* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Equations
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic reforming wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Strengthening mechanisms of materials wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Crystal structure of boron-rich metal borides wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
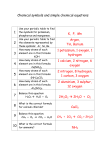
Chemical Equations Describing Chemical Process Chemical Equations Identify the substances involved in a chemical process Distinguish between the reactants and products in a chemical process Allow easy determination of quantities of substances involved in chemical processes Verbal description of a common chemical process: “Methane undergoes combustion in oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water.” The substances: methane: CH4 Oxygen: O2 Carbon dioxide: CO2 Water: H2O The form of an equation: Reactant(s) Product(s) The form of an equation: Reactant(s) One or more substances -the beginning “stuff” Product(s) The form of an equation: Reactant(s) One or more substances -the beginning “stuff” Product(s) Reaction arrow; points toward the product(s) The form of an equation: Reactant(s) One or more substances -the beginning “stuff” Product(s) Reaction arrow; points toward the product(s) One or more substances -the final “stuff” For the reaction of methane: CH4 + O2 CO2 Methane Carbon Water dioxide The reaction Products arrow Oxygen Reactants + H2O For the reaction of methane: CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O H O=O H C O=C=O O H H H H For the reaction of methane: CH4 + O2 CO2 + H 2O H H O=O C O=C=O O H H 4 H atoms, 2 H oxygen atoms H 2 H atoms, 3 oxygen atoms Note, there appear to be more oxygen atoms, fewer hydrogen atoms at the end that at the beginning! For the reaction of methane: CH4 + O2 CO2 + 2 H2O H O=O H C O=C=O O O H H H H H There are enough H atoms in one methane molecule to make two water molecules. …but, oxygen is worse off! H For the reaction of methane: CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O H O=O H C H H O=O O=C=O O H H O H Adjust the total number of oxygen atoms with more O2. Now, oxygen is OK. H For the reaction of methane: CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O H O=O H C H H O=O O=C=O O H H O H All atoms are in the same numbers before and after. H Propane reacts similarly with O2 C3H8 + O2 CO2 + H 2O Propane None of the atoms appear in the same amounts before and after; the equation is UNBALANCED. Propane reacts similarly with O2 C3H8 + O2 CO2 + H 2O None of the atoms appear in the same amounts before and after; the equation is UNBALANCED. There are enough H atoms in one propane molecule to make four water molecules. Propane reacts similarly with O2 C3H8 + O2 CO2 + 4 H2O Hydrogens are OK, but carbons are unequal before and after, still. There are enough carbon atoms in propane to make three carbon dioxide molecules. Propane reacts similarly with O2 C3H8 + O2 3 CO2 + 4 H2O Carbons are OK, but oxygen atoms are still unequal before and after. Adjust the total number of oxygen molecules... Propane reacts similarly with O2 C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 + 4 H2O Now, all atoms are equal in number before and after. The equation is BALANCED. Propane reacts similarly with O2 C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 + 4 H2O Now, all atoms are equal in number before and after. The equation is BALANCED. A “picture” of this reaction: C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 H H C C H H H C HH H + 4 H2O A “picture” of this reaction: C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 H H C C H H H O=O C H O=O O=O HH O=O O=O + 4 H2O A “picture” of this reaction: C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 H H C C H H H O=O C H O=O O=O HH O=O O=O O=C=O O=C=O O=C=O + 4 H2O A “picture” of this reaction: C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 H H C C H H H O=O C H O=O O=O HH O=O O=O O=C=O O=C=O O=C=O + 4 H2O H H H H O H O O O H H H Suggestions to Balance Equations Work with elements that appear in the fewest formulas first (in one formula on “each side” of the reaction arrow. Proceed to elements appearing in greater and greater numbers of formulas. Always check to see that elements are in same numbers on both sides. Practice C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2 Practice C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2 Start with either C or H. Oxygen appears in every formula; save it till last. Practice C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + 6 CO2 There are enough C atoms in C6H12O6 to form six CO2 molecules. Practice C6H12O6 + O2 6 H2O + 6 CO2 There are enough H atoms in C6H12O6 to form six H2O molecules. Practice Six O atoms Twelve O atoms, 6 sets of two C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 H2O + 6 CO2 Twelve O atoms Six O atoms Six O2 molecules are required to provide enough total oxygen atoms to balance. Check 18 total O atoms 18 total oxygen atoms C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 H2O + 6 CO2 Check 12 H atoms 12 total H atoms C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 H2O + 6 CO2 Check six C atoms six C atoms C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 H2O + 6 CO2 Your turn... Al2O3 + H2 H2O + Al Your turn... 1 Al2O3 + 3 H2 3 H2O + 2 Al Your turn... Al2O3 + 3 H2 3 H2O + 2 Al Check: 2 Al atoms 3 Oxygen atoms 6 H atoms 2 Al atoms 3 Oxygen atoms 6 H atoms Your turn... Ca(OH)2 + HCl H2O + CaCl2 Your turn... 1 Ca(OH)2 + 2 HCl 2 H2O + 1 CaCl2 Your turn... Ca(OH)2 + 2 HCl 2 H2O + Check: 1 Ca atom 2 oxygen atoms 2 chlorine atoms 4 hydrogen atoms 1 Ca atom 2 oxygen atoms 2 chlorine atoms 4 hydrogen atoms CaCl2 Your turn... H2O + Mg3N2 Mg(OH)2 + NH3 Your turn... 6 H2O + 1 Mg3N2 3 Mg(OH)2 + 2 NH3 Your turn... 6 H 2O + Mg3N2 3 Mg(OH)2 + 2 NH3 Check: 12 H atoms six O atoms 3 Mg atoms 2 N atoms 12 H atoms six O atoms 3 Mg atoms 2 N atoms Your turn... NH3 + O2 NO + H2O Your turn... 4 NH3 + 5 O2 4 NO + 6 H2O Your turn... 4 NH3 + 5 O2 4 NO + 6 H2O Check: 4 N atoms 12 H atoms 10 oxygen atoms 4 N atoms 12 H atoms 10 oxygen atoms