* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
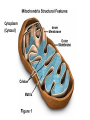
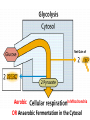
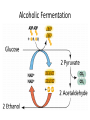
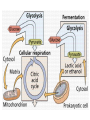
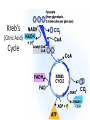
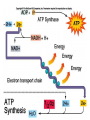
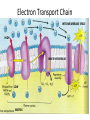
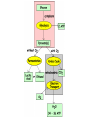
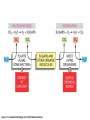
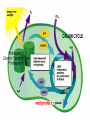
Chemiosmosis CO2 2 H2O 2 32 Cytoplasm (Cytosol) Glycolysis • • • • • Where? = In the Cytoplasm # ATP Produced = Net Gain of 2 Electron Carriers = Produces NADH Oxygen = NOT required (anaerobic) What Happens? = 1 molecule of Glucose is split into 2 molecules of Pyruvic Acid (pyruvate) Net Gain of Aerobic In Mitochondria OR Anaerobic Fermentation in the Cytosol Fermentation • • • • • Where? = In the Cytoplasm # ATP Produced = NONE Electron Carriers = Produces NAD+ Oxygen = NOT required (anaerobic) What Happens? = If oxygen is NOT available, Pyruvic Acid is broken down into either Ethanol & CO2 (yeast) or Lactic Acid (animals) INSTEAD of going through the Kreb’s Cycle Alcoholic Fermentation Kreb’s Cycle • Where? = In the Mitochondria (matrix) • What Happens? = If oxygen IS available, fermentation does NOT happen. • # ATP Produced = 2 • Electron Carriers = Produces 8 NADH and 2 FADH2 • Oxygen = REQUIRED (aerobic) Kreb’s Cycle What Happens? = If oxygen IS available, fermentation does NOT happen. 1. Pyruvic Acid is converted into Acetyl CoA. 2. This joins with oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid. 3. Citric Acid goes through a cycle where CO2 and electron carriers are formed. 4. The 2 original pyruvic acid molecules are completely broken down into CO2 Kreb’s (Citric Acid) Cycle Electron Transport Chain • # ATP Produced = 32 • Electron Carriers = Uses NADH and FADH2 to produce a H+ ion gradient • Oxygen = REQUIRED (aerobic) • Where? = In the Mitochondria (across INNER membrane) Electron Transport Chain • What Happens? = 1. The electron carriers (NADH & FADH2) are used to pump H+ ions across the inner membrane (from the Matrix to the Intermembrane Space). 2. This creates a concentration gradient that allows ATPsynthase to convert ADP into ATP (chemiosmosis). 3. 6 H2O is produced as a byproduct of ETC. Electron Transport Chain INTERMEMBRANE SPACE HIGH INNER MEMBRANE LOW MATRIX 6 O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6 H2O + 36 ATP Krebs 2. Krebs Cycle Oxygen (6 O2) & Glucose (C6H12O6 ) Water (6 H2O) & Carbon Dioxide (6CO2 ) & 36 ATP 3. ETC Cellular Respiration Videos • ETC Animation http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/ Biology/Bio231/etc.html • Mr. Anderson http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gh2P5Cm CC0M • http://www.sciencegeek.net/Biology/review/ U2RespFillin.htm Comparison of Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Chemiosmosis CO2 2 H2O 2 32 Photosynthesis Purpose Sequence of Steps Location Reactants Products Equation Cellular Respiration Purpose Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Break Down Convert Sunlight Carbohydrates into Chemical into Chemical Energy in order to Energy (ATP) to be Build used to Power Carbohydrates for Life Processes use as Food Sequence of Steps Photosynthesis Light Dependent Reaction Light Absorption & ETC (Photosystems 2 then 1) & Chemiosmosis Calvin Cycle Cellular Respiration Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain (& Chemiosmosis) Location Photosynthesis Chloroplast: 1. Light Dependent = Thylakoid 2. Calvin Cycle = Stroma Cellular Respiration Mitochondria: 1. Glycolysis = Cytoplasm (outside mitochondria) 2. Krebs Cycle = Matrix 3. ETC = Inner Membrane Reactants Photosynthesis Light, Water & Carbon Dioxide 1. Light Dependent = Water (6 H2O) 2. Calvin Cycle = Carbon Dioxide (6 CO2) Cellular Respiration Glucose & Oxygen 1. Glycolysis = Glucose 2. Krebs Cycle = Oxygen & Pyruvate (acetyl CoA) 3. ETC = Oxygen, NADH, FADH2, & ADP Products Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Carbon Dioxide, Water, & ATP Glucose & Oxygen 1. Glycolysis = 1. Light Dependent = Oxygen (6 O2), ATP, & NADPH 2. Calvin Cycle = Glucose (C6H12O6) 2 Pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH 2. Krebs Cycle = 2 ATP, 8 NADH, 2 FADH2, 6 CO2 3. ETC = 6 H2O, 32 ATP Equation Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light C6H12O6 + 6O2 Cellular Respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP Review Videos • Mr. Anderson Photos. & CR http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0IJMRsTc wcg