* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Congenital Heart Defects
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
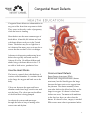
Congenital Heart Defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities in any part of the heart that are present at birth. They occur in the early weeks of pregnancy when the heart is forming. Heart defects are the most common type of birth defect. About 40,000 infants are born with heart defects each year in the United States. The defect may be so slight that it isn’t detected for many years or it may be so severe that the newborn’s life is in danger. Advances in diagnosing and treating heart defects have greatly increased survival. Almost all of the 1.4 million children and adults living with heart defects in the U.S. are able to lead active, productive lives. How the Heart Works The heart is a muscle that is divided into 4 Common Heart Defects sections called chambers. It circulates blood Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) to the lungs for oxygen and back out to the Before birth a large blood vessel (ductus body. arteriosus) lets the blood bypass the lungs because the fetus receives its oxygen from Valves are between the upper and lower the placenta. The ductus normally closes chambers and where large vessels enter and soon after birth so the blood can flow to the exit the heart. The valves prevent backflow lungs for oxygen. If it doesn’t close heart of the blood that is being pumped. failure can occur. Treatment with medicine in the first few days can often close the An electrical system sends messages ductus. If it doesn’t close, surgery is needed. through the heart to keep it beating at the PDA occurs most often in premature babies. correct rate and rhythm. 1 Septal Defects Surgery is needed and is usually done in 3 The inside wall (septum) between the sides stages: in the first two weeks, at 4 to 6 of the heart does not fully form and there is months, and at about 18 months to 3 years. a hole. An atrial septal defect (ASD) involves a hole between the upper chambers. Tetralogy of Fallot A ventricular septal defect (VSD) occurs This is made up of 4 defects: when the hole is between the lower chambers. These defects result in the blood lower chambers of the heart not flowing correctly through the heart – making the heart work harder. The hole may Ventricular septal defect – hole between Pulmonary stenosis – narrowing of be repaired with a procedure or surgery may pulmonary valve and main pulmonary be needed. Small holes may heal by artery (vessel carrying blood from the themselves or may not need to be repaired. heart to the lungs for oxygen) Aortic valve which opens to the aorta Coarctation of the Aorta (large vessel leaving the heart to carry Part of the aorta, the large vessel that carries blood to the body) is enlarged and seems blood out of the heart to the body, may be to leave from both ventricles instead of too narrow for the blood to flow through just from the left side. correctly. Sometimes the narrowed part can be made wider by an inflated balloon during a procedure. In other cases surgery may be needed. If the narrowing is severe, the baby may have serious problems and treatment or surgery is needed soon after birth. Transposition of the Great Arteries The two major vessels leaving the heart (the main pulmonary artery and the aorta) are switched (transposed). Each leaves the heart from the wrong chamber. Surgery is needed Muscle wall of the lower right chamber (ventricle) is thicker than normal. These defects prevent some of the blood from getting into the lungs. The body then does not receive enough oxygen. Babies will have bluish looking skin or have episodes of turning blue when crying or feeding. Surgery is usually done soon after the baby is born. to correct this serious problem in the Diagnosis newborn. Severe congenital heart defects may be diagnosed during pregnancy. If a heart Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome problem is suspected, a fetal This involves a number of structures that do echocardiogram may be done. This uses not fully form on the left side of the heart sound waves to create an image of the heart. such as the left ventricle (lower chamber), When a heart defect is diagnosed in mitral valve, and aortic valve. pregnancy, doctors can plan ahead for treatment after birth. 2 Less severe heart defects are often Drinking alcohol diagnosed when children are older. Chest x- Using cocaine ray, EKG, echocardiogram, or cardiac catheterization may be used. Certain medications may also increase the risk: Minor defects often do not have symptoms. They may be diagnosed during an exam or test for another reason. Acne medication isotretinion Some anti-seizure medicines Thalidomide Treatment Treatment varies depending upon the type Women can take steps before and during and severity of the heart defect. It may pregnancy to reduce the risk of having a include procedures, surgery, medication, and baby born with birth defects: long-term monitoring. Children and adults should continue to see a doctor regularly. Causes and Risk Factors A specific cause of heart defects is micrograms (0.4 mg) of folic acid. Not smoking. Not drinking alcohol or taking drugs during pregnancy. unknown. Both genetic and environmental factors seem to be involved. Research is Taking a daily multivitamin with 400 Seeing a doctor if you are planning to being done to find ways to prevent and treat become pregnant or as soon as you heart defects. suspect you are pregnant and throughout pregnancy. Some heart defects are a part of a pattern of other genetic birth defects such as Down For More Information syndrome or Turner syndrome. Talk with your doctors about your questions In the past 30 years, researchers have found and concerns. at least 10 gene mutations (changes) that can cause heart defects not related to other syndromes. Other factors may increase the risk of heart defects. These include: These may also be helpful resources: American Heart Association www.heart.org 800-242-8721 German measles (rubella) during the first March of Dimes 3 months of pregnancy. www.marchofdimes.com Viral infections (flu) Exposure to some industrial solvents 888-MODIMES (663-4637) (chemicals) 3 NHLBI (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute) www.nhlbi.nih.gov 301-592-8563 U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects 800-232-4636 Dev. 4/14 ©Mount Carmel 2014 4