* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operant Conditioning
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Flagellation wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Residential treatment center wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
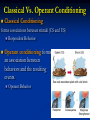
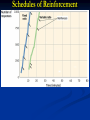
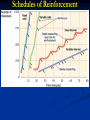
Unit 6 (Mod 27): Operant Conditioning A.P. Psychology Classical Vs. Operant Conditioning Classical Conditioning forms associations between stimuli (CS and US) Respondent Behavior Operant conditioning forms an association between behaviors and the resulting events. Operant Behavior Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning: A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished by a punisher Skinner’s Experiments B.F. Skinner’s experiments extend Edward Thorndike’s law of effect. Thorndike’s law of effect-states that rewarded behavior is likely to occur again & behaviors that are followed by undesirable consequences will happen less often. Skinner’s Experiments Operant Chamber Chamber that contained a bar/key that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food/water reinforce The bar or key is connected to devices that record the animal’s response. Also known as a “Skinner Box” Shaping Shaping The operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior towards the desired target behavior through successive approximations. A rat shaped to sniff mines. A manatee shaped to discriminate objects of different shapes, colors and sizes. Reinforcement Reinforcement (reinforcers): Any event that strengthens (reinforces) the behavior it follows A reinforcement is a reward Types of Reinforcers Types of Reinforcers Primary Reinforcer: An innately reinforcing stimulus Often satisfies a biological need E.g. Pizza Conditioned Reinforcer: A stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforce Also known as a secondary reinforcer E.g. Money Types of Reinforcers Immediate Reinforcer: Behavior results in instantaneous reward Delayed Reinforcer: Behavior is not rewarded immediately In lab experiments, rats do not respond to reinforcers that are delayed more than 30 seconds Humans DO respond to delayed reinforcers: weekly paychecks, end of term grades, etc. Schedules of Reinforcement Reinforcement schedule Continuous reinforcement: Pattern that defines how often a desired response will be reinforced Reinforcement occurs after EVERY desired response Partial reinforcement: Reinforcement occurs only part of the time Acquisition is slower Greater resistance to extinction Schedules of Reinforcement Fixed-Ratio: Reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses E.g. Buy 10 coffees, get one free Variable-Ratio: Reinforces response after an unpredictable number of responses E.g. Slot machines Schedules of Reinforcement Fixed-Interval: Reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed E.g. Checking your mailbox more frequently the closer it gets to its’ normal delivery time Variable-Interval: Reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals E.g. checking text messages frequently when waiting for a text, although no designated time for said text has been established Schedules of Reinforcement Schedules of Reinforcement Schedules of Reinforcement Schedules of Reinforcement Schedules of Reinforcement Schedules of Reinforcement Reinforcement linked to a number of responses (a ratio schedule) produces a higher response rate than reinforcement linked to amount of time elapsed (an interval schedule) Schedules of Reinforcement Reinforcement linked to a number of responses (a ratio schedule) produces a higher response rate than reinforcement linked to amount of time elapsed (an interval schedule) Predictability is important too: unpredictable (variable) schedules produced more consistent responses than predictable (fixed) schedules. Punishment An event that tends to (or is meant to) decrease the behavior that precedes it. 1. Studies of punishment have revealed a few important points: Punished behavior is suppressed, not erased. 2. Punishment teaches discrimination among situations. 3. The spanking likely doesn’t prevent the child from swearing, but it might stop him/her from swearing around his/he parents Punishment can teach fear. 4. It’s a temporary, negative reinforcement of the punishment Child might associate fear not just with the swearing that causes the punishment, but also with the punisher or place of punishment Physical punishment may increase aggression. Physical punishment may model aggression as a way to cope with problems Punishment Punishment Punishment