* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digital Representation of Audio Information
Survey
Document related concepts
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Quantization (signal processing) wikipedia , lookup
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Sound reinforcement system wikipedia , lookup
Instrument amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
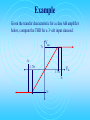
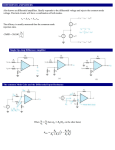
EE599-020 Audio Signals and Systems Amplifiers Kevin D. Donohue Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Related Web Sites The understanding and design of amplifiers are primarily the domain of electrical engineers and technicians. Web sites below related to the design and characterization of amplifiers: http://www.pha.inecnet.cz/macura/audiopage.html http://www.elexp.com/t_audio.htm http://users.pandora.be/educypedia/electronics/amplifierclasses.htm http://links.epanorama.net/links/audiocircuits.html#amp Amplifier Usage in Audio Preamplifier – Amplify small signals to intermediate levels while maintaining good SNR and fidelity. Sometimes performing compression (nonlinear / logarithmic transfer characteristic to prevent hard clipping). Intermediate Stage Amplifier – Amplify and process intermediate level signals with good SNR for mixing, equalization, compression, expansion, and other signal processing effects. Power Amplifier – Amplifies high SNR intermediate level signals to high power levels for driving electroacoustic transducers. Amplifier Performance Efficiency – Output power over Input power (including that of the power supply). Distortion – Total harmonic distortion (THD). For sinusoidal signal inputs, THD is the ratio of power at harmonic frequencies (excluding the fundamental) of the output signal over the total output signal power. Fidelity – Flatness of frequency response characterized by frequency range and transfer function variation in that range. Amplifier Classes Class A - Low distortion, bad efficiency. Output stage with single transistor requires DC biased output (10-20% efficiency). Class B - Crossover distortion, good efficiency. Output stage has 2 transistors so bias current is zero (~80% efficient). Class AB – Reduced crossover distortion, good efficiency. Output stage has 2 transistors with biasing to push signal out of crossover distortion range. Class D – Moderate distortion, high efficiency, operates in switch mode. Good for battery driven applications. Example Given the transfer characteristic for a class B amplifier below, compute the THD for a 3 volt input sinusoid. Vout 7v -3v -0.6v Vin 0.6v -7v 3v Example Given the transfer characteristic for a class AB amplifier below, compute the THD for a 3 volt input sinusoid. 7v Vout -3v -1.75v Vin 1.75v 3v -7v Compressors Compression: In order to improve the dynamic range of a system without overdriving the amplifiers (or other elements in the system) resulting in hard clipping, a softer clip can be applied to more gradually compress the signal amplitude as it approaches the saturation limits of the system. 1 A x(t ) x(t ) y (t ) X T Ax(t ) for x(t) X T for x(t) X T where is between 0 (hard clipping) and 1 (no compression). Expanders Expansion: In order to improve the dynamic range of a system by reducing low level signal inputs, a lesser gain can be applied to the signal components below a certain threshold and a normal linear gain can be applied to signal levels above the threshold. 1 A x(t ) x(t ) y (t ) X T Ax(t ) for x(t) X T for x(t) X T where is between 1 (no attenuation) and (complete attenuation - behaves as a gate). Example Plot the transfer characteristics for compressors and expanders. Process some signals with these and listen for type of distortion/enhancements they produce.