* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 20130508152130
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Illyricum (Roman province) wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Julius Caesar wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican currency wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Cleopatra (1963 film) wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Julius Caesar (play) wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
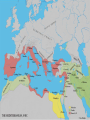
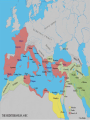
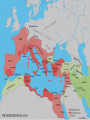
Section 5 Roman Leadership The Reformers Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus • 1st reformer • Became tribune in 133 B.C. • Wanted to set limits to amount of land that could be owned • Ran for re-election (against law) • Senate staged a riot to stop him • He and hundreds of followers were killed Gaius Sempopronius Gracchus • 123 B.C. • Brother of Tiberius • Moved farmers back to country • Sold wheat below market price; eventually was given away • Senate felt threatened and had him killed in 121 B.C. The Generals General Gaius Marius • 107 B.C. • 1st lower class person to be elected to high office • Supported by poor and ex-soldiers • Set up professional army open to all • Offered pay: land, pensions, booty (things taken from the enemy in war) Effects of reforms made by Marius Positive: Negative: Provided jobs Hurt the Republic – loyalty was to general not the Republic Lucius Cornelius Sulla •Opposed Marius •Was given position that Marius wanted •Sulla marched against Rome The Result… Civil War Result of civil war… •Sulla made himself dictator (absolute ruler) •Increased power of Senate The Roman Senate •Doubled in size •Given more duties •Weakened power of tribune •Generals could not hold same army command for more than a year Julius Caesar Julius Caesar • Born July 100 –102 B.C. • Patrician • Father died when he was 16 years old • Was forced into hiding by Sulla • Returned to Rome in 78 B.C. (Sulla was dead) Caesar returns to Rome •Elected as tribune •elected as quaestor 69 B.C. •praetor in 62 BC •Caesar and Bibulus were elected as consuls in 59 B.C. After rule of Sulla… • 60 B.C. • Power was passed to triumvirate (3 people who had equal power) First Triumvirate •Marcus Licinius Crassus •Gnaeus Pompeius (Pompey) – rule by upper-class senators (sealed by marriage to Julia, Caesar’s daughter) •Julius Caesar – rule by one man Caesar’s Discontent • 58 B.C. governor of a Roman province • 55 BC, his partners Pompey and Crassus were elected consuls • In 54 BC, Caesar's daughter Julia died in childbirth Death of Crassus •53 B.C. •Romans were defeated at Carrhae in Syria •Crassus was killed in battle Caesar’s Rise to Power • As governor, built large, strong army that was loyal to him • Conquered northern France, Belgium and invaded Britain • In 50 B.C., he was ordered to break up legions and return Why? Senate, led by Pompey, feared he was growing too strong! Caesar returned to Rome • Entered Rome with his troops • Pompey would not fight; he fled • Caesar pursued him into Greece • 48 B.C., at Pharsalus, Pompey’s legions were defeated Caesar’s Power •46 B.C. was appointed dictator •9 days later, resigned and was elected consul Caesar Goes to Egypt •Caesar pursues Pompey to Alexandria •Pompey was murdered and his head offered to Caesar by young Ptolemy Problems in Egypt • Young Ptolemy and Cleopatra were co-regents of Egypt • Civil War between two • Caesar sided with Cleopatra • Cleopatra moved to estate outside of Rome and had a son Caesarian Caesar’s power continues…. • Was elected consul in 46 B.C. and in 45 B.C. • 45 B.C. – named his grandnephew, Octavian, as his heir • Rome and the Senate continued to bestow honors on Caesar Reforms by Caesar • Redistributed state lands and established new colonies for ex-soldiers • Public works projects – this gave jobs to many • Planned and paid for gladiatorial games • Doubled size of senate • Cut publican activities • Gave citizenship to Greeks, Spaniards, and Gauls • Julian calendar – still used today Caesar did a great deal for Rome… Many feared he would make himself… K I N G Conspiracy •About 60 men, most Senators, plotted against Caesar •On the Ides of March, March 15, 44 B.C., Caesar was assassinated After Caesar’s Death • Power passed to Second Triumvirate • Mark Antony – Caesar’s closest follower – took control of East • Octavian – took the West • Marcus Lepidus – one of Caesar’s top officers, took Africa All three shared control of Rome. Failure of Triumvirate • Worked for a while • Fights broke out • Mark Antony became involved with Cleopatra • Fighting ended in 31 B.C. when Mark Antony was defeated in Battle of Actium Octavian became the sole ruler of the Roman Empire