* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AIM_01-02-S_Real_Numbers
Survey
Document related concepts
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
P-adic number wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Types of Numbers
There are many “types”
of numbers.
Each type can be
grouped into a collection
called a SET.
1.2 S
KM & PP
1
Sets
In general, any collection of
objects is called a SET.
A set can be defined in
several ways:
English:
A description in words
Set Builder:
A mathematical rule
Roster:
A list of the objects or
numbers inside braces
1.2 S
KM & PP
2
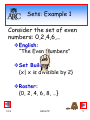
Sets: Example 1
Consider the set of even
numbers: 0,2,4,6,…
English:
“The Even Numbers”
Set Builder:
{x| x is divisible by 2}
Roster:
{0, 2, 4, 6, 8, …}
1.2 S
KM & PP
3
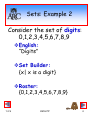
Sets: Example 2
Consider the set of digits:
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
English:
“Digits”
Set Builder:
{x| x is a digit}
Roster:
{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}
1.2 S
KM & PP
4
The Number Line
C
We use a Number
Line
to graph sets of
Real Numbers.
Zero is
Positive
in the
numbers
center.
are on
the right.
1.2 S
Negative
numbers
are on
the left.
KM & PP
5
The Natural Numbers
Natural numbers are
usually the first set that
we learn. They are also
called Counting numbers.
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …}
1.2 S
KM & PP
6
The Natural Numbers
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …}
Here are the Natural
numbers graphed on the
number line:
1.2 S
KM & PP
…
7
The Whole Numbers
The set of Whole numbers
is the set of Natural
numbers along with zero.
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …}
1.2 S
KM & PP
…
8
The Opposite
Each Natural number to
the right of zero has an
Opposite to the left of
zero.
-1 and 1 are Opposites.
-2 and 2 are Opposites.
-3 and 3 are Opposites.
1.2 S
and KMso& PPon...
9
Opposite Numbers
Opposite numbers are the
same distance from zero,
but they are on opposite
sides of zero.
-a and a are opposites.
1.2 S
KM & PP
10
What about Zero?
Two numbers are opposite
if their sum is zero.
-1 + 1 = 0
-2 + 2 = 0
-3 + 3 = 0
Since 0 + 0 = 0
Zero is it’s own opposite.
1.2 S
KM & PP
11
The Integers
The Integers are the
Whole numbers together
with their Opposites.
…
{…,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,…}
1.2 S
KM & PP
…
12
The Rational Numbers
The set of
Rational Numbers
consists of all quotients of
Integers with non-zero
denominators.
a
b
a and b are integers, b 0
1.2 S
KM & PP
13
Convert: Rational
Number to Decimal
To convert a Rational Number
into Decimal form,
divide the numerator by the
denominator.
a
b
b a
A Rational number can
always be converted to a
Terminating Decimal
or a
Repeating Decimal.
1.2 S
KM & PP
14
Conversion Example 1
1
4
0.25
4 1.00
1
0.25
4 Terminating Decimal
1.2 S
KM & PP
15
Conversion Example 2
1
3
0.333...
3 1.0000
1
0.3...
3 Repeating Decimal
1.2 S
KM & PP
16
Conversion Example 3
2
5
0.4
5 2.0
2
0.4
5 Terminating Decimal
1.2 S
KM & PP
17
Conversion Example 4
4
7
0.571428571428...
7 4.0000000000000
4
0.571428...
7 Repeating Decimal
1.2 S
KM & PP
18
Conversion Example 5
0
4
0
4 0
0
0
4 Terminating Decimal
1.2 S
KM & PP
19
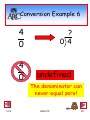
Conversion Example 6
1.2 S
4
0
?
0 4
4
0
undefined
The denominator can
never equal zero!
KM & PP
20
Conversion Example 7
11
8
1.375
8 11.000
11
1.375
8 Terminating Decimal
1.2 S
KM & PP
21
Conversion Example 4
25
6
4.1666...
6 25.00000
25
4.16...
6
Repeating Decimal
1.2 S
KM & PP
22
What about Negatives?
a
a a
b
b
b
The negative sign can be in
front of the ratio or in the
numerator or in the
denominator. Usually, it is
best to place it in the front.
1.2 S
KM & PP
23
What about Negatives?
Example 1
3
4
“Negative three-fourths”
3
4
1.2 S
KM & PP
24
What about Negatives?
Example 2
5
1
2 2.5
2
2
“Negative two and one-half”
5
2
1.2 S
KM & PP
25
Irrational Numbers
Any Real number that is not
a rational number is called
Irrational.
Irrational numbers cannot
be written as the ratio of
integers. The decimal
approximation for an
irrational number will not
terminate or repeat.
1.2 S
KM & PP
26
Irrational Numbers
Here are a few examples of
numbers that are Irrational.
2 1.41421…
3.14159…
13 3.6055512…
e 2.71828…
1.2 S
KM & PP
27
The REAL Numbers
REAL NUMBERS
The set of numbers that
correspond to points on the
number line.
The REAL NUMBERS include
the following:
Natural, Whole, Integers,
Rational, and Irrational
1.2 S
KM & PP
28
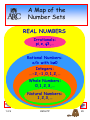
A Map of the
Number Sets
REAL NUMBERS
Irrationals:
pi,e,3,…
Rational Numbers:
a/b with b0
Integers:
…-2,-1,0,1,2,…
Whole Numbers:
0,1,2,3,…
Natural Numbers:
1,2,3,…
1.2 S
KM & PP
29
Order: Small to Large
The Real Numbers are named on
the number line from small to
large. If we choose any two
numbers on the number line, the
number on the left is smaller and
the number on the right is larger.
1.2 S
KM & PP
30
Order: Small to Large
The Real Numbers are named on
the number line from small to
large. If we choose any two
numbers on the number line, the
number on the left is smaller and
the number on the right is larger.
1.2 S
KM & PP
31
An Example:
“Negative three is less than one”
-3 < 1
“One is greater than negative three”
1 > -3
1.2 S
KM & PP
32
> or <
How do these numbers compare?
-5 <
11 >
0
1.2 S
2
-13
<
6
-5 <
0
KM & PP
33
> or <
How do these numbers compare?
-5 <
11 >
0
1.2 S
2
-13
<
6
-5 <
0
KM & PP
34
Absolute Value
The ABSOLUTE VALUE of a
number, |x|, is its distance from
zero on the number line.
|-5|= 5
|5|= 5
1.2 S
KM & PP
35
|x| Examples
|-9|= 9
|20| = 20
|0| = 0
-|-9|= -1|-9|= -19 = -9
1.2 S
KM & PP
36
That’s All for Now!
That’s All for Now!
1.2 S
KM & PP
37
Screen bean sampler
1.2 S
KM & PP
38