* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FET Current Mirrors
Survey
Document related concepts
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
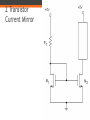
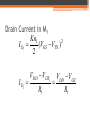
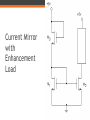
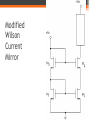
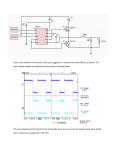
FET Current Mirrors ECE 2204 Current Sources • Ideal independent current sources are difficult to make and are almost impossible to fabricate on an integrated circuit. • Instead, current mirrors are fabricated. ▫ These are circuits that contain two or more FETs, where the drain of one of the FETs is connected to the rest of the circuit. ▫ This FET is operating in the saturation/pinch-off mode. Thus, it can be thought of as a dependent current source. The value of this dependent current source is determined by the operating conditions of the other FETs in the current mirror, not by the operating condition of the rest of the circuit (at least over a certain range of currents). 2 Transistor Current Mirror Common Design in Current Mirrors • At least two transistors ▫ Two transistors are wired in parallel shared VGS ▫ One transistor has the drain and gate tied together VDS > VGS – VTN; it is in saturation Drain Current in M1 Kn1 2 I D1 (VGS VTN ) 2 I D1 VDD VDS1 R1 VDD VGS R1 Bias Condition of M2 • M2 is assumed to also be in saturation. ▫ This depends in part on the rest of the circuit above M2 If the circuit above M2 requires too much current, then M2 will be forced into the triode/nonsaturation region. At which point, the current mirror circuit is not functioning properly – which means someone didn’t design their part of the circuit to the correct specification. Drain Current of M2 I D2 Kn2 2 (VGS VTN ) 2 I D2 W L 2 ID W L 1 1 W L 2 VDD VGS W L 1 R1 Current Mirror with Enhancement Load Modified Wilson Current Mirror