* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution of Populations
Survey
Document related concepts
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary landscape wikipedia , lookup
Sex-limited genes wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Mate choice wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
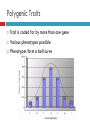
CHAPTER 15: EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS Biology 1 Variation Inherited differences between individuals of a population Can be Physical characteristic Biochemical characteristic Behavioral characteristic If there is no variation for a trait, it is said to be fixed Gene Pool All of genes found within a population Relative frequency of alleles- proportion of gene pool that the allele makes up Sources of Variation Mutation Creates new variation by changing parts of the genetic code Gene Shuffling Creates new variation by the reshuffling of genes during sexual reproduction Chromosome segregation Crossing-over Single Gene Traits • • • • Traits are coded for by a single gene If trait has simple Mendelian (dominant/recessive) inheritance, there are 2 phenotypes possible. If trait has incomplete dominance or codominance, there are 3 phenotypes possible. If trait has multiple alleles, # of phenotypes depends on # of alleles ▫ For example: ABO blood type have 3 alleles with 4 phenotypes possible Natural Selection on Single Trait Genes Occurs if the phenotypes are not equal in their fitness Relative frequencies within the gene pool change as some phenotypes are selected for (or some are selected against) This is evolution (a change in allele frequencies within a population over time) Natural Selection Refresher Polygenic Traits Trait is coded for by more than one gene Various phenotypes possible Phenotypes form a bell curve Natural Selection of Polygenic Traits Directional Selection One phenotype extreme is selected for (or one against) Bell curve is shifted to the left or right Natural Selection of Polygenic Traits (continued) Stabilizing Selection Both phenotype extremes are selected against (average phenotype is selected for) Bell curve narrows Natural Selection of Polygenic Traits (continued) Disruptive Selection Average phenotype is selected against (extremes are selected for) Bell curve splits into two peaks Genetic Drift Change in allelic frequencies due to random effects Effects are seen more in smaller populations Genetic Drift: Bottleneck Effect Event randomly removes large numbers of individuals from a population Many variations can be lost Genetic Drift: Founder Effect Small part of the population removes itself (or is removed) from the larger population Genetic Equilibrium Allelic Frequencies remain the same No evolution Random mating Large population No immigration or emigration No mutation No natural selection Speciation Species - group of individuals that can breed together and produce a fertile offspring Speciation is the process of forming new species from existing species To occur: Populations of one species must be isolated from each other long enough to accumulate enough changes to become two species Types of Isolation Geographical Isolation Populations are separated by a geographical barrier and cannot mate and share genes Types of Isolation Behavioral Isolation Populations are separated by behavioral differences and don’t mate with each other to share genes Temporal Isolation Populations reproduce at different times so they cannot mate together and share genes This leads to… Reproductive Isolation Cannot mate and produce a fertile offspring Occurs because individuals cannot Mate together or Create a zygote or Create a viable offspring or Create a fertile offspring EVOLUTIONARY TRENDS Adaptive Radiation from COMMON DESCENT Species diversifies into many new species EVOLUTIONARY TRENDS Convergent Evolution-Analogous Structure Species evolve to a similar form from different ancestors Both adapt to similar environment Examples EVOLUTIONARY TRENDS Coevolution Species evolve together because of a close ecological relationship Coevolution Examples EVOLUTIONARY TRENDS Punctuated Equilibrium Evolution shows long stable period and then rapid bursts of change