* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Texto - AP European History
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
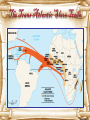
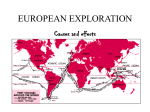
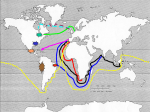
The Age of Discovery Causes of the Commercial Revolution • Population growth- more consumers existed • “Price Revolution”- long slow upward trend in prices – Increased food prices, volume of money and gold/silver – Increase in supply of goods • Emerging states want to increase their power • Rise in capitalism – Led by the middle class New Features • Banking – Fuggers in Germany, Medicis in Italy – Antwerp banking center in the 16th century – Amsterdam takes over at the beginning of the 17th century • Hanseatic League- German states in the middle Ages – Controlled trade in Northern Europe into the 16th century New Features • Chartered Companies – State provide monopolies • Had large fleets and military power • Became their own state in a sense • British East India Co. and Dutch East India Co. • Joint Stock Companies – Investors pooled resources for a common purpose – Today’s corporations New Features • Stock Markets Emerged – Bourse- Antwerp – Investors financed a company through stock • Enclosure Movement – Landowners enclosed their land to improve sheep herding – Boost to textile industry • The “putting-out” industry emerged – Produce items at home to supplement income New Features • New industries: cloth production, mining, printing, book trade, ship building, cannons and muskets • New consumer goods: sugar, rice, tea – Sugar production results in the slave trade in the Atlantic • Mercantilism- 17th century – Nations seek a self sufficient economy – Create a favorable balance of trade where one exports more than they import • Bullionism- acquire as much gold and silver as possible Significance • Slow transition from almost entirely rural society to one that relies on towns • More powerful nation-states • Age of exploration • The “price revolution” – Spurs on more production because sellers could gain more money for their goods • Middle class (bourgeoisie) grows in political and economic importance • Increased standard of living Motivations for Exploration • • “God, Glory, and Gold” Crusades by-pass intermediaries to get to Asia. – • Renaissance curiosity about other lands and peoples. – • • • Creates interest in Asia and the middle East Search for new knowledge Reformation refugees & missionaries. Monarchs seeking new sources of revenue. Fame and fortune. Technological Advances • Cartography – Martin Behaim- terrestrial globe, 1492 – Waldseemuller’s world map, 1507 – Mercator’s map, 1575 The Mercator Projection New Technology • Astronomy helps chart locations at sea • Magnetic compass • Quadrant, Astrolabe, Cross Staff – Used to find latitude • New ship technology – Portuguese Caravel – Lateen sail and rope riggings – Axial rudder – Gunpowder and cannon Caravel Portugal • Motivations- Portugal – Economic-all water route to Asia for spice trade – Religious- sought to find the mythical Prester John (a Christian king somewhere in the East) for an alliance against the Muslims • Prince Henry the Navigator – Financed expeditions to the west coast of Africa – Wanted to find gold Portugal • Bartholomew Dias- rounded the southern tip of Africa in 1488 • Vasco da Gama- took Dias’s route and completed a trip to India in 1498 – Brought back Indian goods- new market in Europe – Blow to Italian monopoly of trade with Asia • Political decline of Italian citystates Portugal • Amerigo Vespucci- explored Brazil (perhaps the first to realize he’d found a new continent) – Cabral had sighted Brazil earlier – America is named after Vespucci • Brazil – Major Portuguese colony – Large numbers of slaves imported for sugar, cotton and coffee production – Significant racial mixing resulted Spain Spain • Christopher Columbus– Financed by Ferdinand and Isabella – 1492- reaches the Bahamas- believes he reaches the “Indies” somewhere west of India – Four expeditions chart most of the Caribbean and Honduras – Ushers in a new era of domination and exploration of the New World Columbus's Four Voyages Spain • Treaty of Tordesillas – To secure Columbus’s discoveries in the New World – Divided between Spain and Portugal – Portugal gets exclusive trade rights to the African slave trade – North-south line drawn down