* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
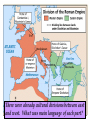
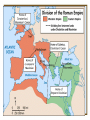
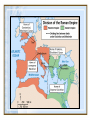
Download Aim: What was the legacy of ancient Rome?
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Review Questions • • • • What group influenced the early Romans? When was the Roman Republic founded? Describe the Roman Republic. What were some key events in Rome’s expansion? • Describe the leadership of Julius Caesar and Augustus. Significance? • What was the Pax Romana? • What were some achievements of Rome? (engineering and law) Review Questions • What group influenced the early Romans? – Etruscans Review Questions • When was the Roman Republic founded? – 509 B.C.E. Review Questions • Describe the Roman Republic. – People voted for officials to represent them – Government divided into 3 branches – 2 Consuls, Senate and Assembly – Patricians (upper class) and Plebeians (lower class) – Plebeians had some say in the Assembly but overall government dominated by Patricians – 12 Tables – laws that included idea of innocent until proven guilty, standard of proof Review Questions • What were some key events in Rome’s expansion? – Punic Wars with Carthage – Rome gained Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica and eventually parts of northern Africa and Spain; Hannibal came close to defeating Rome – Julius Caesar gained Gaul (France) Review Questions • Describe the leadership of Julius Caesar and Augustus. Significance? – People were willing to give up rights (republic) for a dictator that would help them – Both leaders made reforms (gave people land, food, jobs) – Augustus’ rule was officially the beginning of the Roman Empire Review Questions • What was the Pax Romana? – 200 year period of peace and prosperity that began with Augustus Review Questions • What were some achievements of Rome? (engineering and law) – – – – – 12 Tables Roads Aqueducts Domes Arches Aim: Why did Rome fall? Do Now: Quote analysis “With great power comes great responsibility.” “A man may die, nations may rise and fall, but an idea lives on” Explain what this quote means. Did Rome really fall? Recall: What was the Pax Romana? What made Rome a stand out empire? Between 235-284 C.E. there were 26 emperors, only one of which died from natural causes. There were already cultural divisions between east and west. What was main language of each part? 1. How did Emperor Diocletian (286–305) change the boundaries of the roman empires? • Divided Roman Empire into two parts (Western and Eastern) Execution of Christians • Death by burning • Crucifixion • Feeding of Christians to wild animals • Cover in honey and unleash to bees Emperor Maxentius • Consulted witches • Ripped open bellies of pregnant women to somehow see the future • Constantine saw him as a pagan and barbaric • 6 year reign Battle of Milvian Maxentius vs. Constantine 2. How did Emperor Constantine (312-337) change religion in Rome? • 1st Christian emperor • Granted toleration to Christians (used to unite diverse people) • Built Constantinople (made Eastern portion of empire powerful) • Built Church of Holy Sepulchre Economic Reasons “Heavy taxes began to take their toll on the people. Farmers were so disgusted that they abandoned their land. All the middles classes that had prospered for years began to sink into poverty. To make matters worse, reliance on slave labor discouraged Romans from creating new forms of technology. It has also kept wages extremely low, thereby exacerbating the plight of the people.” Gap between rich and poor Economic Problems • Increased taxes (army and government) • Slave labor • Unemployment / inflation Political Reasons “As a Roman citizen, I no longer trust the Roman government. For years, emperors have ruled with only their own interests at heart. They are corrupt and selfish people. The Rome that was once so strong and great has crumbled. It is now divided and weak.” Political Weakness • • • • • Power struggle Quick turnover of rulers Corrupt and ineffective rulers Government lost support Division of the empire Between 235-284 C.E. there were 26 emperors, only one of which died from natural causes Social Reasons “Disease and war have swept through the empire. So many people have died. The empire has done nothing to alleviate this problem. The people of Rome are bewildered and disillusioned by all the chaos. In addition, there are many lives being consumed by poverty. Happiness and Roman pride seem to be abandoned and replaced by despair and disloyalty.” Social Problems • Decrease in population – war and disease • People became selfish and lazy • Lack of patriotism Military Reasons “The Roman government decided to hire foreign soldiers, called mercenaries, to defend its borders. Its own army was beginning to lack training and discipline. However, foreign soldiers felt little loyalty to Rome and could not be trusted. The use of these mercenaries facilitated foreign invasions.” Military Decline • Soldiers – decrease in number / morality/ patriotism • Mercenaries (foreign soldiers who defended borders) • Foreign invasions Invasions • Germanic tribes from northern Europe and the Huns from Asia • 410 C.E. – Rome was sacked by the Visigoths • 476 C.E. – Last Roman Emperor overthrown in the west by the Germanic general Odoacer • Continued invasions and power struggles disrupted trade and manufacturing • In Western Europe, no large scale, centralized, political authority ever established again for any substantial amount of time • In Eastern Europe, empire survived and changed into Byzantine Empire (lasted another 1,000 years) The Huns http://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=VpHMP zk6uI4 Did Rome really fall? “A man may die, nations may rise and fall, but an idea lives on” How might this quote be used to argue that Rome did not fall? “The year was 476. For those who demand to know the date Rome fell, that is it. Others will realize that the fall of Rome was not an event but a process. Or, to put it another way, there was no fall at all – ancient Roman civilization simply evolved into the medieval civilization of the Middle Ages” What is this person saying about the fall of Rome? Bonus Question •In what year did the Romans force out the last Etruscan king and establish a republic? Bonus Question •In what year was Julius Caesar assassinated? Bonus Question •In what year did the Roman Empire fall with the overthrow of the last Roman Emperor? • Which factor do you think was most responsible in leading to the decline and eventual end of the Roman Empire? Explain. Unit Summary “With great power comes great responsibility.” 1. What does this quote mean? 2. In what ways was Rome able to live up to this quote? 3. In what ways did Rome fail to meet the needs of the people?