* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2015 department of medicine research day
Survey
Document related concepts
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Development of analogs of thalidomide wikipedia , lookup
MTOR inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
CCR5 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
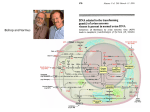
2015 DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE RESEARCH DAY Title of Poster: A Phase 1b/2a, Safety, Pharmacokinetic and Dose-Escalation Study of KD019 in Subjects with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Presenter: Misak Harutyunyan Division: Nephrology ☐Faculty ☐Fellow ☐Resident ☐Post-doc Research Fellow ☐Graduate Student ☐Medical Student ☒Other Principal Investigator/Mentor: Anjay Rastogi, MD, PhD Co-Investigators: Harutyunyan, Misak. Lin, Tabitha. Sharma, Bashar. Arman, Farid. Thematic Poster Category: Clinical Observations and Clinical Trials Abstract Design: This is an open-label, safety, pharmacokinetic (PK), dose-escalation, multicenter study. Rationale: KD019 was originally developed for a solid tumor indication, and is currently being investigated as a cancer treatment. In non-clinical studies, KD019 selectively inhibited key kinases and validated targets in animal models of polycystic kidney disease (PKD). In addition, it has shown either no or extremely weak inhibitory activity of other kinases that should reduce off-target effects. KD019 also has been shown to be a potent inhibitor of receptor and cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases (TKs). The product was specifically optimized to simultaneously inhibit EGFR, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), Src, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2/ KDR), and ephrin receptor B4 (EphB4) tyrosine kinases with high potency, and demonstrated excellent activity in target-specific cellular functional assays. Both the non-clinical results in PKD models and the clinical safety results in human oncology studies suggest that KD019 could be a promising therapeutic in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Purpose: Phase 1b: To determine the safety, plasma pharmacokinetics, and maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of KD019 when administered to subjects with ADPKD. Phase 2a: To evaluate the annualized change in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in subjects with ADPKD when treated with KD019. In addition, exploratory measures of efficacy will be performed throughout both phases of the study. Mechanism: KD019 (formerly named XL647) is a new chemical entity that inhibits multiple tyrosine kinases (TKs) ErbB family members [EGFR and HER2/ErbB2], vascular endothelial growth factor receptor [VEGFR2/KDR]), and Src family kinases. Results: KD019 was shown to rapidly and effectively inhibit tumor growth in trastuzumab resistant models, both in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, KD019 demonstrated potent inhibition of HER2, EGFR and Src signaling in several trastuzumab resistant cell lines, as well as inhibition of c-Met activation, another pathway by which tumors may escape HER2-targeted therapies. KD019 was also shown to be more potent than both the HER2/EGFR inhibitor lapatinib and the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib in inhibiting trastuzumab resistant breast cancer cell growth in vitro. In vivo, results demonstrated that single daily dosing of KD019 strongly inhibited tumor growth in xenograft models of trastuzumab resistance and that Src activity was inhibited in KD019 treated tumors as early as 24 hours after drug administration.