the Atlantic • Portugal gets Brazil and claims in Africa • Spain gets the rest of the Americas The Line of Demarcation (Pope Leo V) Spain • Vasco Nunez de Balboa – Dicovered the Pacific Ocean • Ferdinand Magellan – His ship was the first to circumnavigate the globe – Charted the size of the Pacific • Conquistadores – Created empires by conquering Indians • Cortes- Conquers the Aztecs • Pizzaro- Conquers the Inca Cortez v. Montezuma II The Death of Montezuma II Mexico Surrenders to Cortez Cycle of Conquest & Colonization Explorers Official European Colony! The Spanish Empire • Outright conquering of natives and subjugating their populations • Merchantilist philosophy – Colonies existed for the benefit of the mother country – Mining of silver and gold- 25% of the crown’s total income – Shipped manufactured goods to America and discouraged native industry The Spanish Empire • Structure – Divided into four vice-royalities each led by a viceroy – Audiencias- board of 12-15 judges served as advisor • Highest judicial body Encomienda System • Spanish government sought to reduce savage exploitation of Amerindians – Poorly enforced • Amerindians worked for an owner for a certain number of days per week but retained other land for themselves • Spain imported few slaves because they could compel Amerindians to work The Spanish Empire • Mestizos – Spaniards married Amerindian women creating a mixed race of white and Indian children • Creoles – Spaniards born in the New World to Spanish parents Peninsulares Mestizos Native Indians Creoles Mulattos Black Slaves The Dutch The Dutch • Dutch East India Company (1602) • Expel the Portuguese from Celyon (Sri Lanka) and other Spice Islands (Indonesia) • By 1650- began challenging Spain in the New World and controlled much of the American and African trade France The French • Jacques Cartier- In search of the Northwest Passage – Explored the St. Lawrence River region of Canada • Quebec- France’s first settlement in the New World founded in 1608 England England • Came into exploration relatively late • John Cabot- (1425-1500)Explored the northeast coast of North America – Henry VII not interested in settlements • First permanent settlementJamestown (1607) • Tens of thousands emigratemore than France, Spain, and Portugal Empires in the New World The Old Imperialism • Africa and Asia • Not focused on the acquisition of property but rather trade – Built trading stations • Usually did not remove local leaders but rather worked with them or “puppet” regimes The Columbian Exchange Squash Avocado Peppers Sweet Potatoes Turkey Pumpkin Tobacco Quinine Cocoa Pineapple Cassava POTATO Peanut TOMATO Vanilla MAIZE Syphilis Trinkets Liquor GUNS Olive COFFEE BEAN Banana Rice Onion Turnip Honeybee Barley Grape Peach SUGAR CANE Oats Citrus Fruits Pear Wheat HORSE Cattle Sheep Pigs Smallpox Flu Typhus Measles Malaria Diptheria Whooping Cough Discussion Questions • How did disease lead to the colonization of the New World? – Would Europe have been able to conquer without the aid of disease? – What did the Europeans attribute their success to? – How does this lead to attitudes of racial superiority? • Why would the Columbian Exchange be considered a form of bio-terrorism? Free Response Question • What if the pattern of exploration was reversed? What if the “New World” discovered and attempted to colonize the “Old?” Assuming they had the technology to launch this effort, could the people of the western hemisphere have succeeded in such an attempt? – Due Monday – 1-2 pages- typed and double spaced Triangle Trade The Slave Trade The Trans Atlantic Slave Trade The Slave Trade • • Existed in Africa before the coming of the Europeans. Portuguese replaced European slaves with Africans. – • • • • Sugar cane & sugar plantations- Brazil Dutch West India Co. after 1621 England’s Royal African Co.- late 17th century By 1800- 60% of Brazil’s population and 20% of US Estimated 50 million Africans died or became slaves during the 17th and 18th centuries The “Middle Passage” The “Coffin” Position African Captives Thrown Overboard Impact of European Expansion • • • • Native populations ravaged by disease. Influx of gold, and especially silver, into Europe created an inflationary economic climate. [“Price Revolution”] New products introduced across the continents [“Columbian Exchange”]. Deepened colonial rivalries. New Patterns of World Trade