* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Infinitive
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sanskrit grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Proto-Indo-European verbs wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Germanic weak verb wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Germanic strong verb wikipedia , lookup
Sotho verbs wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish verbs wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek verbs wikipedia , lookup
Kagoshima verb conjugations wikipedia , lookup
Hungarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
German verbs wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
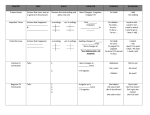
CONCEPT Present tense Imperfect Tense USES Actions that occur now or in general in the present RULES Remove the verb ending and add a new one Actions that happened In the past -ar endings & Are ongoing or habitual actions Preterite tense Positive Tú Commands Negative Tú Commands Actions that happened In the past and are completed actions. aba ábamos abas abais aba aban -ar endings é amos aste asteis ó aron -er/-ir endings ía íamos ías íais ía ían -er/-ir endings í iste ió imos isteis ieron LOOK FOR Stem Changers, Irregulars, irregular YO EXAMPLE Yo hablo IN ENGLISH I talk I am talking Only 3 irregulars: Ser, Ir , & Ver Yo hablaba ... Yo comía ... Yo veía ... Yo iba a ... Yo era ... I used to talk . . . I used to eat . . . I used to watch. . . I used to go to . . . I was (+ adj) … Spelling-changes of -Car, -Gar, -Zar verbs. Stem-changes of -ir Verbs, that stem-change in the present. *ALL IRREGULARS- NO ACCENTS Yo hablé Yo comí. Yo pagué/ Tú pagaste Yo dormí / Él durmió Yo hice. I talked. I ate. I paid / You paid I slept / He slept I made / did. Talk to me! Tells: 1. Conjugate to tú form. A friend or someone your age to do something. 2. Drop the “S”. - Stem-changes in Present tense. ¡Háblame! - 8 irregulars: Ven, Di, Sal, Haz, Ten , Ve, Pon, Sé ¡Ve a casa! Tells: A friend or someone your age NOT to do something. -Irregular yo in Present tense - 5 irregulars: No seas, no vayas, no des, no estés, no sepas ¡No hables! ¡No seas malo! ¡No le des dinero! 1. Add No + inf. 2. Conjugate to Yo form. 3. Drop the “O”. 4. Add the opposite vowel -ar = ES -er/-ir= AS Go home! ¡No estés triste! Don’t talk! Don’t be mean! Don’t give her money! Don’t be sad! Indirect Object Pronouns Answers: To whom? For whom? after the verb. IOPs: me, te, le , nos, os, les Verbs that express Exchange, receiving, giving, telling, etc. For example dar, decir, traer, vender, preparar. You can make the meaning more clear by adding A + name, noun, or pronoun. Direct Object Pronouns Answers: The who? The what ? after the verb. The direct object is the who or what that DIRECTLY receives the action from the verb. The me, te, & nos refers to people. The lo/la & los/las refers to both objects and people. Estar + participle (-ing) DOP’s: me, te, lo/la, nos, os, los/las Present Progressive Equals to the –ing in English Verbs like Gustar Verbs like Gustar: Encantar, faltar, fascinar, molestar, interesar, importar, doler, tocar, caer bien/mal. -ar verbs -ando -er/-ir verbs -iendo A phrase + I.O.P. + 3rd person S/P + Noun(s) IOP’s: me, te, le, nos, os, les. Yo le doy un libro a mi amigo. Yo les voy a decir la verdad a mis padres. I give the book to my friend. I am going to tell the truth to my parents. Yo lo doy. Tú la vendes. Ella la prepara. I give the book. You sell the bed. She prepares the food. Remember: IR stemchangers EI OU Yo estoy escribiendo I am writing. Ella está hablando por teléfono con Mónica. She is talking on the phone with Monica. Remember: The IO Pronoun matches the indirect object of the sentence & The verb conjugation matches the subject of the sentence. A Marta le encanta ir a la escuela. A mí me gustan los carros. School is pleasing to Marta. The cars are pleasing to me.