* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key math skills for the 2014 GED test
Survey
Document related concepts
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
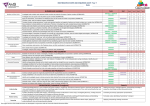
Key math skills for the 2014 GED test Quantitative problem-solving with rational numbers (25%) Whole numbers 1. 2. 3. 4. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with whole numbers. Find multiples (including LCM). Find factors (including GCF). Round whole numbers. Decimals 5. Compare & order decimals (with or without a number line). 6. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals. 7. Round decimals. Fractions 8. Compare & order fractions (with or without a number line). 9. Reduce fractions & convert improper fractions mixed numbers. 10. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with fractions (including mixed numbers). 11. Recognize that a numerical expression with 0 in the denominator (division by 0) is undefined. 12. Convert fractions and decimals (both directions) Negative numbers & absolute value 13. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with positive & negative numbers. 14. Compare and order positive and negative decimals & fractions (with or without a number line). 15. Understand absolute value as distance from zero on a number line. 16. Use absolute value expressions to calculate the distance between 2 points on a number line. [Points may be positive or negative integers, decimals, or fractions.] Ratio and proportion 17. Write ratios. 18. Write and solve proportions. 19. Compute unit rates (e.g., unit pricing, constant speed, people per square mile, BTUs per cubic foot). 20. Recognize and use scale factors with scale drawings. 21. Solve word problems with proportions (including converting units). GED® is a registered trademark of the American Council on Education (ACE) and administered exclusively by GED Testing Service LLC under license. This material is not endorsed or approved by ACE or GED Testing Service. The skills listed here are based on the Assessment Guide for Educators (12/13), the "Revised GED Testing Service® performance standards" (1/16), the “Test-Taker Recommendations for Calculator-Prohibited Indicators” (11/16), and the formula sheet, but some of the language, organization, & simplification is mine. D. Stark 3/28/2017 Key math skills for the 2014 GED test 1 Percents 22. Convert fractions, decimals, and percents. 23. Calculate the percent of a number. [You may also need to be able to find not only the part (% of a number) but also the whole or the percent.] 24. Solve 2-step percent word problems (e.g., interest, tax, sales, tips & commissions). 25. Solve percent change (increase/decrease) word problems. 26. Use the simple interest formula. Exponents & roots 27. Calculate the square of a number & find the square root of a perfect square. Know the 1st 12 perfect squares: 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, 144. 28. Understand the difference between (–3)2 = 9 and –32 = –9 29. Recognize that the square root of a negative number is undefined (in the realm of real numbers). 30. Compute with squares and square roots of decimals and fractions. 31. Calculate the cube of a number & find the cube root of a perfect cube. Memorize the 1st 6 perfect cubes: 1, 8, 27, 64, 125, 216. 32. Compute with cubes and cube roots of decimals and fractions. 33. Use rules of exponents 2 3 23 [e.g., (32)3 = 36 (23)(22) = 25 45/42 = 43 ( ) = 3 5 5 1 ½ 60 = 1 42 = 16 9 =3 3(24) = 3(2)(2)(2)(2) = 48] 34. Simplify & compute with non-perfect square roots. [e.g., √12 = 2√3 ] Scientific notation 35. Convert between scientific and standard notation for large numbers. 36. Convert between scientific and standard notation for small numbers. 37. Solve word problems with scientific notation. [may include computation with numbers in scientific notion and converting answer to scientific notation] Order of operations & word problems 38. Solve one-step and multi-step word problems with basic operations. [Information might be in diagrams and might include decimals, fractions, or scientific notation.] 39. Perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and computation using exponents using basic order of operations. D. Stark 3/28/2017 Key math skills for the 2014 GED test 2 Quantitative problem-solving in measurement (20%) Geometry: 2-D [Dimensions might be decimals or fractions.] 40. Compute the perimeter of the following 2-D shapes: square, rectangle, parallelogram, triangle, trapezoid, regular polygon, composite 2-D shape. 41. Compute the area of the following 2-D shapes: square, rectangle, parallelogram, triangle, trapezoid, regular polygon, composite 2-D shape. 42. Compute the circumference of a circle. 43. Compute the area of a circle. 44. Given the perimeter/circumference or area of any of those shapes (plus any other necessary information), work "backwards,” determining the missing length of a side, radius, diameter, etc. (Dimensions might be decimals or fractions.) 45. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle. 46. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of a leg of a right triangle. Geometry: 3-D [Dimensions might be decimals or fractions.] 47. Compute the volume of the following 3-D shapes: rectangular prism, right prism that’s not rectangular, cylinder, right pyramid, cone, sphere, composite 3-D shape. 48. Compute the surface area of the following 3-D shapes: rectangular prism, right prism that’s not rectangular, cylinder, right pyramid, cone, sphere, composite 3D shape. 49. Given the volume or surface area of any of those shapes (plus any other necessary information), work "backwards,” determining the missing length of a side, height, radius, diameter, etc. Data analysis: statistics [also on the science and social studies tests] 50. Calculate the mean. 51. Calculate the median. 52. Calculate the mode. 53. Calculate the range. 54. Given the mean and all but one data value, work "backwards," determining the missing value. 55. Calculate a weighted average; given the frequency of each data value, calculate the mean. 56. Determine the effects of outliers. Data analysis: tables and graphs 57. Create and interpret tables and perform basic calculations with the data. 58. Create and interpret the following sorts of graphs for categorical data: bar graph, circle graph/pie chart. 