* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Visualization
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Security printing wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Cyberattack wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Mobile device forensics wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
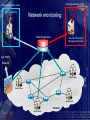
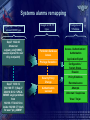
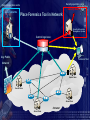
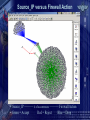
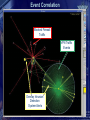
Computer Forensics in Practice Armed Forces of the Slovak Republic mjr. Ing. Albert VAJÁNYI 1Lt. Ing. Boris ZEMEK (c) May 2005 Communication and Information System Control and Operation Centre Information Security Centre InfoSec Centre Chief mjr. Ing. Albert VAJÁNYI Division Chief 1Lt. Ing. Boris ZEMEK (c) May 2005 What is computer forensics anyway? The application of computer investigations and analysis techniques in the interests of determining potential legal evidence. Computer specialists can draw on an array of methods for discovering deleted, encrypted or damaged file information. (Rorrins, 1997) You don’t know what happened on your network. A network forensic analysis tool can effectively answer the difficult question “What happened?” in the aftermath of a security incident. That tool provides a passive network monitoring solution that visualizes the network activity. A network forensics analysis tool can visualize and analyze data from firewalls, IDS, IPS, syslogs, audit systems and more. Key Features of Forensic Tools • Data collection and visualization – Monitor and analyze data from all seven layers of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) stack – Relational, Tree ontology for knowledge base – TCP dump recording: records traffic being monitored in an unprocessed, binary state • Pattern and content analysis – Powerful visualizations expose anomalous activities, providing visibility into network communications before, during and after a suspicious event – Functions irrespective of language using n-gram analysis Key Features of Forensic Tools • Forensic analysis and investigation - Graphical arrangements include source, destination, time, type and duration of communication and content - Rebuild crime pattern - Playback events - Generate reports and visual representations of the suspicious activity - Report on key security and network parameters Forensics Technology Services – FTS • Digital Evidence Recovery It is a technique of finding and extraction evidence. A lot of times the legislative designates how to confidence a digital evidence. • Cyber Forensics Some specialists score incidents to the network. Cyber Forensics shows who made an attack. Forensics Technology Services – FTS • Forensic Data Analysis It is an interpretation of vast multiple data by using visualization techniques. • Document Management Services Making documents accessible helps sharing essential knowledge. In your investigations you can draw upon modern document management tools that allow you to archive, search, find, organising and reproduce documents. Requirements for Forensics Tools COLLECTING ANALYZING Real-Time Traffic Analysis Knowledge Base 2D or 3D VISUALIZATION Post Event Database Meta Data and Content Analysis Context Analyzer Data Visualization Types of Collecting Data All logs are collecting to the Central logs base!!! Types: - IDS/IPS logs - Firewall logs - Sys logs - SQUID logs - Audit system logs - and more Security operation centre Network operation centre Service Alarms Security Alarms Network monitoring Central logs base Security Information Management System Any Public Network Server Farm Server Farm Server Farm Intranet Server Farm Security Information Management What is Security Information Management (SIM)? SIM provides a simple mechanism that allows security teams to collect and analyze vast amounts of security alert data. More specifically, SIM solutions collect, analyze and correlate – in real-time – all security device information across an entire enterprise. Correlated results are then displayed on a centralized real-time console that is part of an intuitive graphical user interface. Security Information Management SIM can be divided into four different phases: 1) 2) 3) 4) Normalization Aggregation Correlation Visualization SIM utilizes normalization, aggregation, and correlation to sift through mountains of security activity data on a real-time basis – correlating events, flagging and rating the potential seriousness of all attacks, compromises, and vulnerabilities. The power of SIM technology allows a relatively small security staff to dramatically reduce the time between attack and response. . Security Information Management Normalization is the process of gathering individual security device data and putting it into a context that is easier to understand, mapping different messages about the same security events to a common alarm ID. Keeping in mind that there are no standards in the security device industry, normalization alone is a tremendous asset to security teams. Aggregation eliminates redundant or duplicate event data from the security event data stream, refining and optimizing the amount of information that is presented to security analysts. Security Information Management Correlation uses software technology to analyze aggregated data, in real-time, to determine if specific patterns exist. These patterns of similar security events often correspond to specific securityattacks – whether denial of service,anti virus, or some other form of attack. Visualization, the final step in SIM, is the graphical representation of correlated information in a single, real-time console. Effective visualization lets security operators quickly identify and respond to security threats as they occur, before they create problems within the enterprise. Systems alarms remapping Original logs from systems around 20 000 types Sep 27 16:22:43 dmzserver su(pam_unix)[10983]: session opened for user nf by root(uid=0) Changed to 100 NF types Forbidden Database Access Access / Authentication / Authorization Application Exploit Privilege Escalation Sep 27 16:36:12 [192.168.177.1] Sep 27 2004 16:36:12: %PIX-6605005: Login permitted from 192.168.177.2/44743 to inside:192.168.177.1/ssh for user "pix_ADMIN“ 9 categories of NF alarms Configuration / System Status Evasion Security Policy Change Policy Violations Authentication succeed Attempts Reconnaissance Unknown / Suspicious Virus / Trojan Security operation centre Network operation centre Service Alarms Security Alarms Place Forensics Tool in Network Security Information Management System Central logs base Any Public Forensics Tool Network Server Farm Server Farm Server Farm Intranet Server Farm Network Forensics Analyzer Examples of Visualization Visualization of Firewall Data • Quickly visualize and understand relationships in firewall data across time • Source_IP ——— # of occurrences ——— Dest_IP Source_IP versus Firewall Action • Source_IP ——— # of occurrences ——— Firewall Action • Green = Accept Red = Reject Blue = Drop Event Correlation Blocked Firewall Traffic VPN Traffic Events Overlay Intrusion Detection System Alerts Exercises of anomaly Exercises of anomaly E – mail: [email protected]