* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter One Learning Goals
Survey
Document related concepts
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
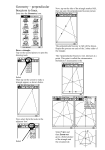
An Informal Introduction to Geometry This illustration shows how to construct a regular pentagon with given side ab. Try it! Chapter One Learning Goals Develop clear language to describe shapes. Write and follow careful directions. Use hand construction tools.* Use a protractor to measure angles Know the invariant property of points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment Know the properties of the special segments assosciated with triangles: median, altitude, angle bisector, and perpendicular bisector. Know their points of concurrency. Indentify invariants-values or relationships that stay the same while other values or relationships change. Use geometry software to construct “unmessupable” figures from their required characteristics.** Use geometry software to measure and investigate geometric figures and to discover invariant properties of classes of figures. Identify the essential properties of rectangles, squares, parallelograms, equilateral triangles, and rhombuses. Search for invariant numbers such as constant sums, products, ratios. Search for spatial invariants such as concurrency, collinearity, perpendicularism, and parallelism. Identify the invariant relationships for the sum of the measures of the angles in polygons. Identify the invariant relationship that exists when a line parallel to tone side of a triangle cuts the other two sides proportionally. Use geometry software to tinker with geometric models. *Basic Compass and straightedge constructions to Know: (There are videos of these on my web page.) Construct a triangle given three side lengths Construct an angle congruent to a given angle Constructing a perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Construct the bisector of a given angle Construct a perpendicular to a given line, both from a point ON the line and from a point OUTSIDE the line. **Geometer Sketchpad constructions to know. ( All un- messupable.) (There is a link to sketchpad help on the web site.) Square Rhombus Circle with radius the same as a given line segment. Equilateral triangle Isosceles triangle/ isosceles right triangle Rectangle Parallelogram Regular polygon with given number of sides(using rotation menu) Altitudes/angle bisectors/medians/perpendicular bisectors of a triangle. Know how to measure angle, lengths, perimeters, areas, ratios, Know how to make and use a table. Additional Vocabulary: centroid, orthocenter, circumcenter, incenter, distance from a point to a line, legs/base of isosceles triangle, skew lines