* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine Review Sheet
Survey
Document related concepts
Progesterone wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
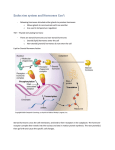
Intensive Biology Chapter 26: Endocrine System (Chapter 27: Reproductive) Review Questions 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions 1. What are two regulatory chemicals the body uses? Compare and contrast the two chemicals. 2. What are the three types of “communicating” cells? What regulatory chemicals are used? 26.2 Hormones affect target cells 1. What are the two different types of hormones? What are the two main hormone signaling mechanisms? Describe each mechanism. 26.3 Overview of Endocrine System 1. Be familiar with the following hormones: Oxytocin, PRL, FSH, LH, ACTH, ADH, Glucocorticoid, Mineralcoricoid, Epinephrine, Norepinephrine, Insulin, Glucagon, Estrogens, Progesterone, Calcitonin, Parathyroid Hormone 26.4 Hypothalamus 1. Why is the hypothalamus considered to be the control center? What kinds of hormones does it secrete? 2. What is the target cell for the hypothalamus? What are the roles of these target cells in return? 26.5 Thyroid 1. Explain the negative feedback mechanism using the production of thyroxine. What happens when the feedback doesn’t work? What is hypo / hyperthyroidism? 26.6 and 26.7 Thyroid / Parathyroid and Insulin / Glucagon 1. Why are calcitonin and PTH said to be antagonistic hormones? Explain the feedback mechanisms involved in maintaining the appropriate level of calcium in the blood and interstitial fluid. Please be sure to include what hormones are involved, where they are produced, what stimulates the production and release of these hormones, what the target cells are and what happens as a result of the hormone being secreted. 2. Explain the negative feedback mechanisms involved in maintaining glucose homeostasis. Please be sure to include what hormones are involved, where they are produced, what stimulates the production and release of these hormones, what the target cells are and what happens as a result of the hormone being secreted. 26.8 Diabetes 1. What is Type I diabetes? What are the causes, symptoms and treatments? 2. What is Type II diabetes? What are the causes, symptoms and treatments? 3. What is hypoglycemia? 26.9Adrenal Glands 1. What hormones are secreted from the adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla? 2. Which hormones are involved in short term stress response and which are involved in long term stress response? What types of responses are triggered? Chapter 27: Reproductive System 27.5 The formation of sperm and ova requires meiosis Spermatogenesis, primary spermatocytes, secondary spermatocytes, oogenesis, primary oocyte, secondary ooctye 1. What are the three major differences between spermatogenesis and oogenesis? 27.6 Menstrual Cycle Ovarian cycle, menstrual cycle, menstruation, LH, FSH, estrogen, progesterone, follicle, corpus luteum, HCG 1. What occurs during the ovarian cycle (what are the two phases) and the menstrual cycle? 2. Which gland/organ/cell secretes FSH, LH, estrogen, progesterone, and HCG? 3. Explain the level of FSH and LH before ovulation. What are the target cells for FHS and LH? 4. What releases estrogen? What type of feedback does estrogen exert on the pituitary gland? 5. What does estrogen do? 6. What triggers a peak in estrogen level? What does this trigger? 7. How is the corpus luteum formed? What hormones does it release and what do the hormones do? 8. What type of feedback do the two hormones estrogen and progesterone have on the pituitary gland hypothalamus? What happens as a result? 9. What happens during pregnancy? Does bleeding occur? Why or why not?