* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Head
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
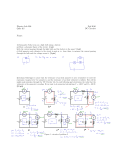
P3 ISA practice 2 – Student practical sheet Investigating power loss in transformers Aim You are going to investigate your hypothesis into power loss in transformers Equipment ● ● ● ● 12 V ac power pack 2 voltmeters (ac) 2 ammeters (ac) 12 V bulb and holder ● ● ● connecting wires 2 pieces of single core thin wire transformer/iron core or 6 inch nail Safety ● Do not confuse the primary coil with 30 turns with the secondary coil with 15 turns. What you need to do 1 Wrap the wire thirty times round the left hand arm of the core. If using a nail then wrap around the left hand end of the nail. 2 Connect one end of this wire to one of the yellow terminals of the power pack, connect the other to the negative or black terminal of the ammeter. 3 Connect the red or positive terminal of the ammeter to the other yellow terminal of the power pack. 4 Connect the voltmeter across the yellow terminals of the power pack. 5 Wrap a second piece of wire around the right hand arm of the core. (If using a nail then wrap around the right hand end of the nail.) 6 Connect one end of this wire to the negative or black terminal of the ammeter. 7 Connect the other end to one terminal of the bulb holder. 8 Connect the other terminal of the bulb holder to the red or positive terminal of the ammeter. 9 Connect the voltmeter across the bulb holder 10 Turn the power pack to 2 V ac setting and switch it on. The bulb is unlikely to light up but the meters should have readings on them. 11 Record the readings on the voltmeter and ammeter connected to the power pack. 12 Record the readings on the voltmeter and ammeter connected to the bulb holder. 13 Turn off the power pack. 14 Reset the power pack to 4v and repeat steps 10-12. 15 Calculate the power at the primary (power pack side) and secondary (bulb holder side) coils 16 Repeat using 6V, 8V, 10V and 12V. Sheet 1 of 2 © Pearson Education Ltd 2011. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 355 356 Primary side voltmeter/V Primary side current reading /A Secondary side voltmeter reading/V Secondary side current reading/A Calculate the percentage loss of power using this formula: secondary power in watts x 100 primary power in watts Calculate the secondary power by multiplying secondary voltage and current together. Calculate the primary power by multiplying primary voltage and current together. Calculations 12 10 8 6 4 2 Power pack setting/V Meter readings Primary power/W Secondary power/W Percentage loss of power P3 ISA practice 2 – Student practical sheet Results chart – Investigating power loss in transformers © Pearson Education Ltd 2011. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Sheet 2 of 2