* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
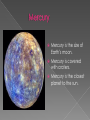
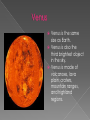
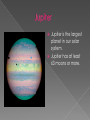
Our solar system has inner and outer planets. Also our solar system has a dwarf planet. All of our planets revolve around our central star, or in other words, a sun. The sun is the central star of the Milky way galaxy. Without the sun we would not be alive. Our sun provides us with light, heat, and energy to live. Mercury is the size of Earth’s moon. Mercury is covered with craters. Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. Venus is the same size as Earth. Venus is also the third brightest object in the sky. Venus is made of volcanoes, lava plain, craters, mountain ranges, and highland regions. Earth is the planet we live on. Earth is the largest inner planet. Earth’s distance from the sun helps the temperature maintain so it can support life. Mars is also called the Red Planet. Mars has two moons Deimos and Phobos. Mars is very small compared to earth. The asteroid belt is in between the outer and inner planets. The asteroid belt is made of rocks and other pieces of stuff. Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. Jupiter has at least 63 moons or more. Saturn has rings around it. Saturn has at least 31 moons. Uranus is a gas giant. Uranus is sideways when it orbits the sun. Neptune is one of the windiest places in our solar system It has at least 13 moons. Pluto is a dwarf planet. Pluto used to be considered a planet but now its considered a dwarf planet. A planet is a big object that orbits a star. Earth is a planet. The inner planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The inner planets are the ones before the asteroid belt. The outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The outer planets are the planets after the asteroid belt. A comet is a ball of ice, rock, and frozen gases. Usually comets are less than 10 kilometers across. Constellations are a group of stars that form an imaginary picture in the night sky. One of the most common constellations is the Little Dipper. During the moon phases there is waxing and waning. When you look at the moon you think there are different shapes of it but it is just the moon phases. A galaxy is a huge system of stars, dust , and gas. The galaxy we live in is called the milky way. This is the powerful telescope called Hubble. There are regular telescopes also but you can only see stars with them. A universe is everything that exists in space. There are galaxies and a whole lot of stars in the universe. Stars are huge superheated gases. The color of the star tells how hot the star is. An axis is an imaginary line going through both poles of a planet. Earth has an axis.