* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mr. McCarthy
Survey
Document related concepts
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli number wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
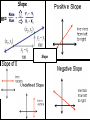
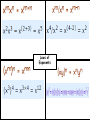
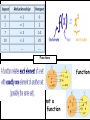
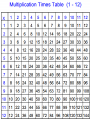
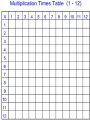
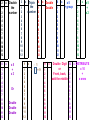
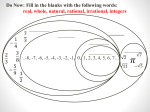
Standard Form Y-Intercept Form Ax+By+C Rise Run intercept Y- Forms of a Line Point Slope Form Parallel–Slopes Same PerpendicularSlopes Negative Reciprocals Slope m= Slope Properties of Addition Additive Inverse Property Properties of Multiplication Distributive Property of Multiplication: Inverse Property of Multiplication: Multiplying the sum of two numbers by If you multiply a number by its reciprocal (multiplicative inverse) the a third number is the same as multiplying each of the two numbers by product is 1. that third number and adding the 9 x 1/9 = 1 product. a x (b+c) = (axb) + (axc) 1/9 x 9 = 1 3 x (6+4) = (3x6) + (3x4) a x 1/a = 1 6 x (20 x 4) = (6 x 20) + (6 x 4) Properties of Multiplication 1/a x a = 1 1/0 is undefined Laws of Exponents With ( ) Laws of Exponents (-2)2 = (-2) × (-2) = 4 Without ( ) -22 = -(22) = - (2 × 2) = -4 With ( ) (ab)2 = ab × ab Without ( ) ab2 = a × (b)2 = a × b × b Laws of Exponents Addition: Subtraction: If a = b then a + c = b + c If -3+a=7 Then, -3+a+3=7+3 a=10 If a = b then a – c = b– c If 8+a=24 Then, 8+a-8=24-8 a=16 Multiplication: Properties of Equality If a = b then ac = bc If a/3=9 Then, 3(a)=9(3) a=27 Division: If a = b and c ≠ 0 then a/c = b/c If 3(a) = 9 Then, a/3=9/3 a=3 Leg Hypotenuse Leg Pythagorean Triples Pythagorean Theorem Distance Formula Special Triangles Functions function not a function Special Binomials (Z is for the German "Zahlen", meaning numbers, because I is used for the set of imaginary numbers). Number Sets Irrational Numbers The numbers you can make by dividing one integer by another (but not dividing by zero). In other words fractions. Q is for "quotient" (because R is used for the set of real numbers). Examples: 3/2 (=1.5), 8/4 (=2), 136/100 Any real number that is not a Rational Number. Transcendental Numbers Any number that is a solution to a polynomial equation with rational coefficients. Any number that is not an Algebraic Number Examples of transcendental numbers include π and e. Includes all Rational Numbers, and some Irrational Numbers. Number Sets Numbers that when squared give a All Rational and Irrational numbers. negative result. A simple way to think about the Real “Imaginary" numbers can seem Numbers is: any point anywhere on the impossible, but they are still useful! number line (not just the whole Examples: √(-9) (=3i), 6i, -5.2i numbers). The "unit" imaginary numbers is √(Examples: 1.5, -12.3, 99, √2, π 1) (the square root of minus one), They are called "Real" numbers because and its symbol is i, or sometimes j. A combination of a real and an imaginary number in the form a + bi, where a and b are real, and i is imaginary. The values a and b can be zero, so the set of real numbers and the set of imaginary numbers are subsets of the set of complex numbers. Examples: 1 + i, 2 - 6i, -5.2i, 4 # Sets Natural numbers are a subset of Integers Integers are a subset of Rational Numbers Rational Numbers are a subset of the Real Numbers Combinations of Real and Imaginary numbers make up the Complex Numbers. Absolute Value The distance between a number and zero |5| = 5 |-5| = 5 5 units 5 units -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Polynomials Add and Subtract Polynomials Binomials Factor Binomials Factor Squares Zeros - Roots Quadratic Exponent Laws Exponent Laws Addition Plus And Total of Increased by Add More than Together Gain Greater Added to All together In all Make Sum Combine Later Perimeter Multiplication Times Double Multiplied by Of Increased by Factor Twice Multiple Each Area Array Area Volume Squared Cubed Power Exponent Radical Radicand Base Subtraction Subtract Decreased by Shared Gave Fewer than Minus Less than Difference Less Loss Parentheses Times the sum of The quantity of Times the difference of Plus the difference of Key Math Problem Solving Words Division Is Quotient Are Reduced Percent Was Simplest form Were Split Divided by Will be Per Yields Divisor Sold for Half Root Zeros of x Equal Percent Formulas 2 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 x Double the number x5 + x3 Or Double Double Double 3 x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Triple 4 the 1 number 2 x Double Double 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 x - 1 + =9 11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 x 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 x x5 + group Double Digit or Front, back, add the middle 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 x x5 + x2 x DISTRIBUTE x 10 + x ones