* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gen 305, presentation 6′, 16
Survey
Document related concepts
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
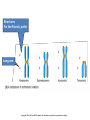
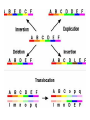
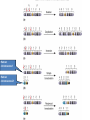
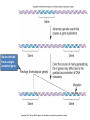
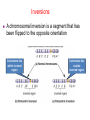
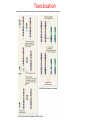
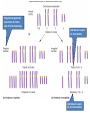
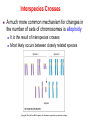
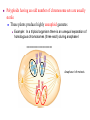
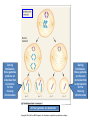
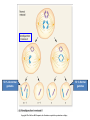
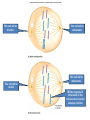
Variation in chromosome structure and number Short arm; For the French, petite Long arm Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display • Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species – Allelic variations are due to mutations in particular genes – Chromosomal aberrations are substantial changes in chromosome structure or number • These typically affect more than one gene • They are quite common, which is surprising Cytogenetics -The field of genetics that involves the microscopic examination of chromosomes Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Human chromosome 1 Human chromosome 21 Deficiencies/ Deletion A chromosomal deficiency occurs when a chromosome breaks and a fragment is lost Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Duplications A chromosomal duplication is usually caused by abnormal events during recombination A repetitive sequence contained multiple times can cause alignment where the alleles don’t actually match. Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Genes derived from a single ancestral gene Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Inversions A chromosomal inversion is a segment that has been flipped to the opposite orientation Centromere lies within inverted region Centromere lies outside inverted region Translocation VARIATION IN CHROMOSOME NUMBER • Chromosome numbers can vary in two main ways – Euploidy • Variation in the number of complete sets of chromosome – Aneuploidy • Variation in the number of particular chromosomes within a set – Euploid variations occur occasionally in animals and frequently in plants – Aneuploid variations, on the other hand, are regarded as abnormal conditions Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Polyploid organisms have three or more sets of chromosomes Individual is said to be trisomic Individual is said to be monosomic In most cases, these effects are detrimental They produce individuals that are less likely to survive than a euploid individual Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Trisomics for individual chromosomes Datura stramonium Genetic variation is a result of various types of changes at the molecular level Changes in chromosome number •Single chromosomes may be lost or gained •A whole set of chromosomes may be inherited Some human aneuploidies are influenced by the age of the parents Older parents more likely to produce abnormal offspring Example: Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) Incidence rises with the age of either parent, especially mothers Familial down Syndrome Complete nondisjunction can produce an individual with one or more sets of chromosomes This condition is termed autopolyploidy Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Interspecies Crosses A much more common mechanism for changes in the number of sets of chromosomes is alloploidy It is the result of interspecies crosses Most likely occurs between closely related species Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display An allodiploid has one set of chromosomes from two different species An allopolyploid contains a combination of both autopolyploidy and alloploidy An allotetraploid: Contains two complete sets of chromosomes from two different species Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Polyploids having an odd number of chromosome sets are usually sterile These plants produce highly aneuploid gametes Example: In a triploid organism there is an unequal separation of homologous chromosomes (three each) during anaphase I Anaphase I of meiosis AnaaAanand two copies of other chromosomes During fertilization, these gametes produce an individual that is trisomic for the missing chromosome During fertilization, these gametes produce an individual that is monosomic for the missing chromosome All four gametes are abnormal Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display 50 % Abnormal gametes 50 % Normal gametes Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display This cell will be trisomic This cell will be monosomic This cell will be monosomic This cell will be normal Will be degraded if left outside of the nucleus when nuclear envelope reforms No synapsis between the 9 radish and 9 cabbage chromosomes Proper synapsis between the 18 radish chromosomes and the 18 cabbage chromosomes Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Octoploid strawberries Hexaploid wheat Triploid seedless fruits Asian carp is a polyploid, a mix of four species, the bighead carp, the black carp, the grass carp, and the silver carp. Mule is a result of a cross between a male donkey (Chr# 62) & a female horse (Chr# 64)