* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Moral Leadership
Internalism and externalism wikipedia , lookup
Value (ethics) wikipedia , lookup
Kantian ethics wikipedia , lookup
Individualism wikipedia , lookup
Ethics in religion wikipedia , lookup
The Moral Landscape wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg wikipedia , lookup
Alasdair MacIntyre wikipedia , lookup
Bernard Williams wikipedia , lookup
Morality throughout the Life Span wikipedia , lookup
Moral disengagement wikipedia , lookup
Morality and religion wikipedia , lookup
Secular morality wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg's stages of moral development wikipedia , lookup
Consequentialism wikipedia , lookup
Moral development wikipedia , lookup
Ethical intuitionism wikipedia , lookup
Moral responsibility wikipedia , lookup
Utilitarianism wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Hill Green wikipedia , lookup
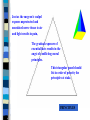
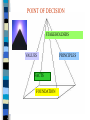
MORAL LEADERSHIP Constructing ethical frameworks in a morally challenged America Presented by Mitch Land, PhD, director Voltaire “Virtue has escaped our hearts and taken refuge on our lips” Histoire de Louis XIV "No legacy is so rich as honesty." William Shakespeare "Oh, what a tangled web we weave, When first we practice to deceive!" -Sir Walter Scott, Marmion "Honesty is the first chapter in the book of wisdom." -Thomas Jefferson “Men occasionally stumble over the truth, but most of them pick themselves up and hurry off as if nothing had happened.” Winston Churchill Moral Dilemmas Robert Dilenschneider Richard Kosmicki “Spin is bad for you, it’s bad for your company and it’s bad for your clients.” Conflicts of Interest Janet Cooke’s 1980 Pulitzer Prize withdrawn because of composite story On April 13, 1981, Washington Post reporter Janet Cooke was awarded the Pulitzer Prize for a story titled "Jimmy's World" about an 8-year-old heroin addict. On April 15 she confessed that there really was no "Jimmy," that he represented a composite of child addicts and that her story was, in fact, fiction. She returned the prize and resigned. Corporate and Government Spin Johnson presidency using “spin” to justify Vietnam War: Gulf of Tonkin Clinton administration casts doubts on female accusers Redefining sexual relations Tabloid Journalism ABC PrimeTime Live uses deception to obtain sensational video images of Food Lion NBC rigs trucks to explode CNN reports serin gas accusation against the Pentagon MEDIA ETHICS “Why, that’s an oxymoron!” Defining Ethics Derived from ethos Ethos = spirit of a culture Moral standards of right and wrong FRAMEWORKS FOR ETHICAL DECISION-MAKING Utilitarianism Deontological Or somewhere in the middle? THE CASE FOR COMMUNITARIANISM Utilitarianism Jeremy Bentham 1781 John Stuart Mill 1863 Utilitarianism Greatest Good for the Greatest Number The End Justifies the Means Deontological Perspective Immanuel Kant 1798 DEONTOLOGY Study of necessity, duty or obligation Moral worth is an intrinsic feature of human actions, determined by formal rules of conduct Moral obligation rests solely upon duty, without reference to the consequences. The Basic Tenets of Utilitarianism Greatest Good for the Greatest Number – moral relativism – the end justifies the means – interpretation subjective – principles are negotiable and disposable End Justifies the Means The Basic Tenets of Utilitarianism It regards "utility as the ultimate appeal on all ethical questions – COMMON SENSE Rightness or wrongness is determined by the overall value of the consequences End Justifies the Means Subtle Weaknesses in Utilitarianism • Utilitarianism depends upon an accurate assessment of the consequences– both long term and short term • Consequences-dependent theory lacks sufficient guidelines for long-term assessment • Its individualist bias oversimplifies complex relationships of family, neighbors, community Subtle Weaknesses in Utilitarianism Utilitarianism’s singular focus neglects competing principles • • Utilitarianism privileges possible consequences over past responsibilities • Utilitarianism confuses an aggregate of individual goods with the common good • Individual liberty has priority over the moral order, and therefore ethics is exterior Moral Relativism Hitler’s Final Solution Separate but Equal: Segregation in America 1600-1964 Milosevic’s Ethnic Cleansing Problematic of Deontology If a precept is true for one, it is true for all. Kant’s Categorical Imperative leaves little room for Consequential Imperative. Principles dominate Consequences. Principles Or Consequences ? Or somewhere between: COMMUNITARIANISM Communitarianism Individuality exists in a context of social reality—not in isolation Human identities are constituted within a social conception of the good Individual rights are NOT the cornerstone of the political order Communitarianism • The communal, our commonness, communitas is the context in which the nature of persons is understood • Morally appropriate action assumes community Critique of Communitarianism • Utilitarianism also considers the group, collective or society generally. - Good conduct is that which results in the greatest good for the greatest number. • Communitarianism is a smoke screen for collectivism—a socialist agenda. • Communitarianism threatens the primacy of the “sacred” individual. - Mill/Kant see individual as the measure of value against the collective of state and society. Critique of Communitarianism • Communitarianism is a disguise for theological mishmash. - An attempt to force universal principles derived from theological belief systems upon others. • Communitarianism would shift the objective of news from unbiased information transmission to an agent of community transformation. Critique of Communitarianism • Communitarianism seeks to foster a common philosophy, which would result in deep psychological turmoil and public sadness. • Such like-mindedness would lead to social