* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Series and Parallel Circuits Computer Lab
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
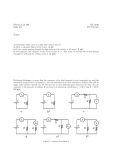
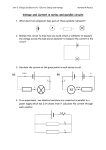
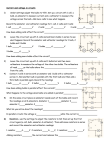
Series and Parallel Circuits Basics Name:_____________________________________________ Directions: 1. Log on to your computer 2. Go to the following website: http://phet.colorado.edu/index.php 3. Click the button that says “Play with sims…” then physics: then electricity 4. Click on the application that says Circuit Construction Kit (DC only). 5. Click “Run now.” You now have the raw material to create a circuit. Take a moment to look over the site and find all the different materials. To build a circuit you will need several wires, light bulbs, batteries, a voltmeter, and a non – contact ammeter. Play with it to see how to grab and manipulate these tools. Click the reset button. A. Series Circuits – have only one path for electrons to flow from one side of the battery to the other. Build a simple series circuit that includes 2 light bulbs and 2 batteries. Your circuit is complete and working when the light comes on and the blue dots begin moving. Draw a picture of your circuit here. What do you think that the moving blue dots represent? _____________________________ Use the tools at the side to get a voltmeter and a Non-contact ammeter. Put the voltmeter near each light bulb and place the red tab at one end and the black at the other. What is the voltage on each lightbulb? __________ ______________ Place the ammeter crosshairs over the moving blue dots. What is the reading near each light bulb? _______ ______ What does this tell us about the current in a series circuit? Remove one of the bulbs leaving a space. What happens to the current? Remove the space by connecting the wires. How does the brightness of the single bulb compare to the brightness of the two bulbs from before? Measure the current with the ammeter. Compare the current reading when there were two bulbs present in the circuit. Measure the voltage with the voltmeter. Compare the voltage reading when there were two bulbs present. B. Parallel Circuits Parallel circuits provide more than one path for electrons to move. Sketch below a parallel circuit that has 2 light bulbs and 2 batteries. Create this using the simulator tool. The blue dots will be moving and both lights will be on once the circuit is complete. Use the voltmeter and non-contact ammeter to measure the voltage and current for each light bulb Voltage:_______ ________ Ammeter:______ _________ How does this compare with your observations in the series circuit with 2 bulbs? Now right click on one of the wires connected to a light bulb. Remove the wire and record your observations. Does this affect the voltage, current, or visually change the appearance of the light bulb? Replace the wire. Now remove one of the wires touching the voltage source. What happened? What is the difference between removing the first wire and the second? Why is this significant?