59. Create and interpret the following sorts of graphs for 1-variable data: dot/line plot, histogram, box plot. 60. Interpret and make the following sorts of graphs for 2-variable data in the coordinate plane: line graph, scatterplot. D. Stark 3/28/2017 Key math skills for the 2014 GED test 3 Probability 61. Determine simple probability (expressed as a fraction or percent). 62. Determine the probability of independent compound events (expressed as fraction or percent). 63. Determine the probability of dependent compound events (expressed as fraction or percent). 64. Calculate combinations. [likely just with counting techniques rather than a formula] 65. Calculate permutations. [likely just with counting techniques rather than a formula] Algebraic problem-solving with expressions & equations (30%) Introduction to algebra 66. Evaluate algebraic expressions (including those with negative numbers and exponents). [also apply a given formula] 67. Translate from words into algebraic expressions (and vice versa). 68. Expand algebraic expressions by using the distributive property. 69. Combine like terms. Linear expressions & polynomials 70. Add and subtract polynomials. 71. Multiply polynomials (including multiplying 2 binomials with FOIL). 72. Factor polynomials: factor out the GCF (reverse of distributive property). 73. Factor trinomials (reverse of FOIL). 74. Divide factorable polynomials. Rational expressions [ADVANCED] 75. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions. 76. Recognize what value(s) might make a rational expression undefined. Algebraic equations [may involve fractions, decimals, negative numbers] 77. Solve one-step one-variable linear equations. 78. Solve two-step one-variable linear equations. 79. Solve multi-step one-variable linear equations. [may have to use distributive property, collect like terms on the same or opposite sides, etc.] 80. Solve literal equations. 81. Translate from words into algebraic equations. 82. Solve word problems involving algebraic equations. Systems of 2 equations [ADVANCED] 83. Solve a system of 2 simultaneous linear by graphing. 84. Solve a system of 2 simultaneous linear by substitution. 85. Solve a system of 2 simultaneous linear equations by linear combination. Inequalities [may involve fractions, decimals, negative numbers] 86. Solve linear inequalities in one variable. 87. Interpret & graph inequalities in one variable on a number line. 88. Translate from words into algebraic inequalities. 89. Solve word problems involving inequalities. D. Stark 3/28/2017 Key math skills for the 2014 GED test 4 Quadratic equations (in 1 variable with real solutions) [ADVANCED] 90. Recognize if given values belong to the solution set of a quadratic equation. 91. Solve quadratic equations using perfect squares. 92. Solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. 93. Solve quadratic equations by factoring. 94. Solve quadratic equations by completing the square. 95. Translate from words into quadratic equations. Algebraic problem-solving with graphs and functions (25%) The coordinate plane: intro 96. Locate & plot points in the coordinate plane. 97. Graph a line in the coordinate plane. [may also need to match equations with their graphs and to determine whether a given point is on a line or is a solution to the equation] The coordinate plane: slope of a line 98. Determine the slope of a line in various ways from a graph. 99. Determine the slope of a line from a table (from 2 points). 100. Determine the slope of a line from an equation. 101. Solve geometric word problems involving slope. 102. Interpret unit rate as the slope in a proportional relationship. 103. Compare proportional relationships represented different ways (e.g., by comparing a distance-time graph to a distance-time equation to determine which object has the greater speed). 104. Use slope to identify parallel and perpendicular lines. The coordinate plane: equation of a line 105. Manipulate various forms of linear equations (e.g., slope-intercept, point-slope). 106. Write the equation of a line with a given slope through a given point. 107. Write the equation of the line that passes through 2 given points. Functions 108. Recognize from a graph whether or not something is a function. 109. Recognize from a table whether or not something is a function. 110. Compare 2 functions represented in different ways—in an equation, table, graph, or words (e.g., to determine which has the greater rate of change). 111. Evaluate linear & quadratic functions represented with function notation. 112. Recognize the following key features of graphs and tables: intercepts, intervals where a function is increasing/decreasing, intervals where a function is positive/negative, relative maximums and minimums, symmetries, end behavior, periodicity. D. Stark 3/28/2017 Key math skills for the 2014 GED test 5 Possible topics for the no calculator part You’ll need to do the 1st 5 of the 50 math questions without a calculator. Once you leave this section, you can’t return to it. 1. Compare and order positive and negative fractions & decimals (with or without a number line). 2. Recognize that a numerical expression with 0 in the denominator (division by 0) is undefined. 3. Find multiples (including LCM). 4. Find factors (including GCF). 5. Use absolute value expressions to calculate the distance between 2 points on a number line. [Points may be positive or negative and may be integers, decimals, or fractions.] 6. Perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, & division, using the order of operations. [Numbers may be integers, decimals, or fractions (including mixed numbers.)] 7. Calculate the square of a number & find the square root of a perfect square. Know the 1st 12 perfect squares: 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, 144. 8. Understand the difference between (–3)2 = 9 and –32 = –9 9. Recognize that the square root of a negative number is undefined (in the realm of real numbers). 10. Compute with squares and square roots of decimals and fractions. 11. Calculate the cube of a number & find the cube root of a perfect cube. Memorize the 1st 6 perfect cubes: 1, 8, 27, 64, 125, 216. 12. Compute with cubes and cube roots of decimals and fractions. 13. Use rules of exponents 2 3 23 8 3 2 5 5 2 3 2 3 6 e.g., (2 )(2 ) = 2 4 /4 = 4 (3 ) = 3 ( ) = 3 = 5 5 125 1 ½ 60 = 1 42 = 9 =3 3(24) = 3(2)(2)(2)(2) = 48 16 14. Simplify & compute with non-perfect square roots. [e.g., √12 = 2√3 ] D. Stark 3/28/2017 Key math skills for the 2014 GED test 6