* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell test reviewsheet 1213 KEY
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
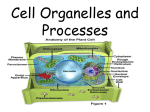
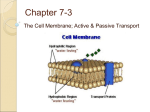
KEY: Cell Test Review Sheet Important Words to know the Meaning of: Stem Cell Organic Molecule Protein Carbohydrate Lipid Nucleic Acid Amino Acid Monosaccharide Nucleotide Fatty Acid – Saturated and Unsaturated Mitochondria Lysosome Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Chloroplast Ribosome Golgi Central Vacuole Prokaryote Eukaryote Polar Non Polar Phospolipid Cholesterol Diffusion Osmosis Proton Pump Endocytosis Exocytosis Hypertonic Hypotonic Interphase G1 S G2 Mitosis G1 Checkpoint G2 Checkpoint M Checkpoint Apoptosis Substrate Product Enzyme Active Site Transport Protein Receptor Specific Questions to Answer to Prepare You for the Test 1. What are the two types of cells? What is the difference between them? Prokaryotic cells do not have internal membranes, a nucleus, and they are much smaller than eukaryotic cells 2. What types of cells have cell membranes? What does the cell membrane do? All cells have membranes, they are semipermeable allowing small non polar molecules in easily 3. What is it called when we keep the internal environment of the cell the same? Homeostais 4. What are the three functions a cell needs to perform? What organelles are needed to perform each function? Homeostasis- membranes, vacuoles, lysosomes, Convert energy- chloroplasts and mitochondria Make proteins- nucleus, ER, ribosomes, Golgi 5. Compare and contrast Plant and Animal cells Plant cells have cell wall, central vacuole and chloroplasts that are not present in animal cells both eukaryotic 6. What are two differences between active and passive transport? Active- use energy, passive- do not use energy. Example- pumps that move from low to high are active 7. Describe the arrangement of the cell membrane. (pictures are acceptable) Label the polar parts, non polar parts, and transport parts. See notes or look at quiz 5% solute 8. Look at the following diagram. Will this cell shrink or will it swell? Swell- water moves in by osmosis 9. What are two ways endocytosis and osmosis are different? Endocytosis uses energy, osmosis is only water movement across a membrane 10. What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion? Osmosis is diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane. Diffusion (high to low concentration occurs with any molecule 11. What would happen to a cell placed in a hypotonic solution?_________it would swell________________ What would happen to a cell placed in a hypertonic solution? __________it would shrink____________ 12. When particles move from a high concentration to a low concentration, this describes a. active transport b. passive transport 13. When particles move from a low concentration to a high concentration, this describes a. active transport b. passive transport 14. What is the goal of mitosis? To separate chromosomes into two cells 15. What are three differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? See above 16. Why are cells small? They need a high surface area to volume ratio in order to get nutrients and waste in and out. 17. What makes a molecule organic? Has carbon and hydrogen (most have oxygen also in biology) 18. What are the 4 types of organic molecules? Protein, carbohydrate, lipid, nucleic acid 19. What are the monomers for each of the 4 types of molecules? What do they look like? Protein- amino acids Carbohydrates- monosacharides Lipids- fatty acids Nucleic acids- nucleotides 20. What are the functions of each of the 4 types of organic molecules? Protein- transport, enzymes, structural, and other Carbohydrates- storage of energy (short term) Lipids- storage of energy (long term), cell membranes Nucleic acids- genetic information storage 21. What are enzymes? Protein catalysts 22. How do enzymes speed up reactions? Lower the energy of activation for reactions 27. Why is the shape of the enzyme important? Enzymes are specific- one enzyme, one reactant 28. What are factors that affect enzyme function? Why do these factors affect enzyme function? pH, temperature, salinity- Enzymes have optimal ranges where they function best 29. Do all cells divide at the same rate? Are all the cells in your body constantly dividing? Cells do not divide at the same rate. Some cells do not divide (ex. Nerve cells), some need to be replaced constantly (ex. Skin cells) 30. What are some possible targets new anti-cancer drugs involving the control of the cell cycle? They target the cell cycle to keep cells from replicating DNA, or moving into synthesis. They also may inhibit mitosis 31. How might cancer and stem cells be related? Both types of cells will divide continuously (cell cycle is not controlled). Cancer may also have its own stem cells. 32. What is the difference between polar and non-polar molecules? Polar are attracted to polar, non polar to non polar. They do not mix with each other. Some of the Important Diagrams to be able to Recognize Major Concepts If you are prepared for the test, you are able to answer the following questions in depth. * Stem Cells: What are Stem Cells? Why is studying them controversial? In what ways could they advance the study of Medicine? * Organic Molecules – What are the 4 types? What are the monomers of each? What are the functions of each? What are examples of each? * Enzymes – What are the six enzyme rules? How do enzymes work? What affects enzyme activity? * Cell Types - What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? What are the differences between plant and animal cells? * Cell Organelles - What are the three major functions of the cell and what are the organelles that perform each function? What are the important structures of each organelle? What function does each organelle perform? * Microscope lab – What were the differences and similarities each cell we saw had? * Cell Membrane– What is the structure of the cell membrane? How does it control what goes in and out? * Cell Transport – What is diffusion? What is osmosis? What are the types of active transport? * Cell Cycle – What are the major parts of the cycle the cells go through? * Control of the Cell Cycle and Cancer – What occurs at each check point? What is cancer? How is the control of the cell cycle and cancer connected?