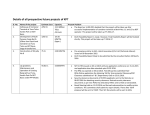
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Four Ways Analytics Think Like You
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Artificial intelligence for video surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Hierarchical temporal memory wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
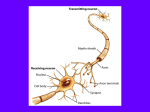
Artificial Intelligence: Four Ways Analytics Think Like You The rise of robotics has mirrored a boom in artificial intelligence (AI)—analytic software that mimics what we know about how humans think. Analytic algorithms power increasingly intelligent machines that perform advanced human tasks. It’s not science fiction —AI analytics are already used in many business applications. Here are four examples of analytics that imitate the way you think, and how they are used. Neural Networks Data (Transactions) INSPIRED BY: Neurons in the brain that store knowledge in their connections to other neurons and the strength of those synapses. Input Layer (Features) Number of Transactions in Last Hour Large Dollar Amounts Merchant Category Code 01001011101010 11000101010101 01010101010101 0101 EXAMPLE BUSINESS USE: Detecting payment fraud. Hidden Layer (Identifies Relationships) HOW IT WORKS: Makes connections between incoming data and specific outcomes, changing the “weight” of connections to learn the relationships between inputs and improve performance. Rapid High-Risk Expensive Transactions Output Layer (Score Calculations) Neuron (processing element) Fraud Score Calculation Time = 40–60 Milliseconds “Weight” Deep Networks INSPIRED BY: How neurons in the brain use multiple stages of processing in the visual cortex to learn to recognize faces and classify objects. EXAMPLE BUSINESS USE: Automatic video analysis and speech transcription. HOW IT WORKS: Combines bits of data into features, assembles features into more complex parts through multiple processing layers. Diagonal Line Node Face Node Cat Node NeuroDynamic Programming Internal State INSPIRED BY: Reward system of the brain, which enables us to learn complex task sequences through pleasurable or painful reward signals, which occur later in time. Learning Rate α Inverse Temperature β Discount Factor γ Action EXAMPLE BUSINESS USE: Automated agents used in travel booking. Environment HOW IT WORKS: Calculates impact of next step and all future possible steps to continually evaluate best next step to reach desired outcome. New State Reward Cyber-Analytics INSPIRED BY: How the brain controls the body and its actions through synapses. EXAMPLE BUSINESS USE: Identifying when malware has taken over computer. HOW IT WORKS: Identifies the command and control relationship between two entities, such as a “bot” on an infected computer and the “bot master” that controls the bot. Bot HTTP C&C Server Botmaster Sources: http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/13747/cyber-crime/http-botnets-the-dark-side-of-an-standard-protocol.html http://theanalyticsstore.com/deep-learning/ https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~eladlieb/RLRG.html www.fico.com/infographics © 2014 Fair Isaac Corporation. All rights reserved.