* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A B C - admms
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
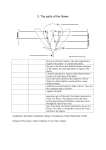
Unit Review, Introduction to Plants 1. During which process do plants capture light energy and carbon dioxide along with water to produce glucose? a. fertilization b. reproduction c. photosynthesis d. cellular respiraton 2. Where would you expect to see a plant that does not have a vascular system? a. In a botanical museum, because they are all extint. b. Deeply rooted in a forest with a trunk that reaches 20 meters or more. c. Low and close to the ground. d. Climbing high while circling the branches on another plant. 3. Describe how flowering plants reproduce through sexual reproduction. 4. Many plants grow in the spring and summer and become dormant during the fall and winter. Explain what triggers dormancy in a plant, and explain the benefits of winter dormancy for those plants. 5. A. Of what importance is N, P, and K in a plant? B. What element does each represent? A. B. 6. Why are nonvascular plants so small? 7. List three ways seedless nonvascular plants are similar to seedless vascular plants. a. b. c. 8. The diagram below shows a cycle of energy flowing between living organisms. Which of the following could the two sides of the diagram represent? A. The left side represents a producer, and the right side represents a consumer. B. The left side represents a consumer, and the right side represents a producer. C. The left side represents an animal that eats plants and the right side represents a plant. D. The left side represents energy created, and the right side represents energy destroyed. 9. The _______________ is the male reproductive structure of flowers. a. Ovary b. Ovules c. Stamen d. Pistil 10. The diagram below shows the process in which plants use energy from the sun. What is this process called? ________________________________ In which plant organelle does this process occur? ________________________________ How does the plant store the energy it gets from the sun? __________________________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________ Is a plant a producer, consumer, or decomposer? ________________________________ 11. Which of the following is a function of stomata? A. absorb sunlight B. release glucose C. release water vapor D. absorb water through the roots 12. The image below shows a type of plant. 12. Which is the correct term for the newly forming leaves seen in the image? A. frond B. leaflet C. rhizome D. fiddlehead 13. Which plant life phase begins when two gametes fuse together to form a zygote? A. sporophyte B. gametophyte C. both sporophyte and gametophyte D. neither sporophyte or gametophyte 14. The following chart describes several different parts of flowering plants. A B C Male reproductive Structure Female reproductive structure Composed of sepals & petals Which of the answers below gives the correct labels for columns A, B, and C? A. A is pistil, B is stamen, C is flower B. A is stamen, B is pistil, C is flower C. A is angiosperm, B is flower, C is fruit E. A is stamen, B is seed, C is gymnosperm 15. Describe the process of photosynthesis in detail. In your description, include the words glucose, chlorophyll, chemical energy, carbon dioxide, oxygen, and cellular respiration 16. What part of a plant’s leaves allows the plant to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen? A. stem B. cuticle C. stomata D. chloroplasts 17. The diagram below shows a flower, with several of its reproductive parts labeled. Which labels correctly identify the male and female reproductive structures of the flower? A. A and B are female structures, C and D are male structures B. B. B and C are female structures, A and D are male structures C. C. A and C are female structures, B and D are male structures D. D. A and D are female structures, B and C are male structures 18. Which of the following best explains why many plants experience dormancy? A. longer days B. more rainfall C. shorter nights D. stomata close in leaves The following diagram shows a plant. What structural feature is missing from the above diagram, and what is one of its functions? 19. A. roots; absorb sunlight B. roots; supply plants with water C. stems; store extra food D. stems; hold the plant upright