* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download P-59 Frequency of associated congenital heart defects in Down
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
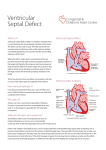
P-59 Frequency of associated congenital heart defects in Down syndrome. Hyder S.N., Mukhtar N. , Aziz Z . Children hospital &The Institute of Child health, Lahore.Pakistan Patients with Down syndrome are prone to have congenital heart defects. Study was done to find the frequency of congenital heart defects in children with Down’s syndrome in Children Hospital Lahore. Material & Methods: The descriptive study had directed by the Department of Cardiology in The Children’s Hospital and the Institute of Child Health, Lahore, in year 2015. Fifty-eight phenotypically Down syndrome children coming to the cardiology department for echocardiography from birth to 13 years were included in this study. The 2 –dimension echocardiography had been done after detailed history and physical examination. Results: Congenital heart defects were found in 29 out of 58 patients (50%). Among the affected patients, 16 (55.2%) were males and 13 (44.8%) females with ratio of 1.2:1. Acyanotic lesions were common (79.31%) than cyanotic lesion (20.69%). Among the isolated lesions ventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus and complete atrioventricular defects were the commonest defects (20.69%) each, followed by pulmonary atresia (6.89%), tetralogies of Fallot, transposition of great arteries and double outlet right ventricle (3.45%) each. Among the mixed lesions ventricular septal defect with atrial septal defect was most common (6.89%), followed by Coarctation of aorta patent ductus arteriosus, univentricle with atrial septal defect, and double outlet right ventricle and pulmonary atresia (3.45%) each. Conclusion: Heart defects are found in 50% children with Down syndrome. The commonest in acyanotic lesion are ventricular septal defect, in cyanotic cardiac lesion pulmonary atresia and in case of mix lesion ventricular septal defect with atrial septal defect were found. Key Words: Down syndrome, Congenital heart disease, Transposition of great arteries, Pulmonary atresia, Tetralogy of Fallot’s, Ventricular septal defect.