* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 3 S. 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Sexually dimorphic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
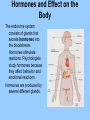
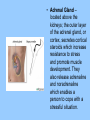
Chapter 3 Section 3 The Endocrine System Obj: Identify the hormones secreted by the major glands of the endocrine system and the role each one plays. Hormones and Effect on the Body The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones stimulate reactions. Psychologists study hormones because they affect behavior and emotional reactions. Hormones are produced by several different glands. • Pituitary Gland – lies just below the hypothalamus; responsible for the secretion of many different hormones that affect various aspects of behavior such as the growth hormone. Oxytocin and prolactin affect females in relation to pregnancy and mothering. • Thyroid Gland – produces thyroxin which affects the body’s metabolism – it’s rate of converting food to energy. People with too little thyroxin have hypothyroidism and are often overweight. If too much thyroxin, develop hyperthyroidism, and they are excitable, unable to sleep, and experience weight loss. • Adrenal Gland – located above the kidneys; the outer layer of the adrenal gland, or cortex, secretes cortical steroids which increase resistance to stress and promote muscle development. They also release adrenaline and noradrenaline which enables a person to cope with a stressful situation. • Testes and Ovaries – produce the hormones testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone that play an important role in the development of primary and secondary sex characteristics and have psychological as well as biological effects. • Testosterone – male sex hormone, although females have small amounts of it. It is a kind of steroid…affecting muscle mass, etc. It also stimulates the sex drive and raises self-esteem. Primary sex characteristics are involved in reproduction, secondary sex characteristics, such as beard growth, distinguish males and females but are not directly involved in reproduction. • Estrogen and Progesterone – female sex hormones, although low levels are found in men. Together, they regulate the menstrual cycle. Changes in levels have been linked to PMS.