* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Variation/Artificial Selection
Rotating locomotion in living systems wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
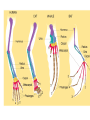
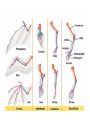
Chapter 15.3 – Darwin Presents His Case Darwin’s Book On The Origin Of Species By Means Of Natural Selection – In this book, Darwin presented his ideas of natural selection (mechanism of evolution) • Based on the ideas of Alfred Wallace • Wrote an essay that summarized evolutionary change Natural Variation/Artificial Selection • Natural variation differences among individuals of a species – Variation is inherited • Artificial selection/selective breeding nature provides the variation among different organisms, and humans select those variations that they find useful Struggle For Existence • Members of each species compete regularly to obtain food, living space, and other necessary items for life key factor in struggle is how well suited an organism is to its environment Survival Of The Fittest Individuals that are better suited to their environments survive and reproduce most successfully – Natural selection • Over time, natural selection causes a change in the inherited characteristics of a population. It directs these changes in ways that increase a species’ fitness in its environment Fitness and Adaptation • Fitness – – The ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment Result of adaptations • Adaptations – – Any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival can be physical, behavioral, or chemical Descent With Modification • Each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time – Implies all living things are related to other • Common descent all species, living and extinct, were derived from common ancestors Darwin’s Evidence for Evolution Fossils Anatomy Embryology and Biochemistry Genetics Fossil Evidence • Fossil trace of an organism living long ago – Mold or cast in a rock • Bones or whole organisms are preserved – Sand/ clay surrounds the dead organism • Sediments turn into rock • Some organisms remain unchanged, while in others, minerals filter into the body > rock > petrified Fossils The Fossil Record • Layering gives clues to when organisms lived. – Lower layers= older and simpler body structure – Upper layers= more recent with complex body structure • Shows that strong similarities to existing organisms Fossil Layers Homologous Structures • Structures that have different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissue – Exs: wings, flippers, arms the more homologous structures shared, the closer their relationship Vestigial Organs • Structures w/ no function in the living organism, but may be used in the ancestors. may be homologous with still-used structures in other related organisms Comparative Embryology • Embryo early stages of a developing plant or animal • The study of developing organisms; shows the relationships not obvious in the fully grown organism. Comparative Biochemistry • The study of organisms on a biochemical level • Ex: Structure of hemoglobin- amino acid sequence reveals relationships • Provides the most fundamental evidence for evolution Genetic Evidence • Population all organisms within a breeding group – Constant change over time due to mutation, nondisjunction and fertilization. • Production of new alleles and genetic recombination could be called the raw materials of evolution. Direct Observation • Change that occurs rapidly on a regular basis can be observed directly. • Reaction of penicillin to bacteria • Evolution causes serious health problems – Antibiotic/ disease resistance – Flu – Pests ( weeds and insects) resist chemicals