rock. ~ The crust is divided into two major divisions: continental crust and oceanic crust. ~ The continental crust is usually much thicker and less dense than the oceanic crust . ~ Continental crust is made up of granitic rocks, oceanic crust is made up of basaltic rocks. Below the crust, is the mantle. This layer is mostly solid rock and the thickest layer. This layer is also separated from the crust by a thin boundary called the Moho. Together the crust and the upper portion of the mantle is called the lithosphere. The lithosphere is divided up into sections called plates. ZONES OF EARTH CONT. Below the lithosphere, is the other portion of the upper mantle called the asthenosphere. In this section, seismic waves decreased in velocity. The asthenosphere is said to be plastic like, that is at least partly molten. Much of the magma and lava is thought to originate here. Beneath the mantle, the Earth’s core is divided into two parts – the inner core and the outer core. EARTH’S CRUST The earth’s crust is divided into two major divisions: continental crust and oceanic crust The continental crust makes up the continents and larger islands. This crust is made largely of granitic rocks and it is less dense than oceanic crust. The oceanic crust makes up the crust beneath the oceans. This crust is made largely of basaltic rocks and it is more dense than continental crust. The Earth’s crust is composed of low-density rocks with a mixture of granitic and basaltic compositions. Granite Basalt ALL OF THE OCEANIC AND CONTINENTAL PLATES