* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Click Here To
Survey
Document related concepts
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
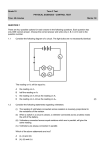
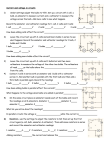
GRADE 9: CHEMISTRY EXAM REVIEW Please write all answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1) What are the postulates of the particle theory of matter? 2) What is a physical change? Give two examples of physical changes. 3) What is a chemical change? List the indications that a chemical change may have taken place. 4) What are physical PROPERTIES of matter. Give two examples. 5) What are QUALITATIVE PHYSICAL PROPERTIES? Give two examples. 6) What are QUANTITATIVE PHYSICAL PROPERTIES? Give 2 examples. 7) Jess has an object that weighs 13.6 g and has a density of 2.7 g/cm3. What is the mass of the object? 8) Tony has a piece of an unknown metal. It is 32 cm3 and weighs 156 g. What is the density of the metal? 9) What are some examples of chemical PROPERTIES of matter? 10) Matter is classified into several different categories. Give an example of each type of matter. 11) Describe any patterns that you see on the modern periodic table (i.e./ groups/columns and periods/rows). 12) Who is accredited for the modern periodic table? 13) Name and locate the 4 chemical families we discussed in class. How many VALENCE electrons do each of the elements in that family have? 14) Describe the current view of the atom by answering the following questions: a) What is in the nucleus of the atom? b) What surrounds the nucleus? c) How many electrons fit in each shell/orbit? 15) State the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the following atom and describe how you got your answer. 15 P 30.974 14) What does the atomic number represent? 15) What does the atomic mass represent? 16) Which halogen is the most reactive? Why? 17) Which metal is most reactive? Why? 18) Draw a Bohr-Rutherford diagram of potassium. 19) What is the electron arrangement for a) magnesium? b) sulfur? 20) What do you call a charged atom? 21) What types of elements form IONIC COMPOUNDS? 22) Using Bohr-Rutherford diagrams show how the aluminum and chlorine would bond. - What would be the name of that compound? - What would be the chemical formula for that compound? 23) What type of elements form molecular/covalent compounds? GRADE 9: BIOLOGY EXAM REVIEW 1. Define the following: Trophic level Biotic factor Food chain Food web Producer Consumer Omnivore Carnivore Decomposer Scavenger Autotroph Heterotroph Lithosphere Hydrosphere Atmosphere Biosphere Biome Extinct Extirpated Bioaccumulation 2. Explain the difference between biotic and abiotic factors. Give examples of each. 3. Describe the process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. What are the chemical equations that represent each process? Explain the important relationship between these processes on the planet. 4. What is the carbon cycle? Using a diagram, depict this cycle. 5. What is the nitrogen cycle? Using a diagram, depict this cycle. 6. Explain how acid rain is created. What are the two main gases released into the atmosphere that contribute to acid rain? What are the impacts that acid rain can have on an ecosystem (both terrestrial and aquatic)? 7. How does burning fossil fuels contribute to climate change? Explain the process of global warming. 8. What are the by-products of burning coal vs. natural gas? 9. Name and briefly describe each of Canada’s Biomes. 10. Explain what an invasive species is using an example. How can invasive species impact ecosystems and why? What can we do remove invasive species? 11. What is bioaccumulation? Using a diagram, illustrate how this process happens in ecosystems. Why is it a concern? GRADE 9 SCIENCE: ELECTRICITY REVIEW 1) Define the following terms: conductor insulator electric current potential difference power voltmeter ammeter resistor series circuit parallel circuit dry cell grounding 2) Describe (with reference to sub atomic particles) how a neutral object becomes: a) POSITIVELY charged and b) NEGATIVELY charged 3) What is the electrostatic series? 4) Describe how you could use the electrostatic series to determine the charge of two different neutral objects. 5) We learned about three different methods of charging with regards to static electricity. These were (1) charging by friction, (2) charging by contact and (3) charging by induction. For each of these methods, summarize the charge of the objects BEFORE the charge (if any) and the charges of the objects after charging has occurred. 6) How do you ground and object? 7) What is the purpose of a lightening rod at the top of a building? 8) A light bulb connected to a 9 V source has 2 A of current flowing through it. What is the resistance of the bulb? 9) An electrical device pulls 5.9 A of current through it when hooked up to a 250 V source. What is the power rating of that device? 10) REVIEW other current electricity word problems. 11) What are the relationships (I,R and V) in a series and parallel circuit? 12) If you add bulbs to a series circuit, the more bulbs you add the _______ the brightness of each bulb gets. However, if you add bulbs to a parallel circuit the brightness of each bulb __________________________. 13) When hooking up a circuit, ammeters (that measure ______________) are always placed ______________________ where as voltmeters (that measure_____________) are always placed ___________________. 14) List the circuit symbols that we learned about in class and beside each symbol record what they represent. 15) List the four factors that affect the resistance of a wire. Describe if each factors increases or decreases resistance. 16) List some types of objects that make good (a) insulators (b) conductors 17) Understand CIRCUIT CALCULATIONS (using circuit RELATIONSHIPS) 18) Draw a schematic diagram with the following criteria: a) a series circuit with 3 bulbs and a resistor. An ammeter will measure the current RETURING to the source and a voltmeter will measure the second bulb. b) A parallel circuit with 4 bulbs connected in parallel. ONE switch will affect 3 of the bulbs. A voltmeter will be set up to measure each bulb and an ammeter will measure the current leaving the source. 19) Summarize any ALTERNATIVE forms of energy. Draw diagrams of how each of these alternative forms of energy are generated. GRADE 9 SCIENCE: ASTRONOMY EXAM REVIEW 1) Name the 8 planets in order of their proximity to the sun. 2) How are the first 4 planets similar? 3) How are the 4 gas giants similar? Why do they have gas surrounding them while the inner planets do not? 4) What is the cause of Jupiter’s Great Red spot? 5) What type of star is our Sun? What is the final fate of our Sun? 6) What is a solar system composed of? A galaxy? The Universe? 7) (a) In your OWN WORDS explain the solar nebula theory. (b) According to this theory, should all planets be roughly the same age? (c) According to this theory should they all rotate in the same direction? (d) According to this theory should all the planets orbit in the same direction? On the same plane? 8) What is FUSION? At what temperature does fusion begin? 9) Define: (a) astronomical unit (b) light-year. When are each of these units used to measure distance? 10) What are stars made of? 11) How long are the lives of: (a) low mass stars (b) intermediate mass stars and (c) massive stars. 12) What is a NEBULA? 13) All stars are formed from nebulas. Depending on their mass they will become different things. What is the fate for each type of star? 14) Define luminosity. 15) Where is the asteroid belt found in our solar system? 16) (a) In your own words, describe the Herzsprung-Russell diagram. (b) State star colours in order from hottest to coolest. 17) Do all the planets rotate in the same direction? On the same plane? If not, explain. 18) (a) What is gravity? (b) How is gravity important in the construction of a solar system? (c) How is gravity important in the structure of the universe? (d) Why is gravity a cause of the ultimate end of a solar system? 19) What does it mean when you say a star is in “Main Sequence”? 20) What are sunspots? 21) (a) Name the three different types of galaxies. (b) What is the name of the galaxy we live in? (c) What type of galaxy do we live in? 22) What is the definition of a planet? Why is Pluto no longer considered a planet? 23) Why and how do we experience the 4 seasons? 24) How has Canada contributed to the space program, specifically the International Space Station? What are the pros and cons of our involvement? 25) What advancements in technology have we uncovered through space exploration programs?