* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adaptive Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Co-operation (evolution) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Kin selection wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Mate choice wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary landscape wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
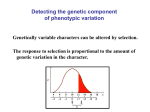
Adaptive Evolution Natural selection is the mechanism of adaptive evolution Adaptive Evolution • Organisms are adapted to their environment Converging Evolution • Some very different species are subject to the same environmental pressures Genetic Variation is the starting material • Genetic variation leads to phenotypic variation differential success • Discrete characters – Single gene locus • Quantitative characters – Polygenic, vary along continuum Phenotypic Polymorphism • 2 or more distinct phenotypes exist in high enough frequencies to be noticeable • Does not apply to traits that vary along a continuum These traits are polymorphic at genetic level but not at phenotypic level Variation Between Populations • Geographic variation – Differences between geographically separated populations of the same species • Environmental conditions vary, natural selection acts differently Evolutionary Fitness • Fitness= contribution that an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation • Relative fitness= contribution of one phenotype relative to the alternative phenotype – Highest success = 1 – Relative success is compared to 1 • 80% =.8 Selection • Depends on relative fitness – Directional – Disruptive – Stabilizing Directional Selection • Shifts bell curve in one direction • Population arrives in new environment • Environment changes – Black bears during ice ages Disruptive Selection • Extremes are favored over intermediate phenotype • Can eventually lead to speciation. – Galapagos finches Stabilizing Selection • Intermediate is favored over extremes • Maintains status quo • Reduces variation – Birth weight Preserving Variation • Stabilizing and Directional selection reduce variation • Variation needs to be maintained for species to be able to evolve to changing environment – Diploidy – Balancing selection – Neutral Variation Diploidy • Diploid= two copies of each chromosome • Hidden genetic information • Harmful, recessive alleles can be hidden – Only show if individual is homozygous • Hidden alleles could become advantageous if environment changes Balancing Selection • Heterozygote advantage – Negative alleles are maintained if heterozygote has an advantage over homozygotes • Sickle cell trait Frequency Dependant Selection – Fitness declines when one morph becomes too frequent – Advantage is only an advantage if a few have it and the rest are vulnerable • Blue Jays eating camouflaged moths Neutral Variation • Some traits have no impact on fitness – Un-translated genes – Silent Mutations Sexual Selection • Sexual dimorphism • Intrasexual selection – Within the same sex – Competition for mates • Intersexual selection – Between different sexes – Mate selection Mate Choice • Male fitness depends on number of offspring • Female fitness depends on quality of offspring – Jacana=role reversal • Showy characteristics are an indicator of overall health?? Why Sexual Reproduction? • Requires larger population • Slower population growth rate – Only half of total population produces offspring • Risks associated with finding mates • What is the advantage??? Some ideas • Natural selection acts on variation • Recombination increases variation – Resistance to disease – Co-evolution with pathogens Why Can’t Natural Selection Create Perfect Organisms? • Limited by historical constraints – Can only act on what already exists • Birds with 4 limbs and wings… • Adaptations are compromises – Multiple activities in various environments • Seals • Chance and natural selection interact – Chance events make a difference • Storm blows birds off course • Selection can only edit existing variation – New alleles don’t arise on command/necessity • HIV resistance