* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleus/Nucleolus
Survey
Document related concepts
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
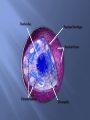
Zachary Knott Biology 101 The nucleus is the cell’s control center It issues instructions to that control cell activities It stores hereditary information Nuclear envelope: special kind of membrane that bounds the surface of the nucleus Acts as a barrier between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, but substances need to pass through it Nuclear Pores: openings that form when the two membrane layers pinch together The DNA of eukaryotes Form by dividing into several segments and associating with protein After cell division the chromosomes uncoil forming threadlike structures called chromatin The chromatin is then available for protein synthesis Cite for several hundred genes that encode rRNA rRNA: ribosomal RNA Where ribosome subunits assemble Nucleolus Nuclear Envelope Nuclear Pores Chromosomes Chromatin Huntington’s Disease Caused by a faulty gene being present on chromosome 4 Having the faulty gene leads to damage of the nerve cells in areas of the brain Result: gradual physical, mental, and emotional changes The Huntington Disease Association http://www.hda.org.uk/charity/whatishd.html What is chromatin? 1. A. B. C. D. A barrier between the nucleus and the cytoplasm The place where ribosome subunits assemble Uncoiled DNA that is used in protein synthesis The cell’s control center What is the role of nuclear pores? 2. A. B. C. D. A special kind of membrane that bounds the surface of the cell It contains proteins that allow RNA in and out of a the cell Forms a barrier between the nucleus and the cytoplasm allowing certain to pass through it Openings that form when two membranes pinch together