* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download second punic war
Survey
Document related concepts
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
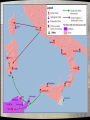
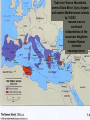
The Punic Wars Latium • During the period of the first kings around 509 BC there were actually very many cities in Italy – and Rome was just one of them. • The Italian Peninsula is located right in the heart of the Mediterranean Sea. – Rome is located right in the heart of Italy on a large plain known as Latium. After the establishment of the Republic, the Romans began to conquer southern Italy. • They used a good idea to help them. – They told everybody that if any city needed help fighting a war, the Romans would be happy to help them. – Soon a city did ask for help, when its neighbors were attacking it. – The Romans sent troops and fought off the neighbors. – But when the war was over, the Romans announced that they were going to leave Roman soldiers in this city, to keep the city safe. • But when there are Roman soldiers living in the middle of your city, you pretty much have to do whatever the Roman Senate says! – In this way the Romans took over all of southern Italy. Carthaginian Empire Former Phoenician trading post Commercial city Had western Mediterranean empire Felt threatened by Rome’s rise to dominance in Italy The Punic WarsDispute over control of Sicily and trade routes in the western Mediterranean coupled with Rome’s expansion to the toe of Italy brought Rome into conflict with the powerful North African city-state of Carthage Carthage had been founded as Phoenician colony 500 years earlier Carthage Result was the three Punic Wars 264-146 BC These conflicts, so disastrous for Carthage, were inevitable. • Between Carthage and Italy lay the huge island of Sicily; – Carthage controlled the western half of Sicily, – but the southern tip of the Italian peninsula put the Romans within throwing distance of the island. • When the city of Messina revolted against the Carthaginians, – the Romans intervened – Security being in their National Interests, – and the first Punic War erupted. FIRST PUNIC WAR • Primarily a naval war – Tactics involved maneuvering your ship in such a way so that you could ram and sink enemy • Carthage very good at this because of long experience as naval power • Rome had small navy and little experience in naval warfare – Defeated time and time again by larger and more experienced Carthaginian navy ROME WINS THE FIRST ONE • Rome would not surrender – Finally turned the tables on Carthage by changing rules of naval warfare • Equipped ships with huge hooks and stationed soldiers on ships – Would hook enemy ship, pull it nearby, and board it with soldiers – Converted naval warfare into mini-land battles • Something Rome was very good at • Won First Punic War as a result Mercenary War • Immediately following the war, Carthage's mercenaries revolted over a pay dispute and occupied a number of important Punic cities in North Africa and Sardinia, beginning the Mercenary War. – Miraculously, Carthage was able to defeat the mercenaries in North Africa, – meanwhile Rome used the Mercenary revolt as an excuse to invade and conquer the islands of Sardinia and Corsica – Thus by 238 BC, Carthage had lost all of her islands in the Central Mediterranean SECOND PUNIC WAR • Carthagian general Hannibal surprises Romans, leads army from Spain, through southern France and the Alps, and invades Italy from the north – Defeats Roman armies sent to stop him several times but hesitates to attack Rome itself • Too well fortified • Settles instead on war of attrition in hope of destroying Roman economic base The arrival of Hannibal’s army in Italy sparked off numerous rebellions against Roman rule • and Hannibal decisively defeated Rome in a number of battles, – – • including the two worst military defeats of its history, the Battle of Lake Trasimene, and the Battle of Cannae. Roman allies in the south of Italy literally ran to Hannibal's side; – the whole of Sicily allied itself with the Carthaginians. – In addition, Philip V, who controlled most of the mainland of Greece, – began his own war against Roman possessions in 215 BC. Fabian Strategy • Eventually Rome appointed a dictator: – Quintus Fabius Maximus • They relied on employing the strategy of avoiding direct conflict with Hannibal in Italy – Known as the Fabian Strategy • Meanwhile, Hannibal was thwarted in his attempts to invade Rome. – He tried to incite revolt among the tribes of Italy, but most feared Rome's wrath should Carthage lose, – and they remained with Rome for the most part. ROME WINS THIS ONE TOO • Unable to defeat Hannibal in Italy, a Roman army sailed across the Mediterranean, landed in North Africa, and headed for Carthage – Led by patrician general Scipio Aemilius Africanus – Hannibal forced to leave Italy to protect Carthage • Defeated at the Battle of Zama, fought outside the walls of Carthage Hannibal In 201, a treaty was signed, which was very punitive. Carthage had to surrender her navy, all territorial claims in Spain, and had to pay reparations in the amount of 10,000 talents over 50 years. 10,000 talents is worth about 150,000 year's wages Death and Legacy • Hannibal survived the Battle of Zama, Helped rebuild Carthage, but eventually had to run away. He fled from court to court offering his services to anyone who would fight Rome. Finally in 183 B.C. Romans found him in Asia Minor (modern day Turkey) and forced him to surrender. As they guarded him, he secretly took poison and ended his life. • Hannibal shows the necessity of political goals being more important than military accomplishment. Legacy – This was the defining historical experience of the Romans. • • – They had faced certain defeat with toughness and determination and had won against overwhelming odds. For the rest of Roman history, the character of being Roman would be distilled in the histories of this desperate war against Carthage. The Second Punic War turned Rome from a regional power into an international empire: – • – it had gained much of northern Africa, Spain, and the major islands in the western Mediterranean. Because Philip V of Macedon had allied himself with Hannibal • – and started his own war of conquest, the second Punic War forced Rome to turn east • • in wars of conquest against first Philip and then other Hellenistic kingdoms. Took over Greece, Rome Rome Successor Macedonia, eventually always some of Asia Minor, responded became kingdom Syria, weary inAegean the of Rome drawn into the and eastern Mediterranean increasingly playing belief thisthat endless called islands affairs thein by achieving refereeing on 133 Roman BC aof role balance aid and successor kingdoms of their realized power incessant inthat the the east wars wascontinued against better than each independence having otheroneof the successor successor kingdoms kingdom threaten becomeRoman too powerful interests and challenge Rome THIRD PUNIC WAR • Carthage finished after Second Punic War – Hannibal committed suicide – Economy shattered – Lost all territory to Rome – But some Romans feared it might revive someday and challenge Rome again • Notably Cato the Elder – Pushed for another war that would wipe Carthage off the face of the map Cato the Elder Carthage Returns? – Carthage had, through the first half of the second century BC, recovered much of its prosperity through its commercial activities, • – although it had not gained back much power. The Romans, deeply suspicious of a reviving Carthage, demanded that the Carthaginians abandon their city and move inland into North Africa. • The Carthaginians refused • They were a commercial people that depended on sea trade, ROME WINS A THIRD TIME • Due to Cato’s persistent efforts, Rome declares war against defenseless Carthage – Wins easily – Entire population of city sold into slavery – Everything of value carried back to Rome – Everything else burned and dumped into the sea – Site sown with salt so that nothing would ever grow there again – Carthage completely disappeared The end result of the Second Punic War… was the domination of the known world… by Rome. SUMMARY • Roman Republic was strongly rigged to work only in the interests of the wealthy classes – No way a sincere reformer could “work within the system” to change things • Everything was stacked against him • The only way to effect change within this rigged system was to either threaten or use violence against the ruling class • The rigged structure of government in republican Rome was therefore the first factor that contributed to the growth of political violence in the city-state