* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.) Point: A location in space (no size) 2.) Line: a series of points that
Survey
Document related concepts
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
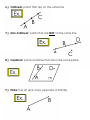
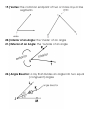
GEOMETRY VOCABULARY 1.) Point: A location in space (no size) 2.) Line: a series of points that extend in two opposite directions (never ends) 3.) Plane: flat surface, no thickness 4.) Segment: part of a line consisting of two points, called endpoints 5.) Length of a Segment: the distance from A to B 6.) Collinear: points that are on the same line 7.) Non-Collinear: points that are NOT on the same line 8.) Coplanar: points and lines that are in the same plane 9.) Finite: has an end; stops (opposite of infinite) 10.) Circle: the set of all points in a plane r distance from point C 11.) Diameter: the distance across a circle through its center 12.) Radius: a segment from the center of a circle to a point on the circle. It is ½ the diameter; all radii have the same length 13.) Figure: set of points in a plane (refers to shapes) 14.) Geometric Construction: a set of instructions for drawing points, lines, circles, and figures 15.) Equilateral Triangle: a triangle in which all 3 sides are the same length 16.) Regular Hexagon: a six sided polygon where all sides and all interior angles are the same measure 17.) Ray: a portion of a line that has one endpoint and extends infinitely in the other direction 18.) Angle: a figure formed by two rays with a common endpoint called a vertex 19.) Vertex: the common endpoint of two or more rays or line segments 20.) Interior of an Angle: the ‘inside’ of an angle 21.) Exterior of an Angle: the ‘outside of an angle 22.) Angle Bisector: a ray that divides an angle into two equal (congruent) angles 23.) Degree: a unit of angle measure 24.) Zero Angle: a ray that measures 0o 25.) Straight Angle: a ray that measures 180o 26.) Right Angle: an angle that measures 90o 27.) Equidistant: the same distance 28.) Midpoint: the point that is exactly halfway between two other points; it divides a line segment into two congruent segments. 29.) Perpendicular: two lines that intersect to form right angles 30.) Perpendicular Bisector: a line that passes through the midpoint and forms a right angle with a segment 31.) Concurrent: A set of lines that all intersect at the same point is said to be concurrent 32.) Point of Concurrency: the point of intersection of concurrent lines 33.) Circumcenter: the point of concurrency for the three perpendicular bisectors of a triangle 34.) Incenter: the point of concurrency for the three angle bisectors of a triangle 35.) Median: the line that connects a vertex of a triangle to the midpoint on the corresponding side 36.) Centroid: the point of concurrency for the three medians of a triangle 37.) Altitude: the perpendicular line that goes from the vertex of a triangle to the corresponding side 38.) Orthocenter: the point of concurrency for the three altitudes of a triangle 39.) Centroid Theorem: states that the centroid of a triangle is located of the way from each vertex to the midpoint of the corresponding side