* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 4E03: Population Genetics Course Outline: Term II, 2010
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
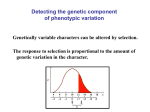
Biology 4E03: Population Genetics Course Outline: Term II, 2010 Student Evaluation: Mid Term : 20% Tutorials: (problem assignments) : 20% Final: 60% Part I. Dr. Richard Morton Week 1: Introduction to Population Genetics; Genetic Variation Topics: Define population genetics and applications to other disciplines. Review basic genetic background including genes and alleles, mitosis and meiosis, and replication, transcription, translation; discuss types and causes of genetic variation Readings: Halliburton Chapter 1, 2 Utami et al. (2002) Male bimaturism and reproductive success in Sumatran orang-utans. Behavioral Ecology 13:5):643-652 Week 2: HWE Topics:Assumptions of Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium and the implications of violating these assumptions. Application to studies of genetic load and age-dependent natural selection. Chi square test, degrees of freedom. Readings:Halliburton Chapt 3 Laundey S. and Hedgecock D. (2001) High genetic load in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas . Genetics 159: 255-265 Week 3: More HWE; Linkage Disequilibrium, Population Subdivision, Inbreeding, and Gene Flow Topics:Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium, allelic expectations at X-linked loci and sex-biased allele frequencies. Intro to linkage disequilibrium and applications to human evolution. Readings:Halliburton Chapt 4 pp. 91-110; 120-125 Tishkoff et al. (1996) Global patterns of linkage disequilibrium at the CD4 locus and modern human origins. Science 271: 1380-1387 Garrigan and Hammer (2006) Reconstructing human origins in the genomic era. Nature Reviews Genetics 7: 669-680. Week 4: Human evolution and the Out of Africa Hypothesis; Linkage Disequilibrium (continued), Gene Flow, Genetic Drift Topics:Out of Africa versus Multiregional hypotheses; evidence from mitochondrial and nuclear DNA. D - the linkage disequilibrium coefficient, Dmax and Dmin, r - the recombination parameter. Linkage disequeilibrium in humans. Tajima's D Readings:Halliburton Chapt 6 (all),Chapt 7 pp. 221-262, Chapt. 10 pp. 405-407 Nordborg et al. (2005) The pattern of polymorphism in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Biology 3(7):e196 Week 5: Genetic drift, non-random mating, inbreeding Topics:The binomial coefficient and binomial equation. Application of binomial equation to HWE, LD, and drift. The Poisson distribution and the impact of variance in reproductive success and the effective population size. Inbreeding, assortative and disassortative mating, inbreeding depression. Readings:Halliburton Chapt 8, pp. 269-281; 286-294; Chapt. 9 (all) Hoelzer, G. A. (1997) Inferring phylogenies from mtDNA variation: mitohondrial-gene trees versus nuclear-gene trees revisited. Evolution 51(2):622-626. Week 6: Neutral Theory; Coalescence Topics:Discussion of the neutral model; fundamentals of coalescent theory. Readings:Halliburton, Chapt 10 (all) Week 7: Mid Term Break Part II. Dr. Rama Singh Week 8. Natural Selection I: Basic Theory Meaning of natural selection, requirement for natural selection, life cycle and components of fitness, basic models of selection, dynamics of allele frequency change, stability analysis and equlibrium frequency, population fitness, maintenance of variation: overdominance, underdominance selection in fitness, examples of natural selection in nature , concept of dminance in fitness, concept of marginal fitness- of alleles and genotypes, evolution of population fitness, Fundamental theorem of natural selection, Wrights concept of fitness landscape, and fitness peaks and valleys Reading: Halliburton Chapter 5 Week 9. Natural Selection II. Maintenance of Genetic Variation Two locus theory: Concept of linkage disequilibrium (LD), Role of selection and recombination in maintaining variation, Balancing Selection: maintenance of variation/polymorphism, Overdominance vs. under dominance, varying environment, Antagonistic selection, Selection in opposite direction in males vs. females, Selection in temporally varying environment, Frequency Dependent Selection: Negative frequency dependent selection, Examples of frequency Dependent Selection, Fitness at Equilibrium, Sexual selection: Concept of male and female fitness, the need for sexual selection theory, nature of sexual dimorphism, evolution of sexual dimorphism, female choice and other theories Reading: Halliburton Chapter 12 Week 10: Gene Flow and Population differentiation Concept of heterozygosity in hierarchical populations, Calculation and meaning of Fst, theoretical derivation of Fst, relation between Fst and gene flow (Nm), relation between Fst, H and Nm, measuring gene flow from Fst, distribution of Fst at loci and role of selection, gene flow between mainland and Island. Reading: Halliburton Chapter 9 Week 11: Molecular Evolution Cost of selection (1-W) and limit to genetic polymorphisms, neutral theory of evolution, rates of evolution and the concept of molecular clock (constant rates), rates of substitution (k), concept of effective neutrality (mean s << 1/2N), effective neutrality and levels of H in small vs. large populations, concept of synonymous (ks)and non-synonymous(ka) substitution, use of Ka/Ks ratio to test selection within and between species, generation time effect on k, relation between population size, generation time and substitution rate Reading: Halliburton Chapter 10 Week 12: Quantitative Genetics and Phenotypic Evolution Concept of genotype, phenotype and environment, Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL), components of phenotypic variance, calculation of heritability, concept of covariance/ genetic correlation between relatives, broad sense and narrow sense heritability, meaning of heritability, heritability of traits within and between populations, calculation of heritability from selection experiment, relation between selection response (R) and selection (S), selection response in quantitative traits, effects of long-term selection on population fitness, phenotypic Selection in Nature, directional, stabilizing and disruptive selection, stabilizing selection and maintenance of variation Reading: Halliburton Chapter 13