* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download role of respiration in glycolysis, co2 and h20 production
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
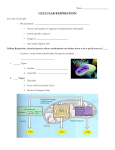
ROLE OF RESPIRATION IN GLYCOLYSIS, CO2 AND H20 PRODUCTION AIMS AND OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, student should be able to: • Define cellular respiration • Define metabolism • Know role of oxygen in respiration • Know glycolysis • Know citric acid cycle • Know electron transport chain LECTURE OUTLINE CELLULAR RESPIRATION OR 'OXIDATIVE METABOLISM' Set of the metabolic reactions that occur in cells to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the oxidation of one molecule and the reduction of another. METABOLISM The fate of dietary components after digestion and absorption constitutes intermediary metabolism. Metabolic pathways fall into three categories: 1. Anabolic pathway – synthesis of compound constituting body structure and machinery e.g. Protein synthesis 2. Catabolic pathway – involves oxidative processes that releases free energy in the form of high energy phosphate or reducing equivalents e.g. Respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation 3. Amphibolic pathway – have more than one function and occur at the cross road of metabolism acting as link between anabolic and catabolic pathway e.g. citric acid cycle OVERVIEW OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION ROLE OF OXYGEN Oxygen is vital to the process of cellular respiration Reactant in glycolysis, necessary for the breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid Waste product of Kreb's cycle Required to build the acetylCo-A molecule Final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain AEROBIC AND ANEROBIC RESPIRATION Aerobic - Organisms using oxygen as a final electron acceptor in respiration Anerobic – organisms not using oxygen (C6H12O6) is oxidized to CO2 and H2O, releasing energy (ATP) in the process C6H12O6 (aq) + 6 O2 (g) → 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (l) CELLULAR RESPIRATION Cellular respiration can be broken down into 4 stages This process occurs partially in the cytoplasm, and partially in the mitochondria. 1. Glycolysis 2. Transition reaction 3. Citric acid cycle (kreb’s cycle/ tricarboxylic acid cycle 4. Electron transport chain (respiratory chain) GLYCOLYSIS Occurs in the cytoplasm. Metabolic pathway Anerobic process One Glucose (C6H12O6) is broken down to 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. Resulting in the production of 2 ATPs for each glucose molecule Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 Pi + 2 ADP → 2 pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H+ + 2 H2O TRANSITION REACTION Occurs in mitochondria Pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl-CoA and CO2 by the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex(enzymes). CITRIC ACID CYCLE (KREB’S CYCLE/ TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE) Acetyl Co-A is produced in the presence of oxygen Enters citric acid cycle Occurs inside mitochondrial matrix Completely oxidized to CO2 and H2O liberating ATP via oxidative phosphorylation NAD+ is reduced to NADH Acetyl CoA→→→→→→→→→→2CO2 3 NAD + FAD + GDP + Pi 3NADH + FADH2 + GTP ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN (RESPIRATORY CHAIN) Occurs in cristae of mitochondria Collects and transports the reducing equivalent and directs them to their final reaction with oxygen to form water