destruction, psychological alienation and personal immorality. Principles Truth Justice Freedom Humaneness Stewardship Values Varied expressions of principles Truth = integrity, honesty, trustworthy Humaneness = kind, gentle, caring Stewardship = generous, frugal, good managing Justice = fairness, equality Freedom = liberty, self-expression The Potter Box FACTS PRINCIPLES VALUES STAKEHOLDERS Two-Dimensional Analysis Analysis always builds on assumptions Even though assumptions often hide Or they lie buried beneath social pressures Three-Dimensional Analysis Moral reasoning is always built upon a philosophical foundation whether or not the decision maker is aware of it. 3-D Analysis builds upon a philosophical foundation 3-D Analysis The base of the pyramid of moral reasoning represents the philosophical foundation. The pyramid of our moral reasoning is always constructed upon this philosophical base. From our mental arrangement of the case facts through the prioritizing of the principles and values to the eventual list of stakeholders we move to a point of decision. FOUNDATION BASED ANALYSIS Utilitarianism Communitarianism PRINCIPLES FACTS VALUES Bullet the case facts that give rise to the ethical dilemma. Cut through the fat of details to expose the raw nerves of moral crisis. FACTS Just as the surgeon’s scalpel exposes unprotected and unsedated nerve tissue to air and light results in pain, The gradual exposure of essential facts results in the angst of conflicting moral principles. This triangular panel should list in order of priority the principles at stake. PRINCIPLES Principles and values are closely related. Principles can be understood as the major nouns that organize the nouns and verbs of values. Moral values can always be linked to five major principles: truth, justice, liberty, humaneness and stewardship. VALUES The principle of truth informs my honest behavior, trustworthy actions, my decisions of integrity and so on. The principle of humaneness should prompt merciful acts, kind behavior toward my neighbors, and the gentle treatment of children, animals, the weak and so on. This triangular panel should list in order of priority the principles that emerge from an elaboration of the essential facts. VALUES The fourth triangular panel lists the stakeholders in order of priority. Analyzing the facts and the competing principles and values will evoke the following questions: Who has the most to gain and who has the least to gain as we move toward the point of decision. Conversely, who has the most and least to lose? STAKEHOLDERS POINT OF DECISION STAKEHOLDERS VALUES FACTS FOUNDATION PRINCIPLES Establish the facts Texaco involved in litigation over racial discrimination. Texaco executives are recorded using racial slurs. Jesse Jackson calls for nationwide boycott. Peter Bijur addresses Texaco employees. Facts Peter Bijur dismisses three executives. Bijur announces Texaco’s intolerance for racial discrimination. Bijur announces steps for re-education. Jesse Jackson calls off the boycott. Principles Truth telling Justice Humaneness Freedom Stewardship Moral Values & Non-moral values Fairness Full Disclosure Honesty Frugality Professionalism Stakeholders & Loyalties Texaco Employees Stockholders Texaco CEO Customers The three guilty executives Which Framework for Bijur? Utilitarianism Alternatives Communitarianism – Rawl’s Veil of Ignorance – Aristotle’s Golden Mean – Judeo-Christian Agapism Communitarianism Applied All principles were involved in the Texaco Case. Principle of Humaneness clashed with other principles No possibility of “redemption” or “rehabilitation” for Texaco Executives. Texaco Executives didn’t “Apologize” Possible Alternative Steps framed in Communitarianism • Reprimand Executives who used racial slurs • Have Executives publicly apologize and ask forgiveness from offended parties • • Demote Executives Require sensitivity training on the part of Executives ABC PrimeTime Live Vs. Food Lion Establish Facts Prioritize Values Prioritize Stakeholders and Loyalties Prioritize Principles Establish the Facts ABC goes undercover to investigate food-handling abuses Cameras record alleged abuses PrimeTime Live broadcasts sensational story Food Lion suffers great financial loss Food Lion sues ABC Jury finds in favor of Food Lion Moral Values Non-Moral Values Telling an accurate story (TRUTH) Protecting the public health (HUMANENESS) Holding Grocer accountable (STEWARDSHIP) Punishing wrongdoing (JUSTICE) Making a profit Satisfying ratings Telling visual story Telling a compelling story Betting both sides of an issue Obtaining authoritative sources VALUES : MORAL Vs NON-MORAL NON-MORAL Obtaining authoritative sources • Getting both sides of an issue • Telling a compelling story • Telling visual story • Satisfying ratings • Making a profit • Moral Values Telling an accurate story (TRUTH) • Obtaining the truth with integrity (TRUTH & JUSTICE) • Protecting the public health (HUMANENESS) • Holding the grocer accountable (STEWARDSHIP) • MORAL VALUES Telling an accurate story (TRUTH) • Obtaining the truth with integrity (TRUTH & JUSTICE) • Protecting the public health (HUMANENESS) • Holding the grocer accountable (STEWARDSHIP) • • Obtaining authoritative sources • Getting both sides of an issue • Telling a compelling story • Telling visual story • Satisfying ratings • Making a profit NON-MORAL VALUES PRIORITIZE STAKEHOLDERS FOOD LION ABC News Stockholders Advertisers Viewers Producers Management Other Employees Stockholders Suppliers Customers Management Food & Drug Administration Legal System Identifying loyalties Who has the most to lose? Who has the most to gain? PRIORITIZE PRINCIPLES Truth Telling Humaneness Justice Stewardship Philosophical Framework? Utilitarianism Perspective Moral Imagination in search of Alternatives -- Communitarianism Alternative Scenario Enter Food Lion without lying Consensus decision making on the outtakes Invite independent examination of food after it leaves the store Other?