* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: : Earth Science Mr. Herman Exeter SHS Chapter 10.3
Survey
Document related concepts
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
Geology of the Death Valley area wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Mackenzie Large Igneous Province wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
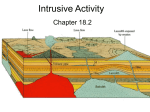
Name: _____________________________________Date: ________________ Earth Science Mr. Herman Exeter SHS Chapter 10.3 Intrusive Igneous Activity Vocabulary Pluton Sill Laccolith Dike Batholith Objective Describe the major igneous intrusive features such as dikes, sills, and laccoliths, and how they form. Describe batholiths and how they form. Plutons Plutons are intrusive igneous structures that result from the cooling and hardening of magma beneath the surface of Earth. Intrusive igneous bodies, or plutons, are generally classified according to their shape, size, and relationship to the surrounding rock layers. Plutons Sills and Laccoliths are plutons that form when magma is intruded close to the surface. Sills resemble buried lava flows and may exhibit columnar joints. Laccoliths are lens-shaped masses that arch overlying strata upward. 1 Dikes Dikes are tabular-shaped intrusive igneous features that cut across preexisting rock layers. Many dikes form when magma from a large magma chamber invades fractures in the surrounding rocks. Batholiths Batholiths are large masses of igneous rock that formed when magma intruded at depth, became crystallized, and subsequently was exposed by erosion. An intrusive igneous body must have a surface exposure greater than 100 square kilometers to be considered a batholith. 2 3